Network visibility is one of the key factors that have a direct impact on your network security, especially with wireless networks. The greater the visibility, the more control you have over your network. Certificate-based authentication with a public key infrastructure (PKI) helps improve network visibility to a great degree. Digital certificates contain unique information about the client or the device that cannot be replicated or stolen and are signed by a reputed Certificate Authority, thus validating the client’s identity.
Effectively identifying user or device identity can help in segmenting the network users more efficiently, which ultimately leads to a well-structured and secure network. Combining certificate authentication with SAML(Security Assertion Markup Language) in Google Workspace will seamlessly segment users as they automatically enroll for network access.
During the configuration process, admins can assign attributes to your network users that denote user groups within your organization. Based on the user’s role, seniority, job function, or countless other factors, you can distribute countless use policies and network settings. The customization can be as simple or complex as required.
As a result, network users enroll once for network access and are authorized for the life of their certificate. It provides comprehensive visibility context concerning who is connected to the network and what they are browsing. For accurate reporting and a network organized around your policies, turn to certificate solutions for Google Workspace SAML.
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) for Certificate-Based Authentication
PKI uses transport layer security protocol to facilitate communication between client and server at the time of authentication, an EAP protocol that is considered secure, while user authentication is done using an x.509 client certificate signed by a valid and reputed Certificate Authority, thus ensuring only authorized client or device is getting access to your network.
WPA-2 enterprise with EAP-TLS (Extensible Authentication Protocol-Transport Layer Security) is considered the most secure. There is the option to allow network connection only after successfully completing server certificate validation. Mutual authentication, or matching both the server and client certificates, makes this EAP authentication method almost impenetrable of all EAP methods.
Managing PKI can seem like a daunting task. However, SecureW2’s Managed PKI solutions, which are designed to work across operating systems, offer an easy-to-use graphical interface for viewing and managing your certificates from certificate issuance to revocation with just a push of a few buttons. Our industry-exclusive Identity Lookup with LDAP & SAML Identity Providers allows user identity lookup in real-time at the time of authentication.
Integration Process Overview of WPA2-Enterprise With Google Workspace
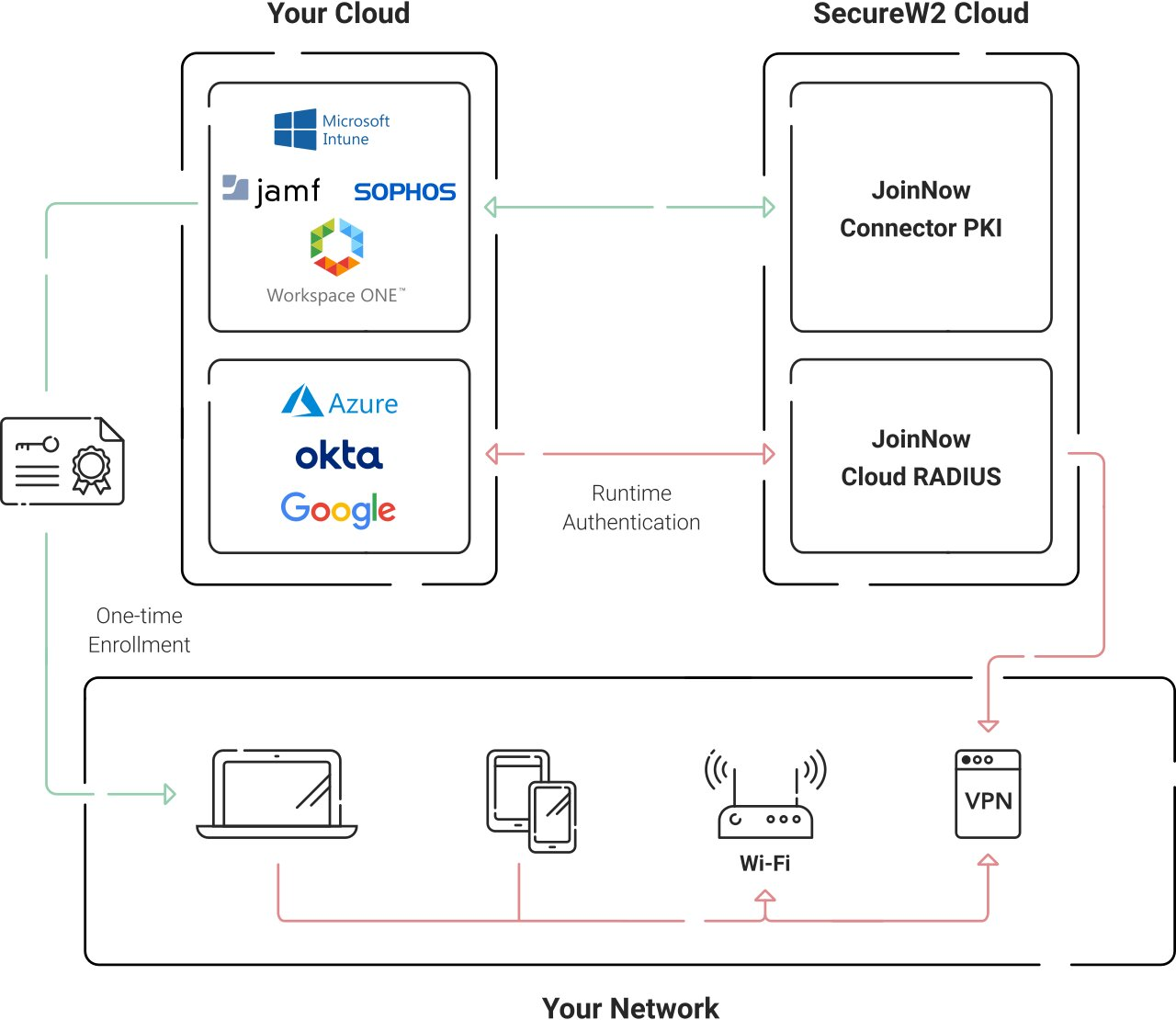
Configuring a WPA2-enterprise environment with a Google Workspace service account can be a complicated task that requires a careful weaving of multiple complex components such as PKI, Certificate Authority, certificate enrollment and management system, and RADIUS EAP-TLS authentication to design the entire infrastructure. When properly configured, it enhances your network security by giving a network administrator much better network visibility with real-time control over access management, making it the best security guard you can invest in for network security.
SecureW2’s solution is integrated with the Google Workspace SAML application, allowing a network administrator to easily connect users to the network while maintaining a high level of control. Digital certificates issued and managed using a PKI solution provide great network security infrastructure in a WPA-2 enterprise environment.
Below is the process overview for configuring WPA2-enterprise with the Google Workspace (G-Suite) SAML application.
- Add the SAML Identity Provider to SecureW2
- Configure the SAML IDP in the Google Admin Console
- The SAML Identity Provider provides context concerning who is connected to the network and ensures that only approved network users are authenticated.
- Configure Attribute Mapping
- Set specific attributes to segment the network into groups based on their identity within the organization.
- Configure Network Policies to be Distributed
- Based on these network policies, administrators can dictate the websites, applications, files, and more that different network user segments can access.
Prerequisites
- An active subscription to Google Admin Console with Admin privileges.
- Access to create a Google Service Account
- An active subscription to JoinNow Management Portal and JoinNow Cloud Connector.
Certificate Issuance Configuration
The following are the configurations for certificate issuance:
- Creating a SAML Identity Provider
- Creating a SAML Application
- Configuring Attribute Mapping
- Policy Management (Authentication Policy, Policy Engine Workflow, and Enrollment Policy)
Creating a SAML Identity Provider in SecureW2
An identity provider (IDP) is the system that proves the identity of a user/device. Creating an IDP in SecureW2 tells the Cloud Connector system how to connect to your Google Workspace user database, verify user credentials, and issue certificates.
- Log in to the JoinNow Management Portal.
- Navigate to Identity Management > Identity Providers.
- Click Add Identity Provider.
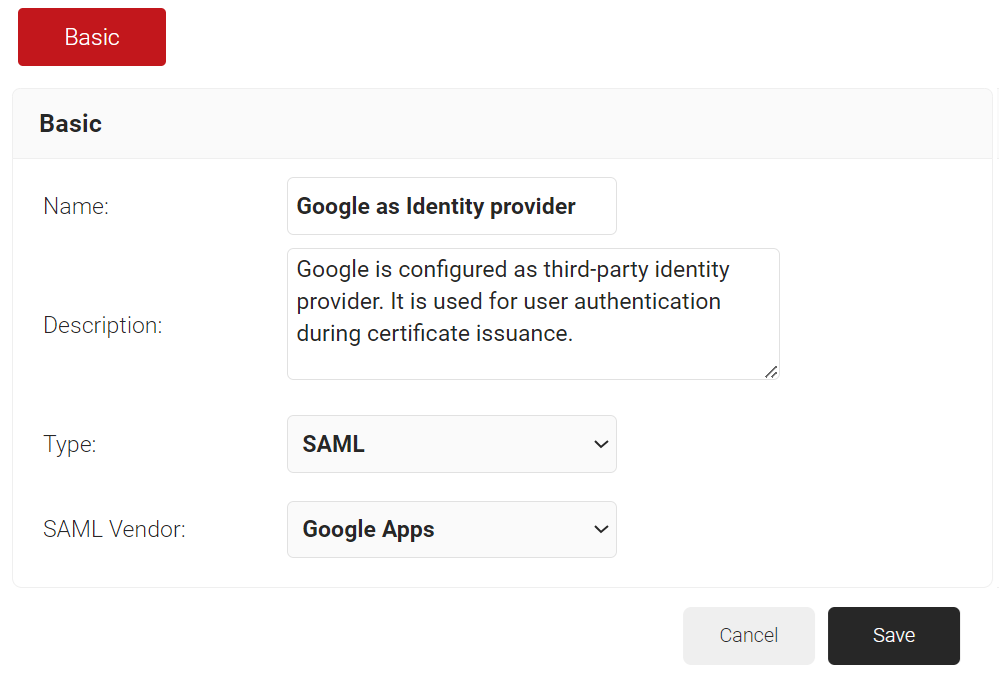
- In the Basic section, enter the name of the IDP in the Name field.
- In the Description field, enter a suitable description for the IDP.
- From the Type drop-down list, select SAML.
- From the SAML Vendor drop-down list, select Google Apps.
- Click Save.
 Now, SecureW2 Cloud Connector knows how to exchange information with your provider’s user database.
Now, SecureW2 Cloud Connector knows how to exchange information with your provider’s user database.
Creating a SAML Application in Google
The SAML application is a crucial connection between the IDP and SecureW2. The SAML application allows users to enter their credentials, which are then passed to the IDP for verification. The IDP verifies the user’s identity and then sends attributes to the SAML application, which then passes the attributes to SecureW2 for certificate issuance.
To create a SAML application in Google:
- Log in to your Google Admin Console.
- From the menu, select Apps > Web and mobile apps.
- Click Add app and select Add custom SAML app.
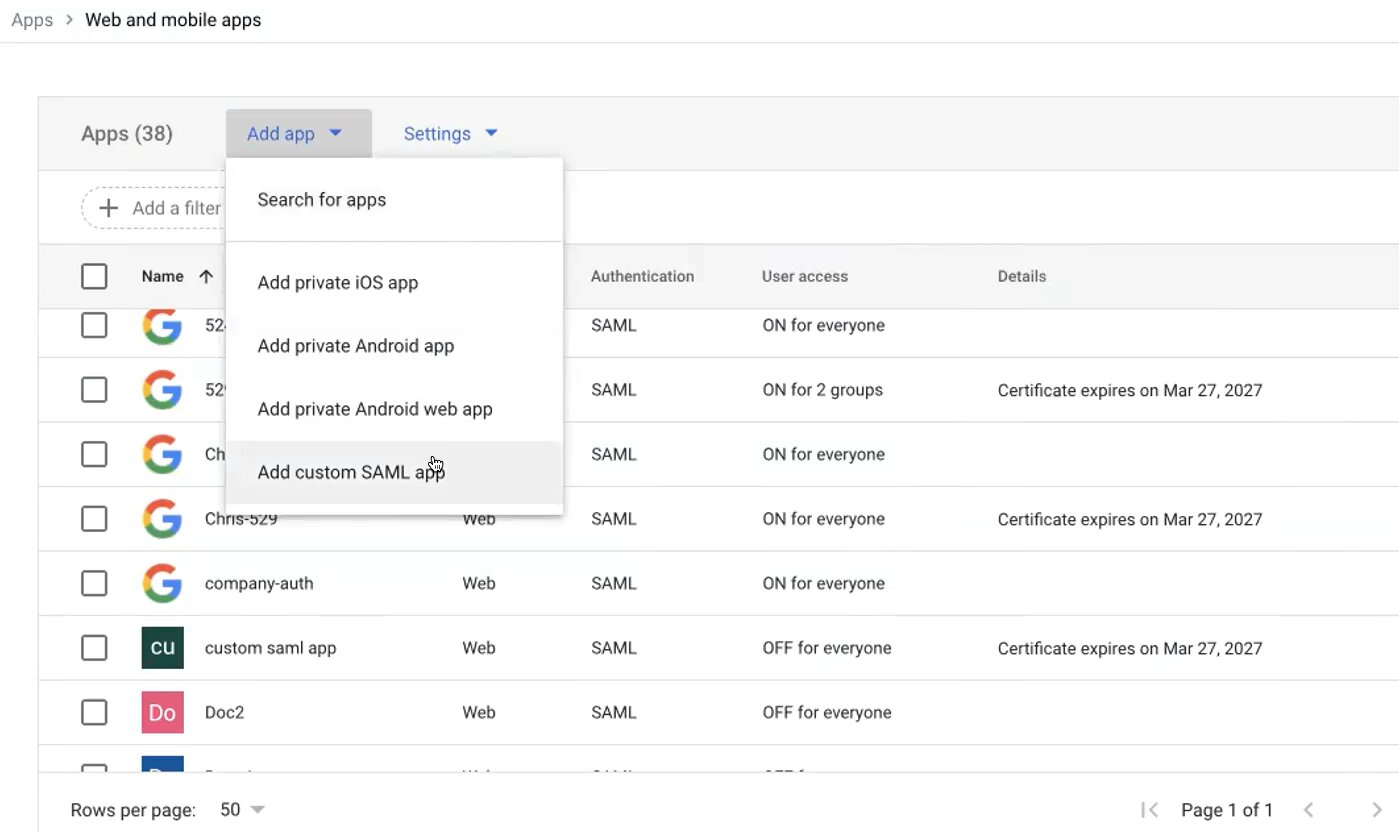
- In the App name field, type a unique name for the app and click CONTINUE.
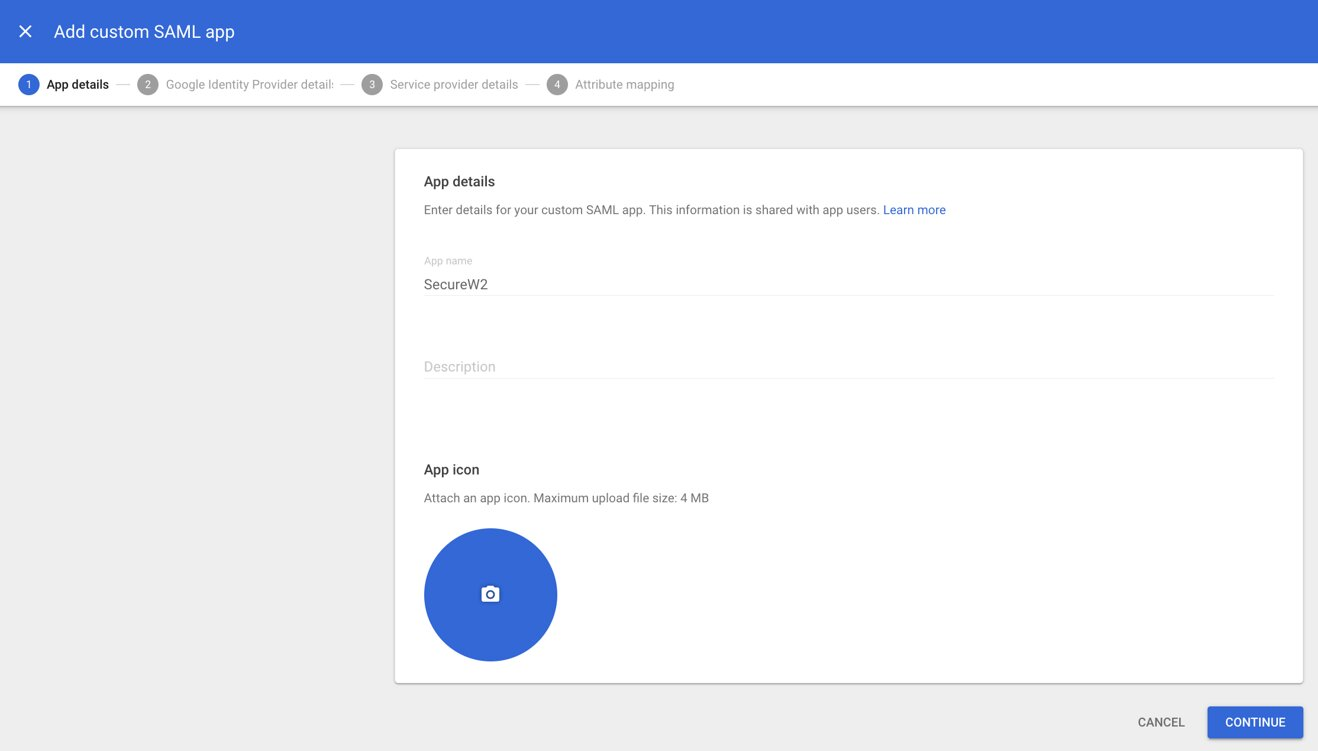
- Under Option 1, click the DOWNLOAD METADATA button and save the metadata file (.XML) on your computer. You need to import this metadata file to the JoinNow Management Portal.
- Click CONTINUE.
- In the JoinNow Management Portal, go to Identity Management > Identity Providers.
- On the Identity Providers page, click the Edit link for the newly added SAML application.
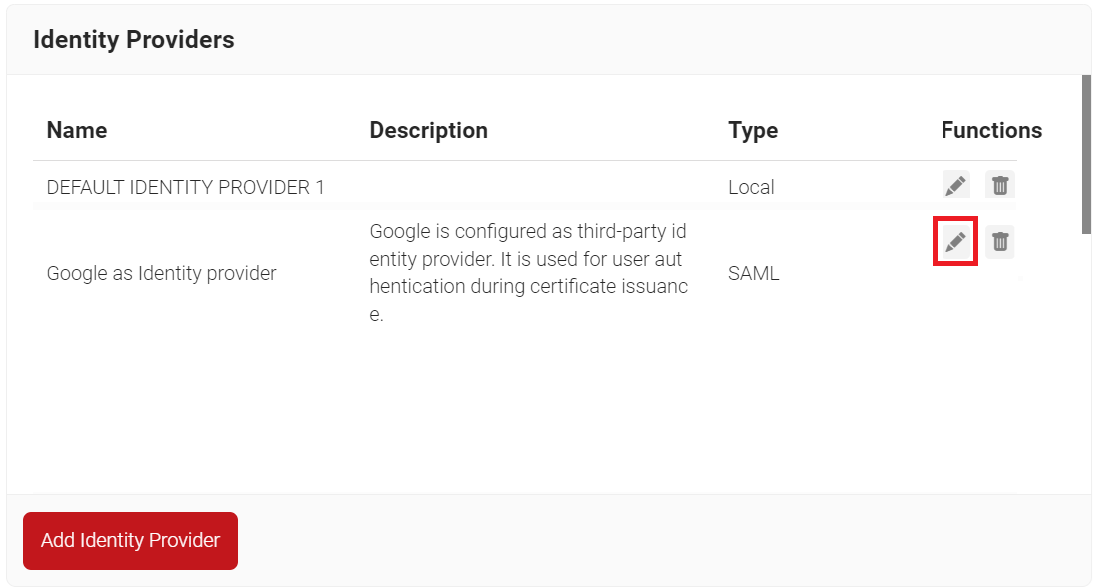
- Click the Configuration tab.
- In the Service Provider (SP) Info section, copy the ACS URL and Entity ID values to your clipboard.
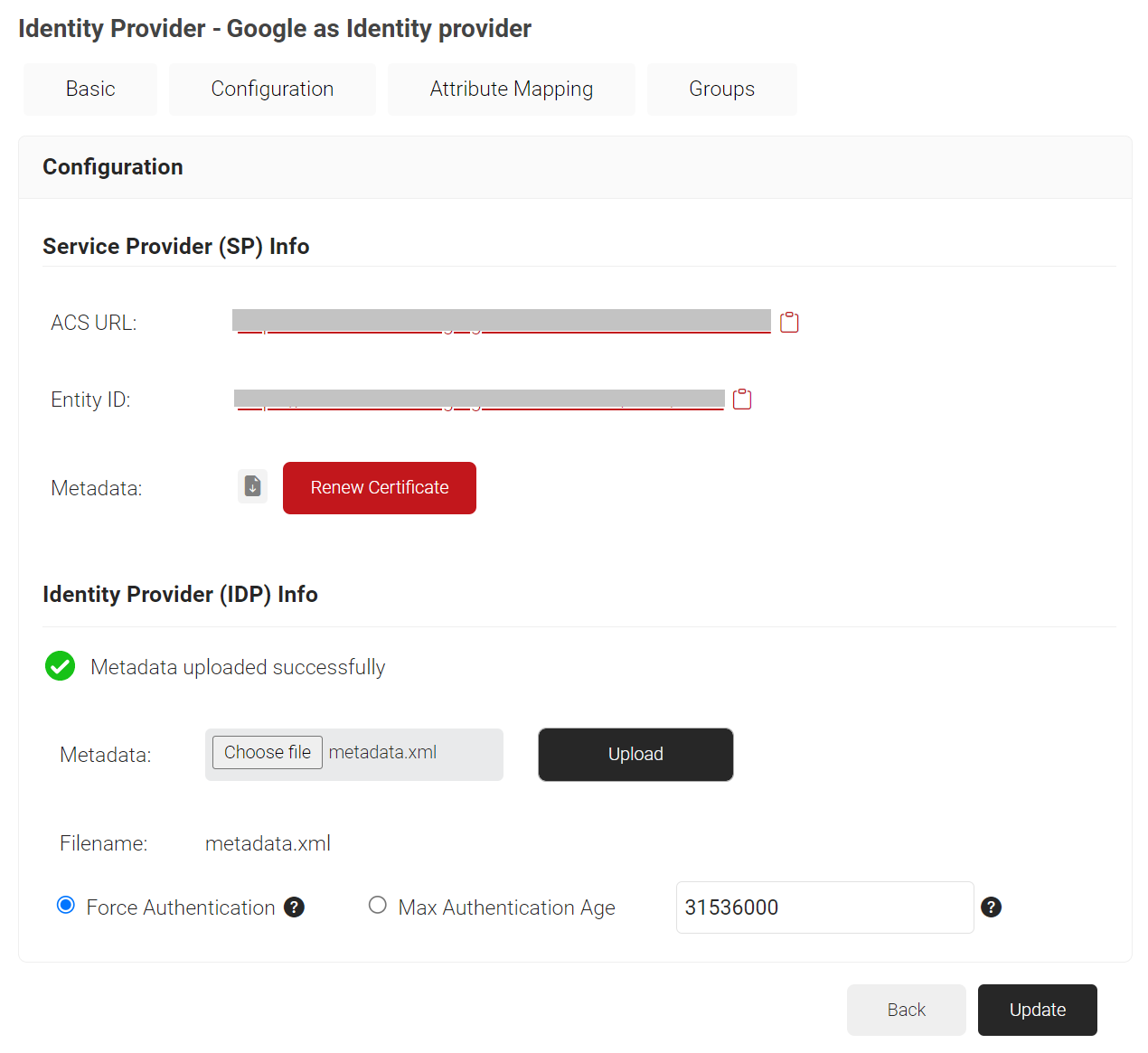
- In the Identity Provider (IDP) Info section, for the Metadata field, click Choose file and select the metadata (.XML) file that you downloaded earlier from Google SAML Apps.
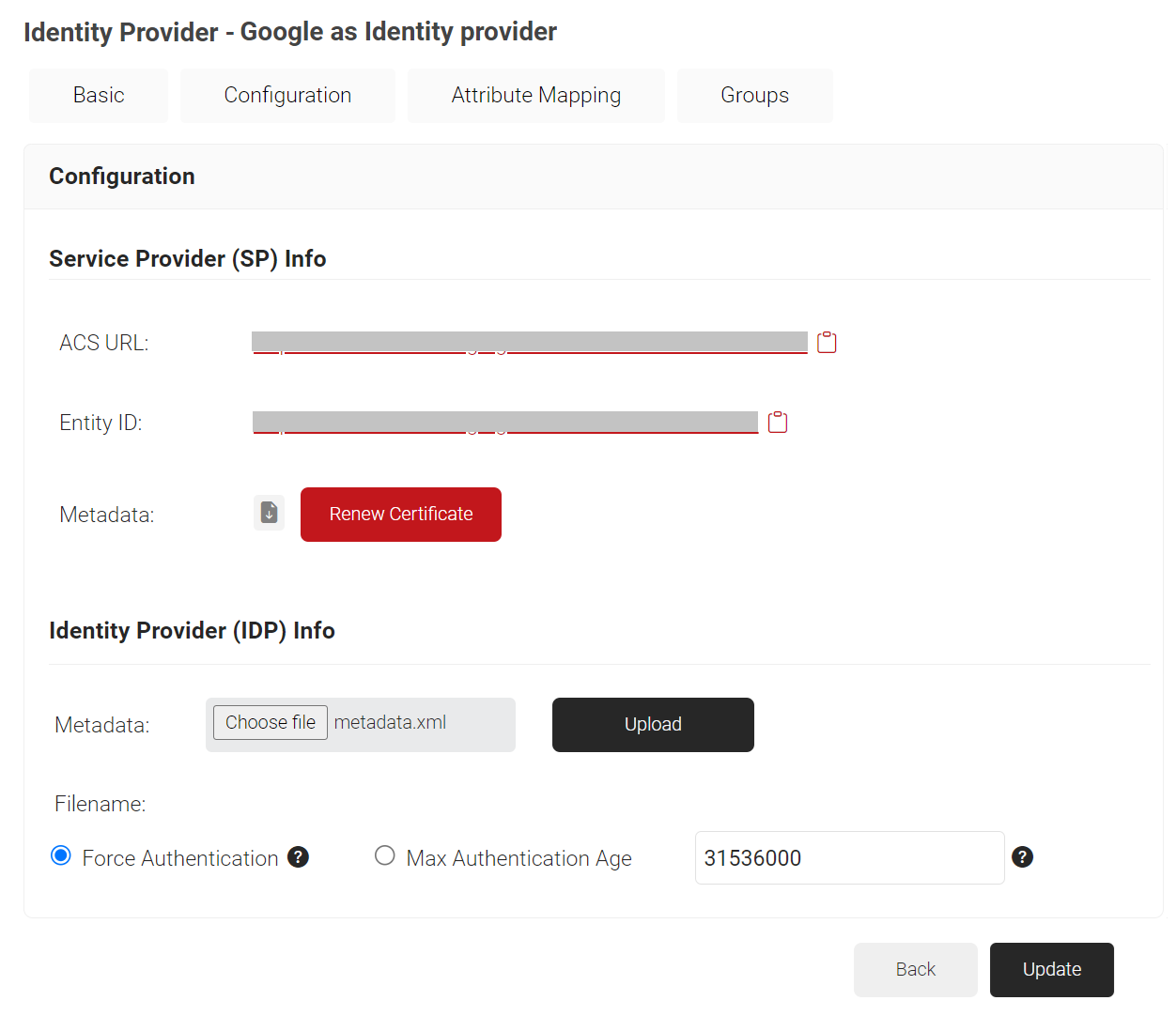
- Click Upload and then click Update.
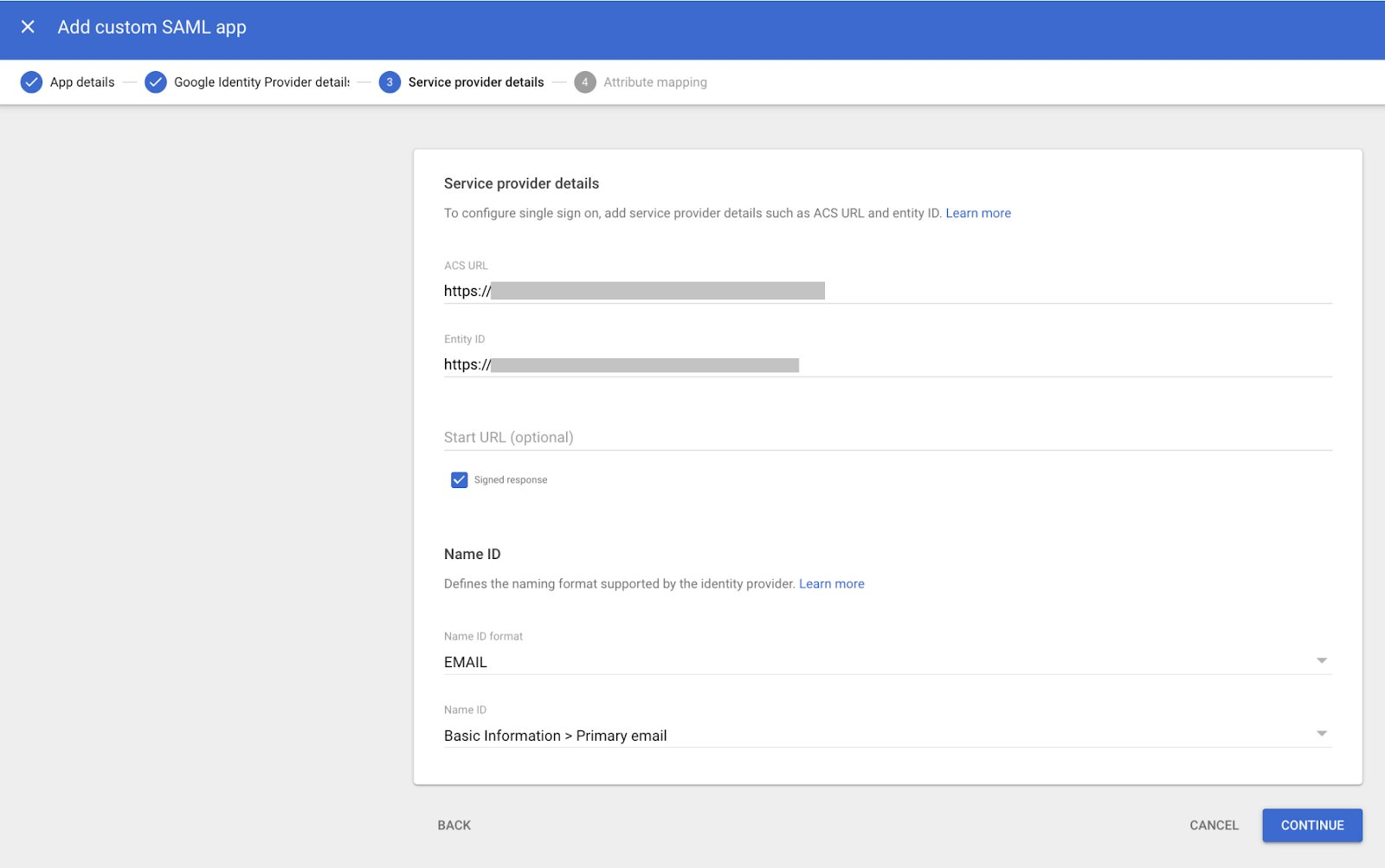
- Go to Google SAML Apps, and on the Service provider details screen, add the ACS URL and Entity ID (obtained in step 10).
- Check the Signed response checkbox.
- From the Name ID format drop-down list, select EMAIL.
- From the Name ID drop-down list, select Basic information > Primary email.
- Click CONTINUE.
- Click Finish on the Attribute Mapping screen.
Configuring Attribute Mapping in Google
- On the Google Admin page, scroll down to Attribute Mapping.
- Click ADD MAPPING to configure the attributes to be encoded in the certificate.
NOTE: Your directory will likely have a name and an email. - From the Google Directory attributes drop-down list, under Basic Information, select Primary email.
- In the App attributes field, type Email.
- Click ADD MAPPING again.
- From the Google Directory attributes drop-down list, under Basic Information, select First name.
- In the App attributes field, type FirstName.
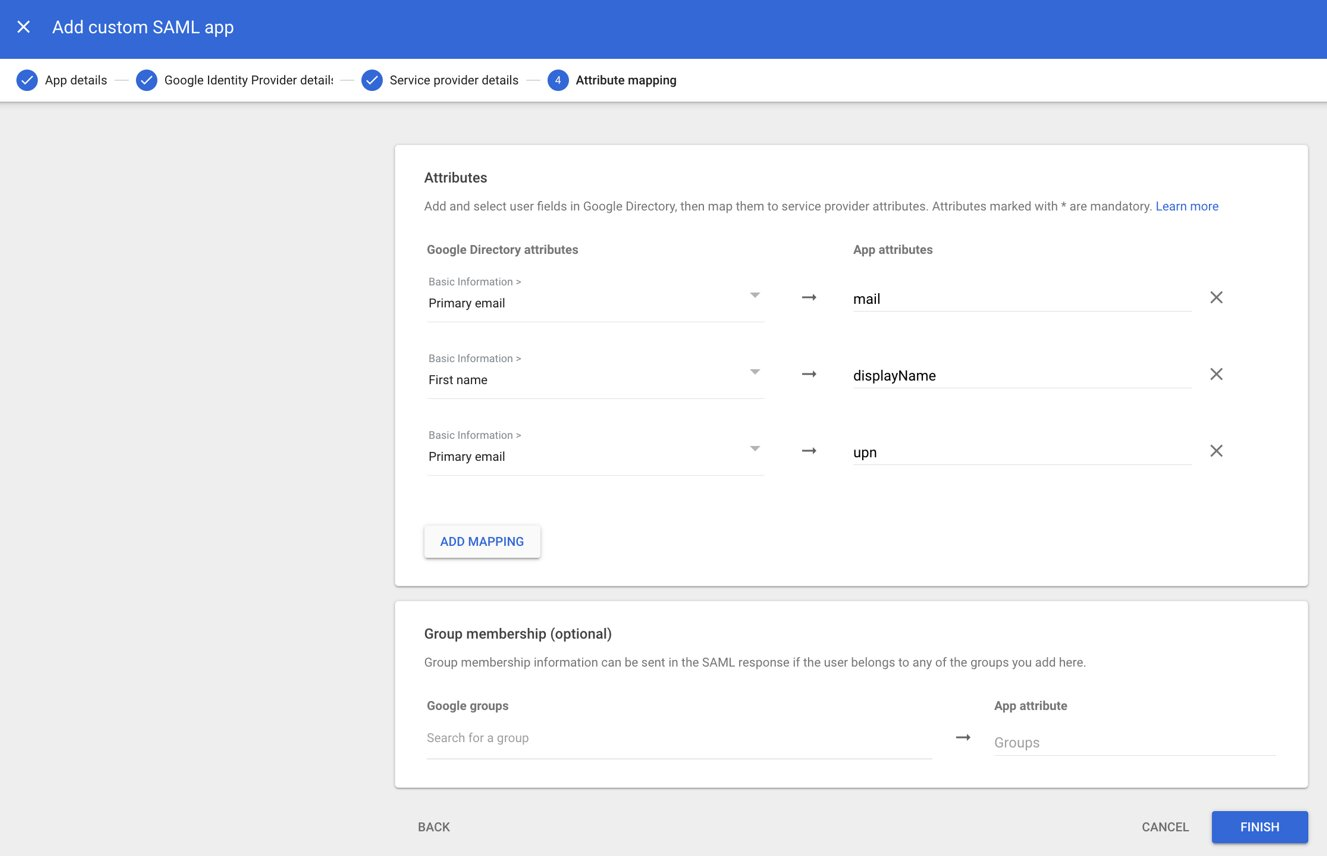
- Click FINISH
After Google identifies the users that are trying to connect, it sends their name and email to SecureW2, which SecureW2 populates in the certificates. The attributes that Google sends are populated in the variables in the certificates.
- In the JoinNow Management Portal, navigate to Identity Management > Identity Providers.
- Click the Edit link for the SAML application that you created earlier.

- Click the Attribute Mapping tab.
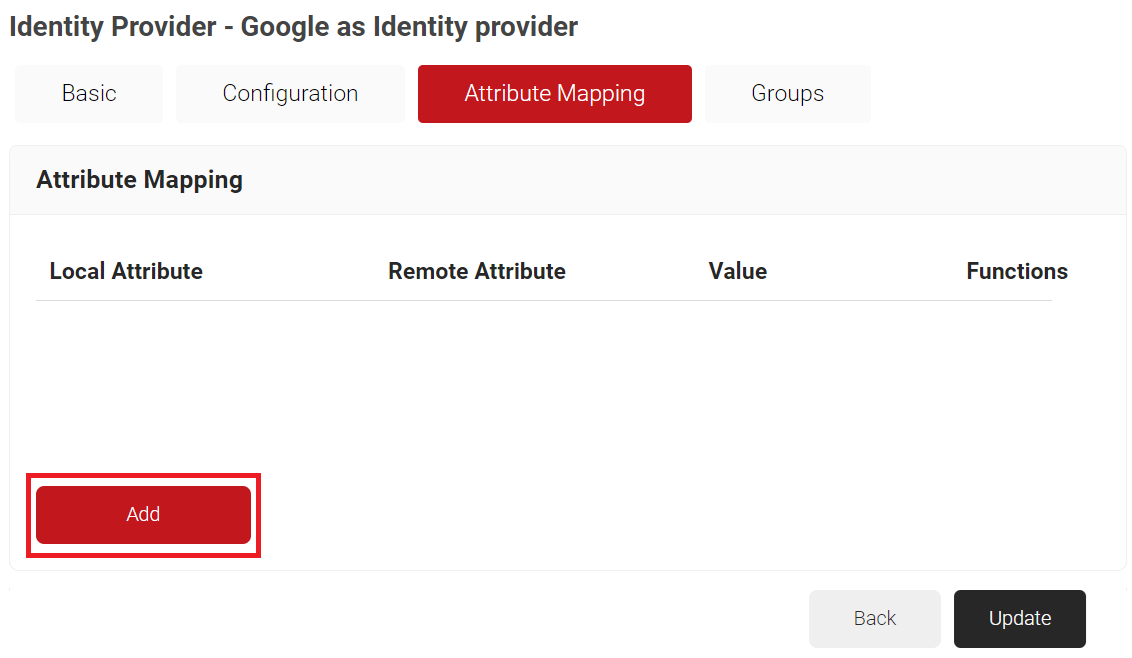
- Click Add.
- In the Local Attribute field, enter email as the name of the variable.
- From the Remote Attribute drop-down list, select Email.
- Click Next.
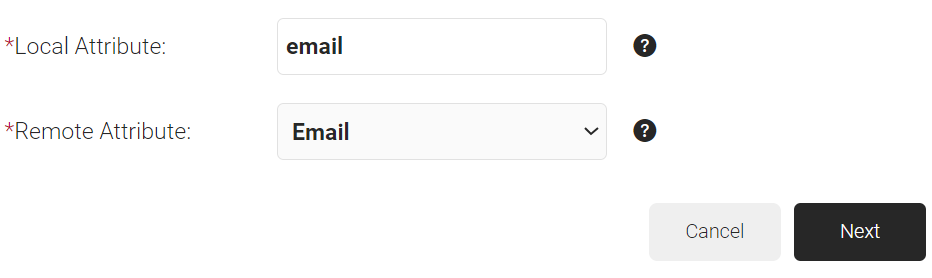
- Click Add.
- In the Local Attribute field, enter displayName as the variable’s name.
- From the Remote Attribute drop-down list, select User Defined. Enter FirstName in the field that appears next to the Remote Attribute field.
- Click Next.
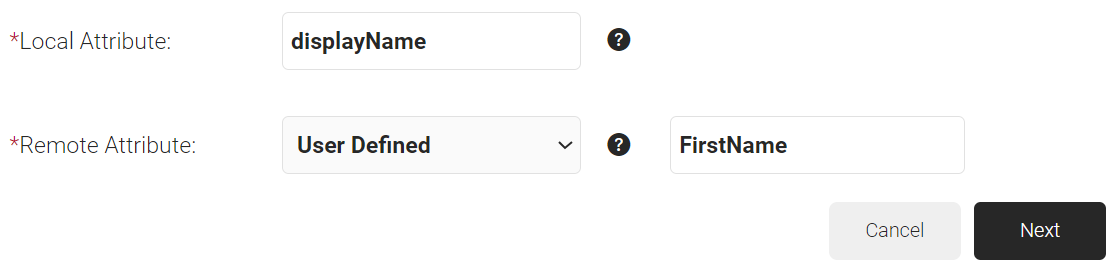
- Click Add.
- In the Local Attribute field, enter upn as the name of the variable.
NOTE: When using digital certificates for eduroam authentication, the request includes the UPN, which contains the username and realm. This helps identify the user’s organization and ensures RADIUS requests are routed correctly. - From the Remote Attribute drop-down list, select User Defined. Enter Email in the field that appears next to the Remote Attribute field.
- Click Next.
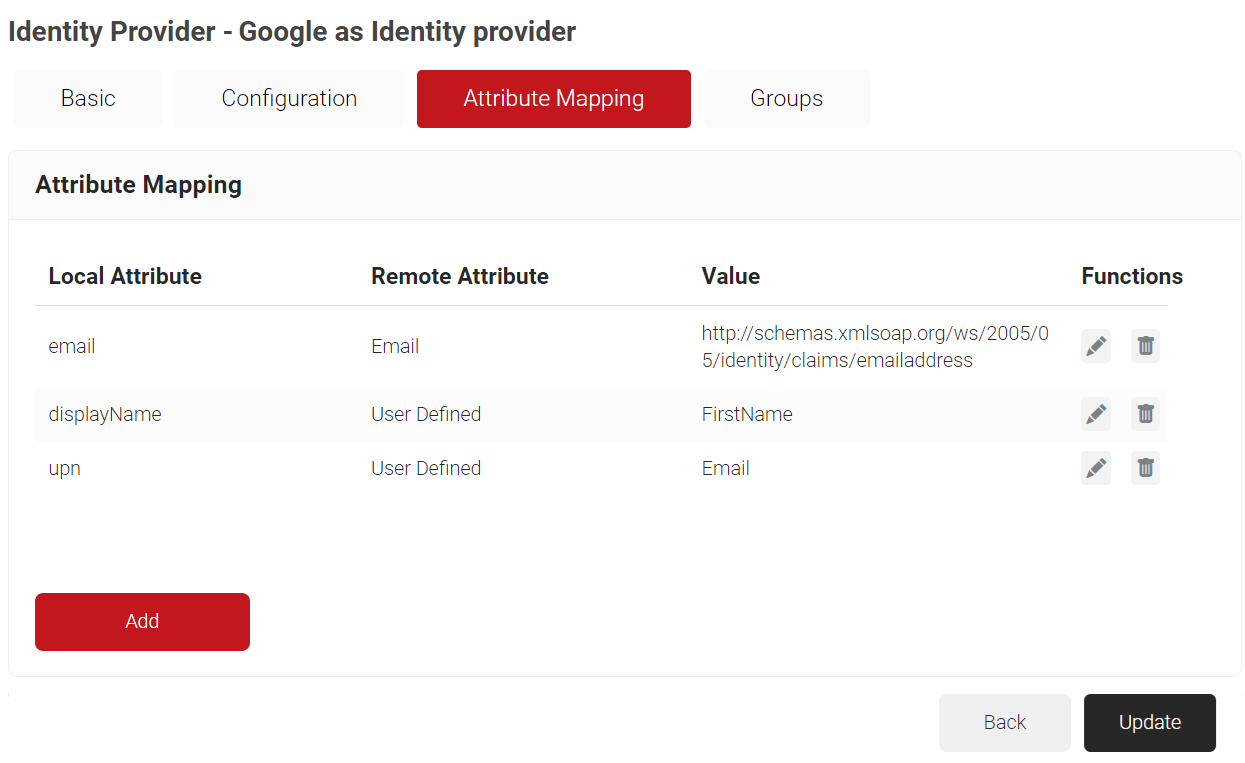
- Click Update.
The attributes are now configured, and you can view them under certificates. To do so:
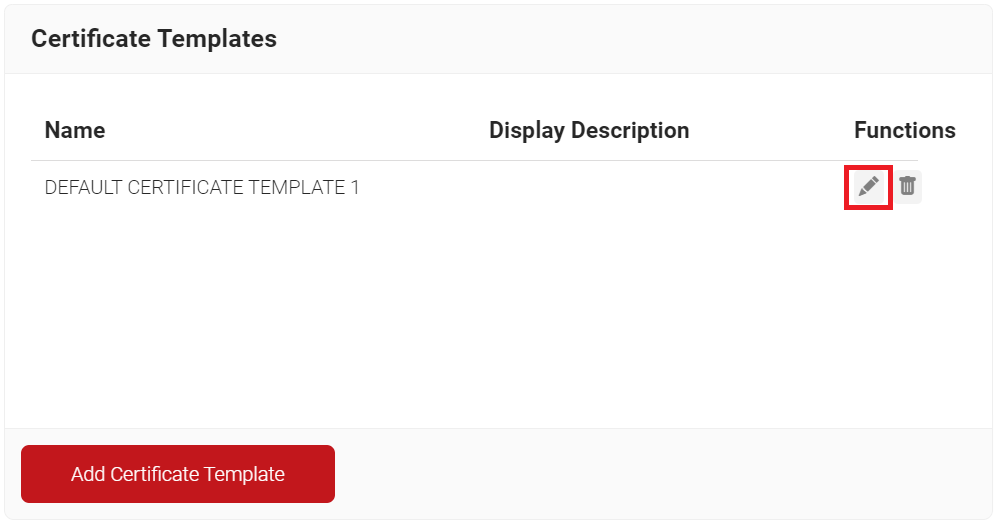
- Navigate to Dynamic PKI > Certificate Authorities.
- Scroll to the Certificate Templates section and click the Edit link for DEFAULT CERTIFICATE TEMPLATE 1.
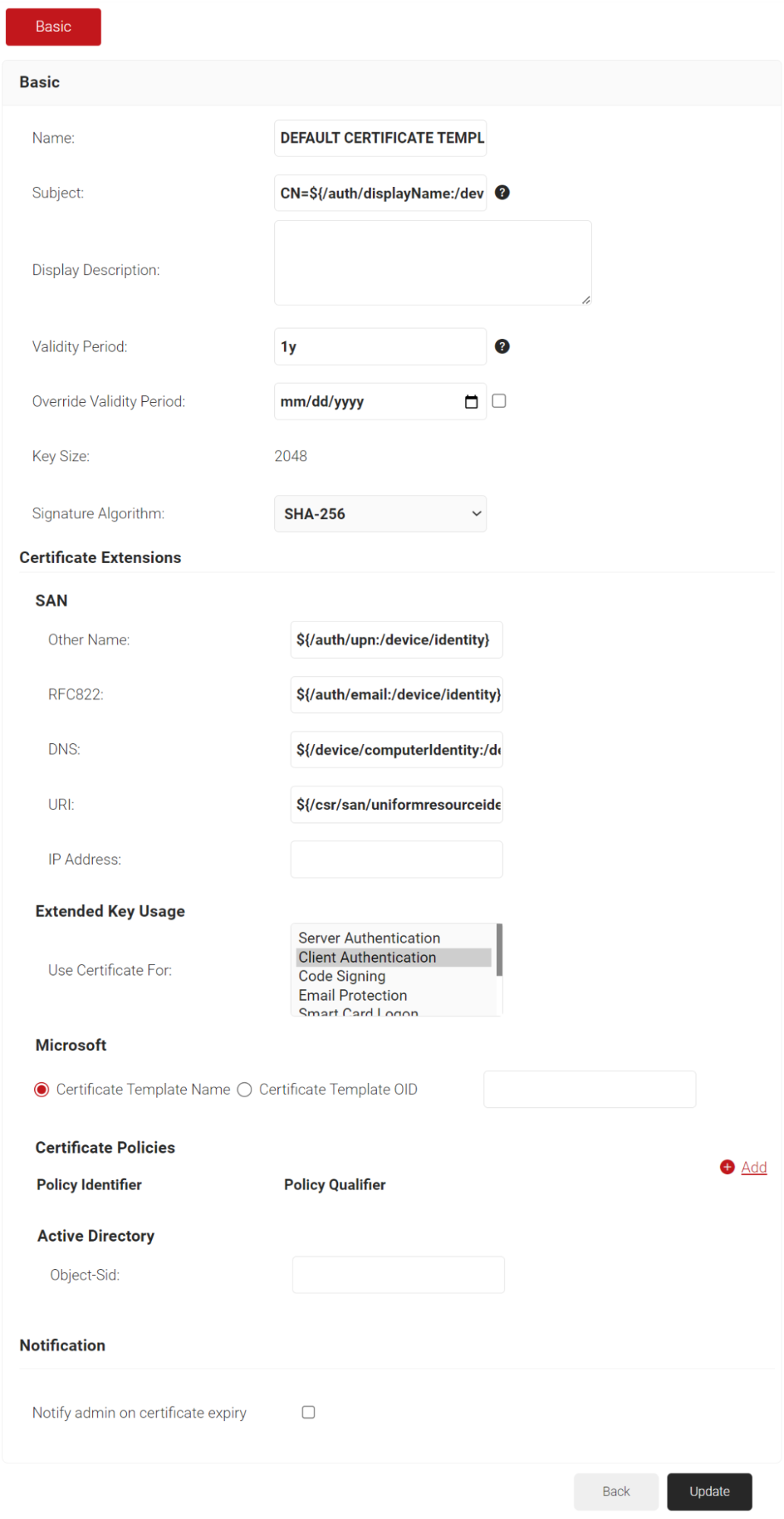
- Under the Basic section, note that the displayName variable is encoded as Subject.
- Under SAN, note that the upn is encoded as Other Name, and email is encoded as RFC822.
Policy Management
SecureW2 PKI supports integration with Google Workspace using SAML to authenticate users and issue certificates based on policies configured in the JoinNow Management Portal. The following policy components must be set up: the Authentication Policy for SAML-based user authentication, the Policy Engine Workflow to categorize users and devices, and the Enrollment Policy to manage certificate issuance.
The Authentication Policy links the Identity Provider to the network profile and is required to authenticate users with the specified Identity Provider. The Policy Engine Workflow allows you to define and create roles based on attributes and groups retrieved from the Identity Provider. These roles can then be assigned a unique Enrollment Policy for certificate issuance and used to trigger a Network Policy.
Creating an Authentication Policy
An Authentication Policy can be created from the Authentication Policies page. If you’ve already set up an authentication policy through Getting Started, you can either edit it with the required values or create a new one.
To create a new Authentication Policy, perform the following steps:
- Navigate to Policy Management > Authentication Policies.
- On the Authentication Policies page, click Add Authentication Policy.
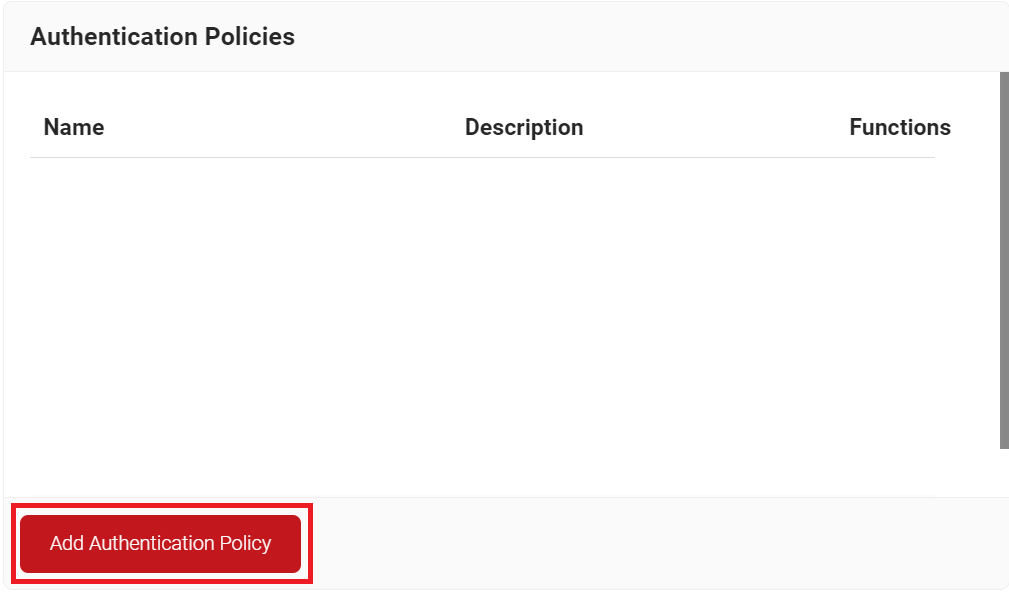
- In the Basic section, enter the name of the Authentication Policy in the Name field.
- In the Display Description field, enter a suitable description for the Authentication Policy.
- Click Save.
- Click the Conditions tab.
- In the Profile drop-down list, ensure that your network profile is selected.
- Click the Settings tab.
- From the Identity Provider drop-down list, select the IDP you created earlier (refer to the Creating a SAML Identity Provider in SecureW2 section).
- Select the Enable User Self Service check box.
- Click Update.
Creating a Policy Engine Workflow
To configure a Policy Engine Workflow:
- Navigate to Policy Management > Policy Engine Workflows.
- Click Add Policy Engine Workflows.
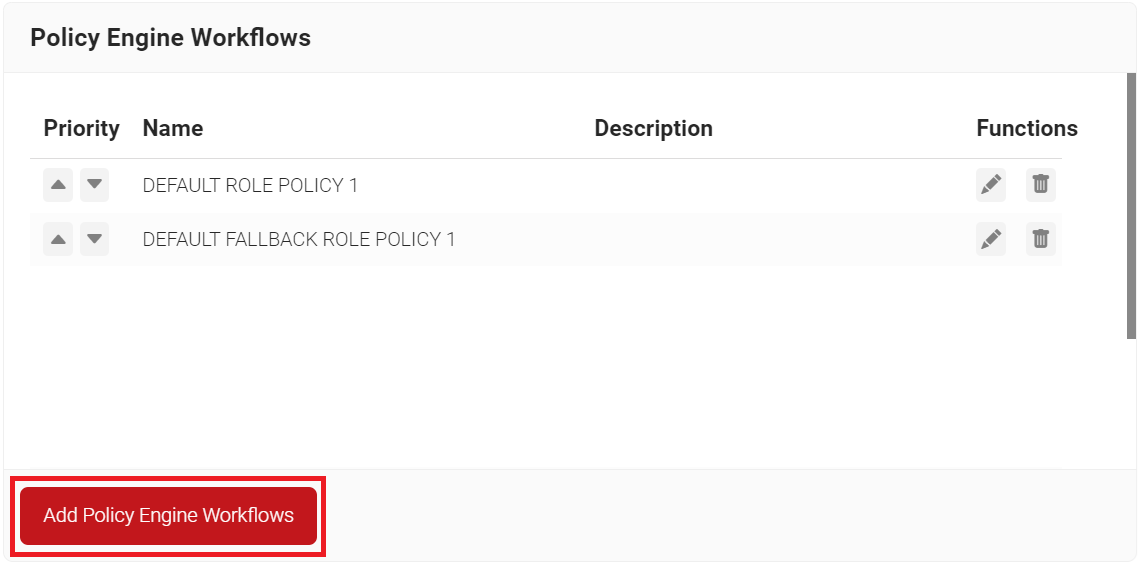
- In the Basic section, enter the name of the policy engine workflow in the Name field.
- In the Display Description field, enter a suitable description for the policy engine workflow.
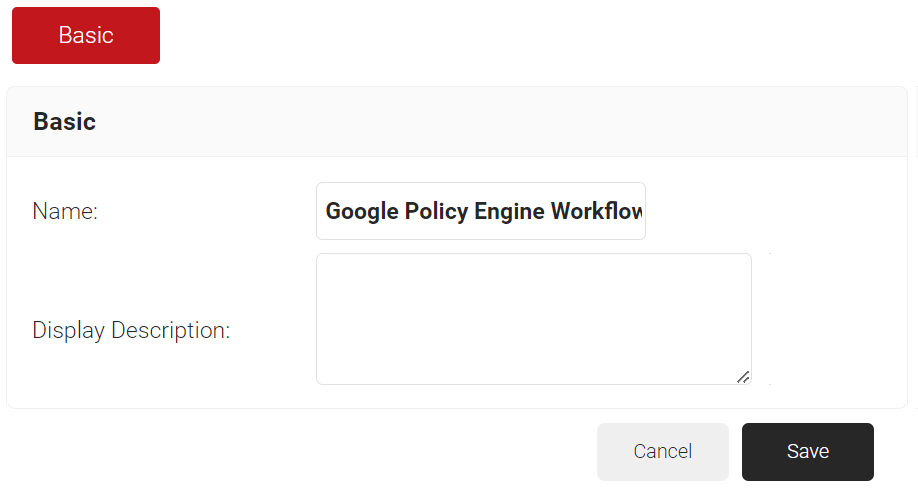
- Click Save.
- Select the Conditions tab.
- From the Identity Provider drop-down list, select the IDP that you created earlier (refer to the Creating a SAML Identity Provider in SecureW2 section).
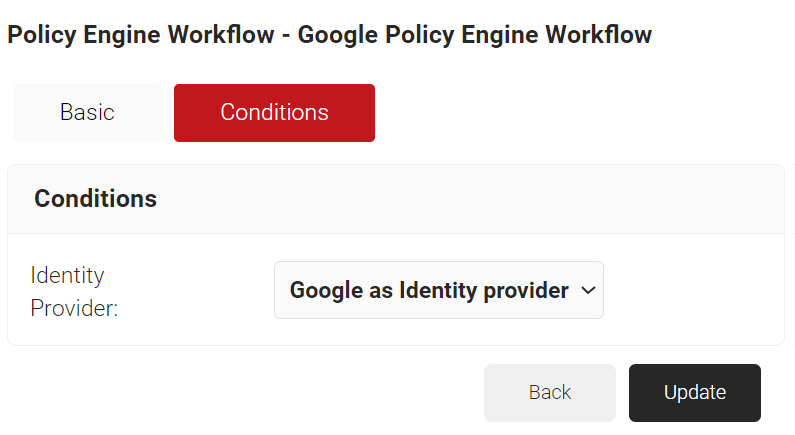
- Click Update.
Creating an Enrollment Policy
Now, the lookup can be used before the certificate issuance as a dynamic check. To trigger the lookup during the certificate issuance, map the policy engine workflow (created in the Creating a SAML Policy Engine Workflow section) in the enrollment policy created below:
- Navigate to Policy Management > Enrollment Policies.
- Click Add Enrollment Policy.
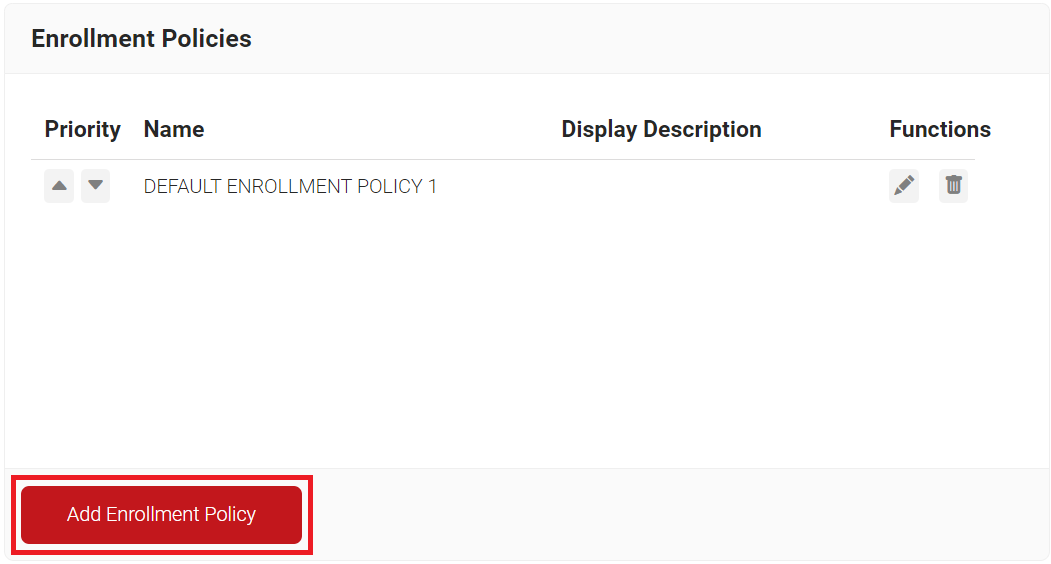
- In the Basic section, enter the name of the enrollment policy in the Name field.
- In the Display Description field, enter a suitable description for the enrollment policy.
- Click Save.
- The page refreshes, and the Conditions and Settings tabs are displayed.
- Select the Conditions tab.
- In the Conditions section, from the Role drop-down list, select the role policy you created earlier (see the Creating a Policy Engine Workflow section).
- From the Device Role drop-down list, select DEFAULT DEVICE ROLE POLICY.
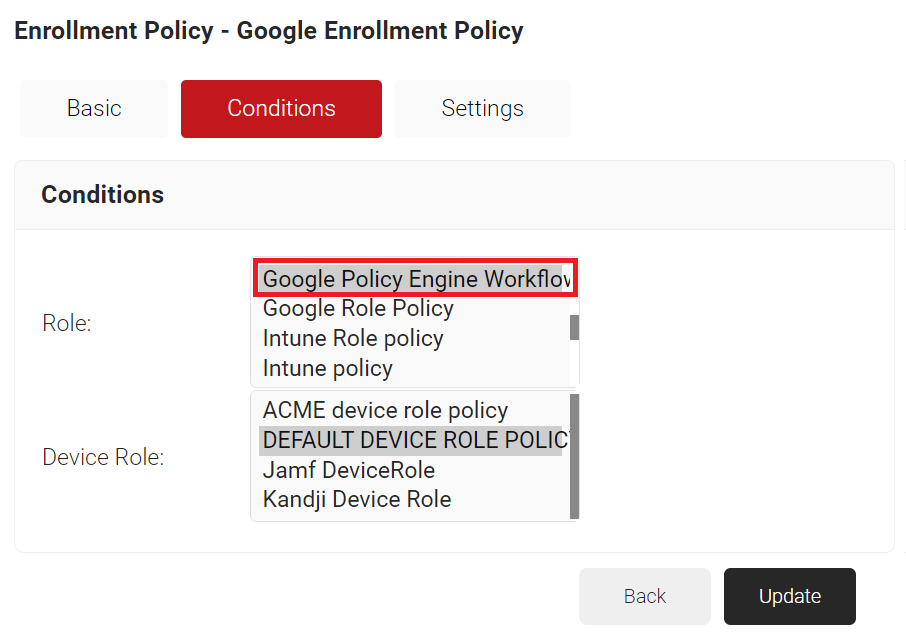
- Click Update.
Network Authentication Configuration
During the RADIUS EAP-TLS authentication, the user or device will present the 802.1X client certificate, and the RADIUS, as an authentication server, will verify the relevant information from the certificate against the existing users in the Identity Provider. If it matches the IDP and the certificate is not expired, or on the Certificate Revocation List (CRL), the user or device authentication is completed and is granted access to the network.
Now, we will create an Identity Lookup provider in SecureW2 to connect our Identity Provider service account to lookup users, in this case, Google Workspace, groups, and their devices.
The following are the configurations for network authentication:
- Creating a New Project
- Creating A Service Account and a JSON Key File
- Delegating Domain Wide Authority to Service Account from Google Admin Console
- Creating a User in Google Admin Console
- Creating a Role with Read-only Access
- Creating an Intermediate CA for Google Workspace Integration
- Creating a Certificate Template for Google Lookup
- Creating a Google Workspace Identity Lookup Provider
- Configuring Policies (Account Lookup Policy, Policy Engine Workflow and Network Policy)
Configuring Google
The following are the high-level steps required to configure Google IAM & Admin console for dynamic lookup with JoinNow:
Creating a New Project
The Google Service Account must be created in the IAM & Admin console. Log into the Google IAM & Admin console using the link here.
To create a new project in the Google service account:
- Log in to the Google Service Account.
- Click the Select a Project drop-down list at the top of the page.
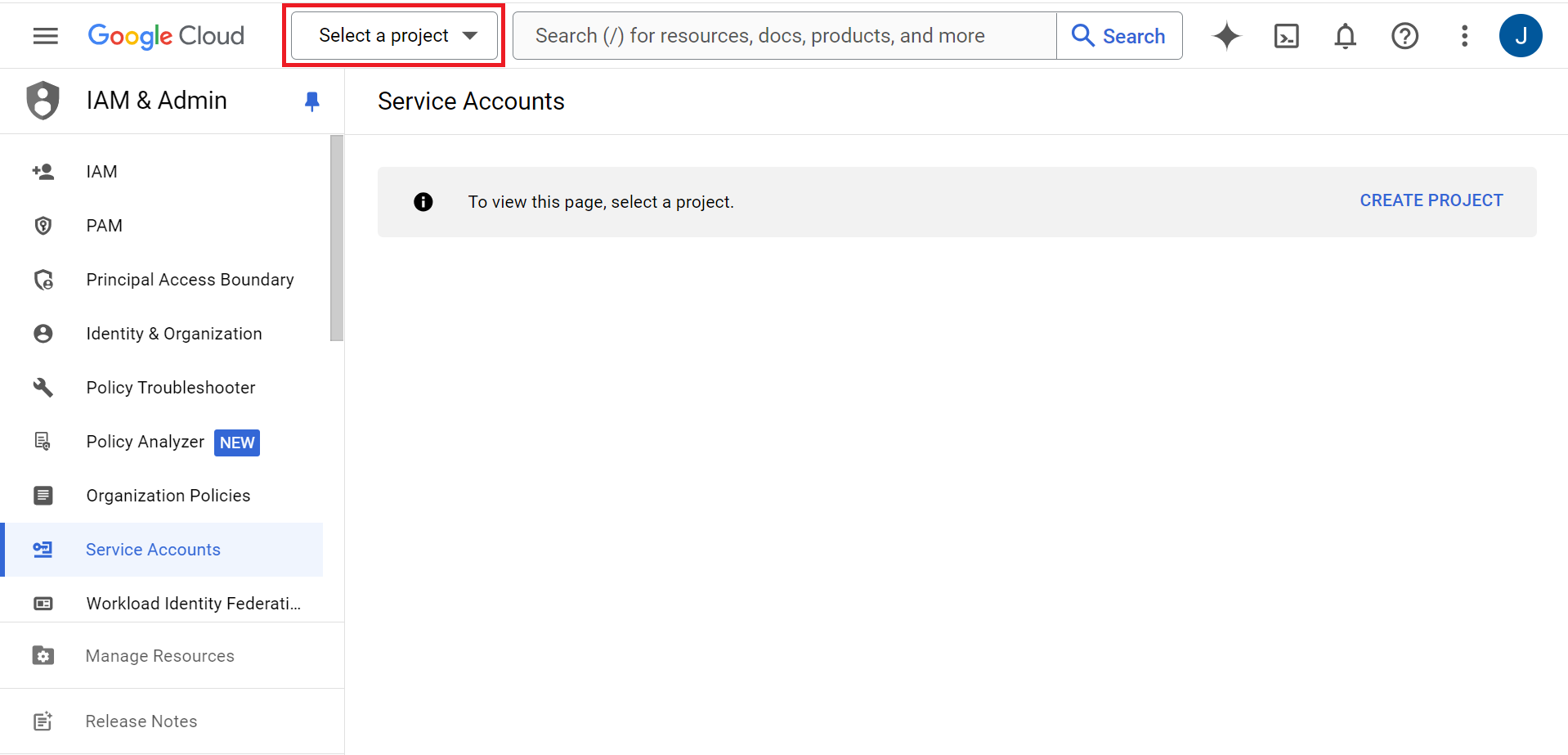
- Click NEW PROJECT.
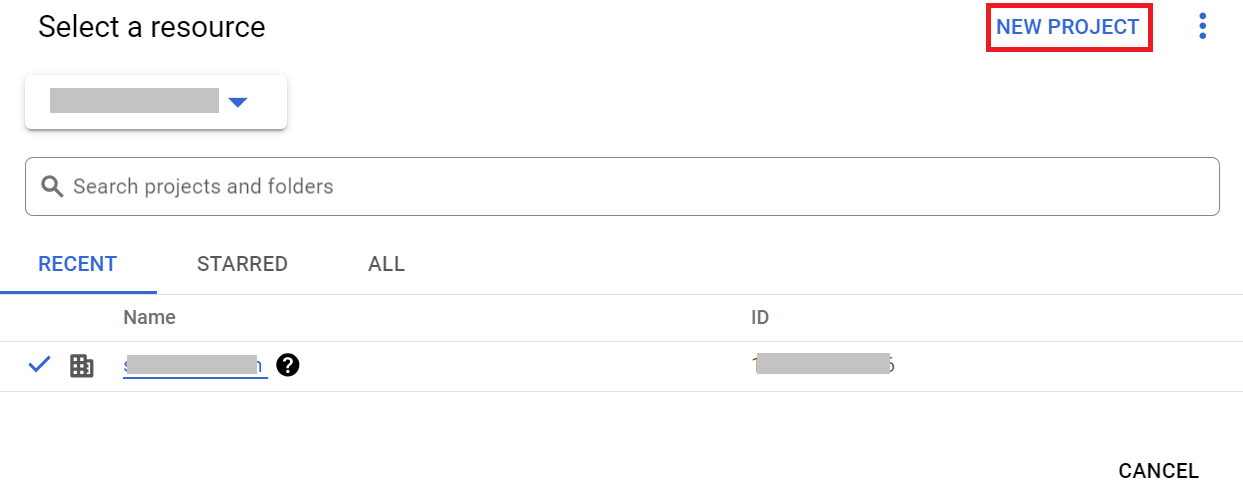
- On the New Project page, enter a name for the project in the Project name field.
- From the Organization drop-down list, select the required organization for the project.
- From the Location drop-down list, select the parent organization.
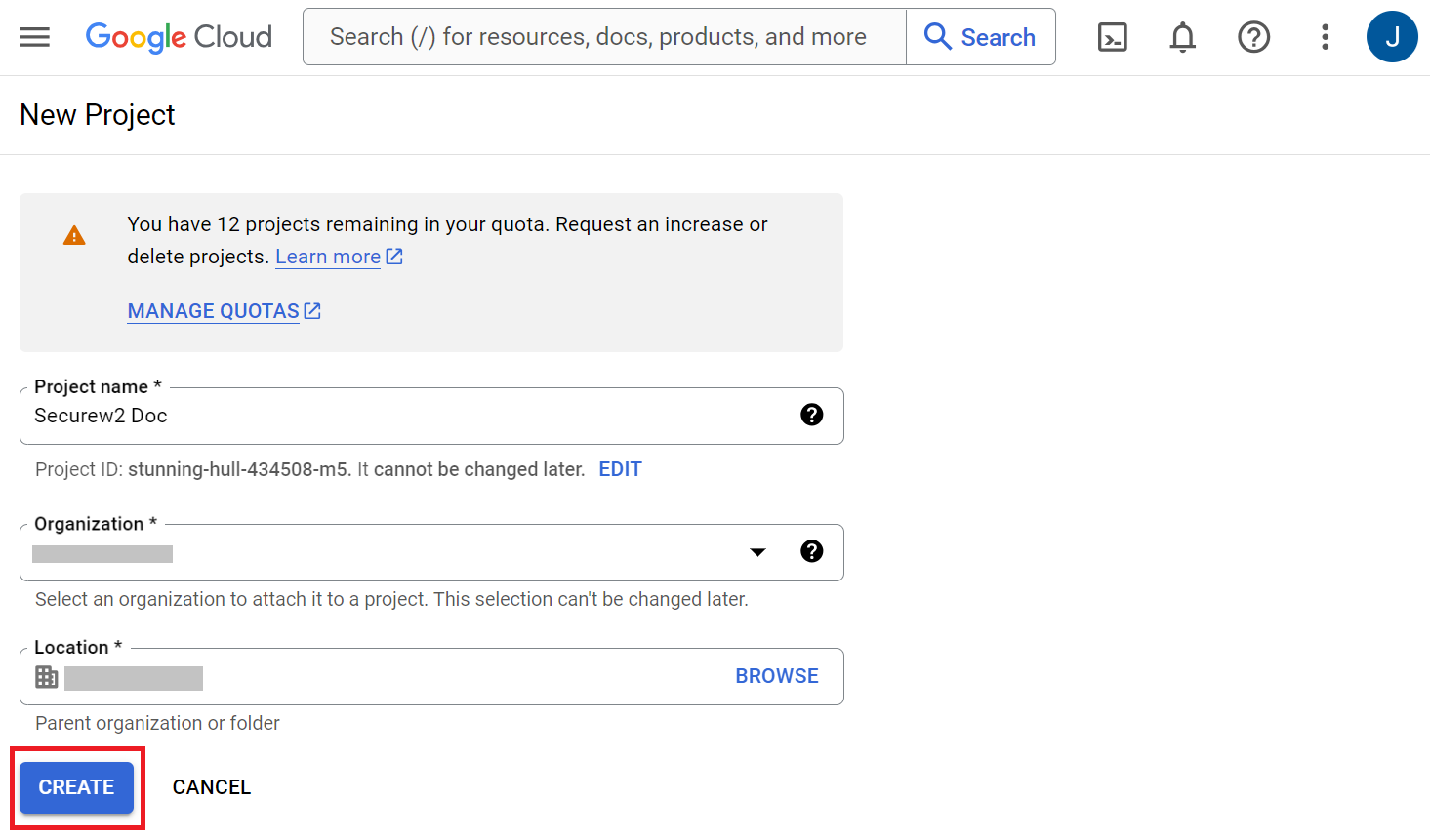
- Click Create.
Creating A Service Account and a JSON Key File
JoinNow needs a Google Service Account to authorize communication with Google to do a lookup operation on behalf of the service account. To create a Service Account in Google:
- From the left menu pane, click Service Accounts.
- Click + CREATE SERVICE ACCOUNT.
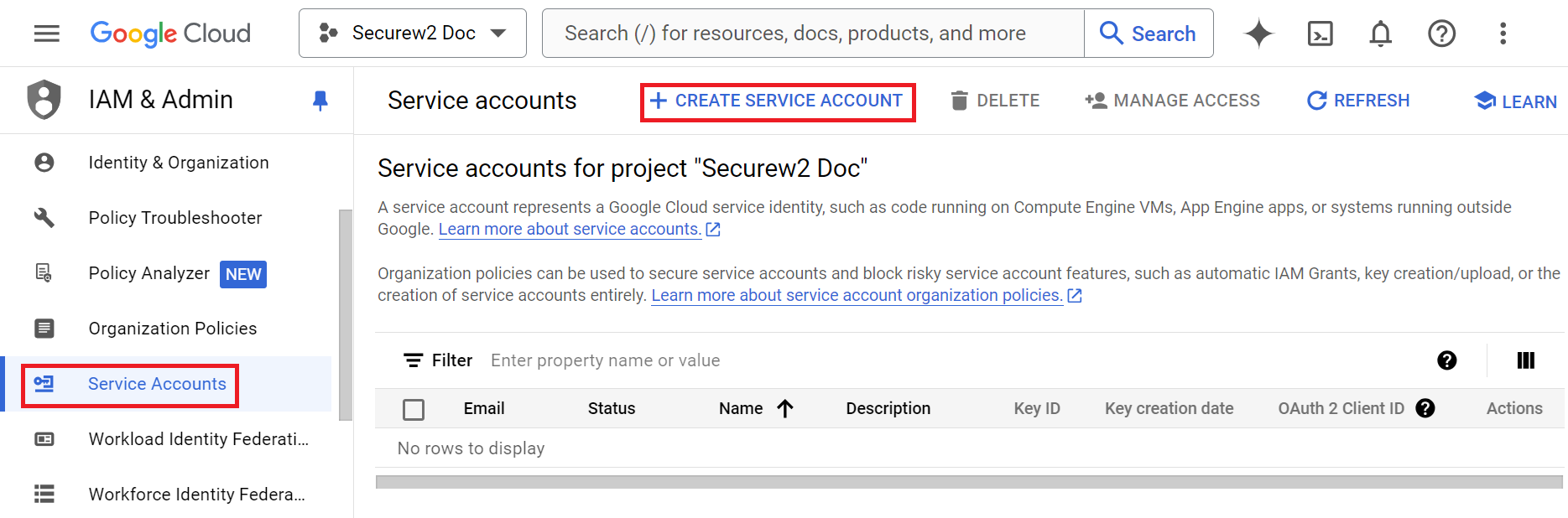
- In the Service account name field, enter a name for your service account. By default, the service account name entered previously is automatically used as the Service account ID. You can either use this default name or enter a new one.
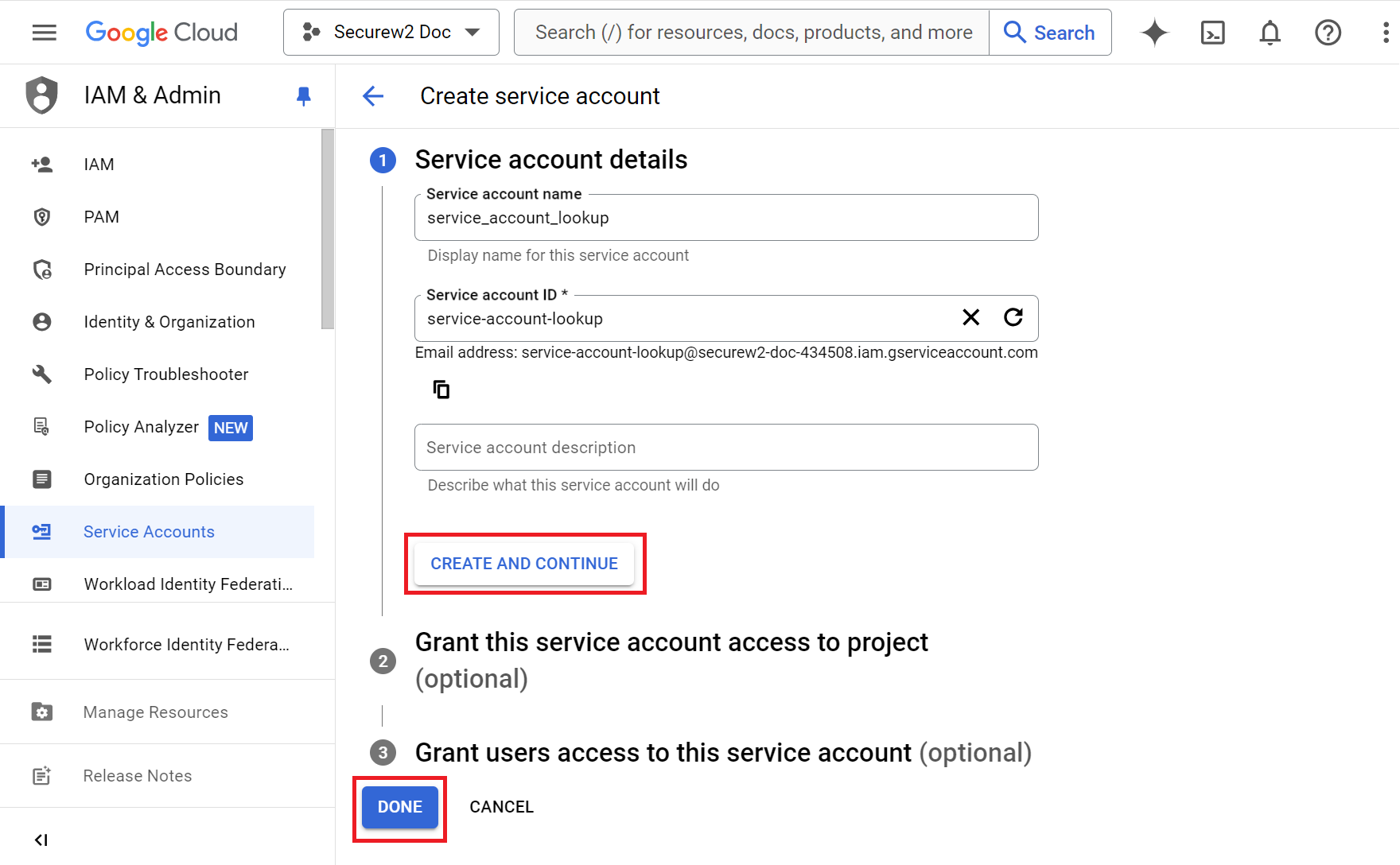
- Click CREATE AND CONTINUE.
- Click DONE. The required service account will be created.
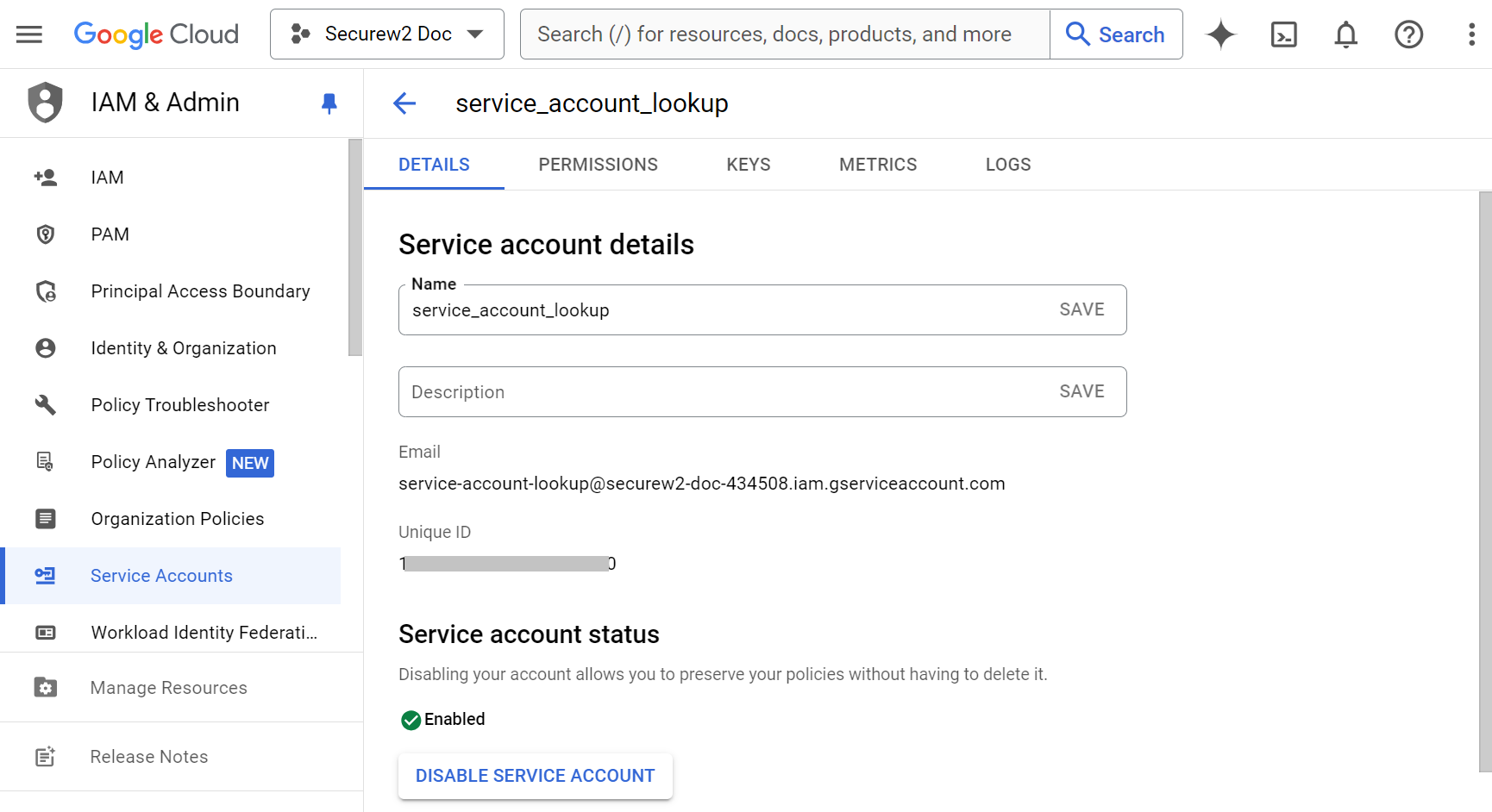
- Click on the recently created service account link.
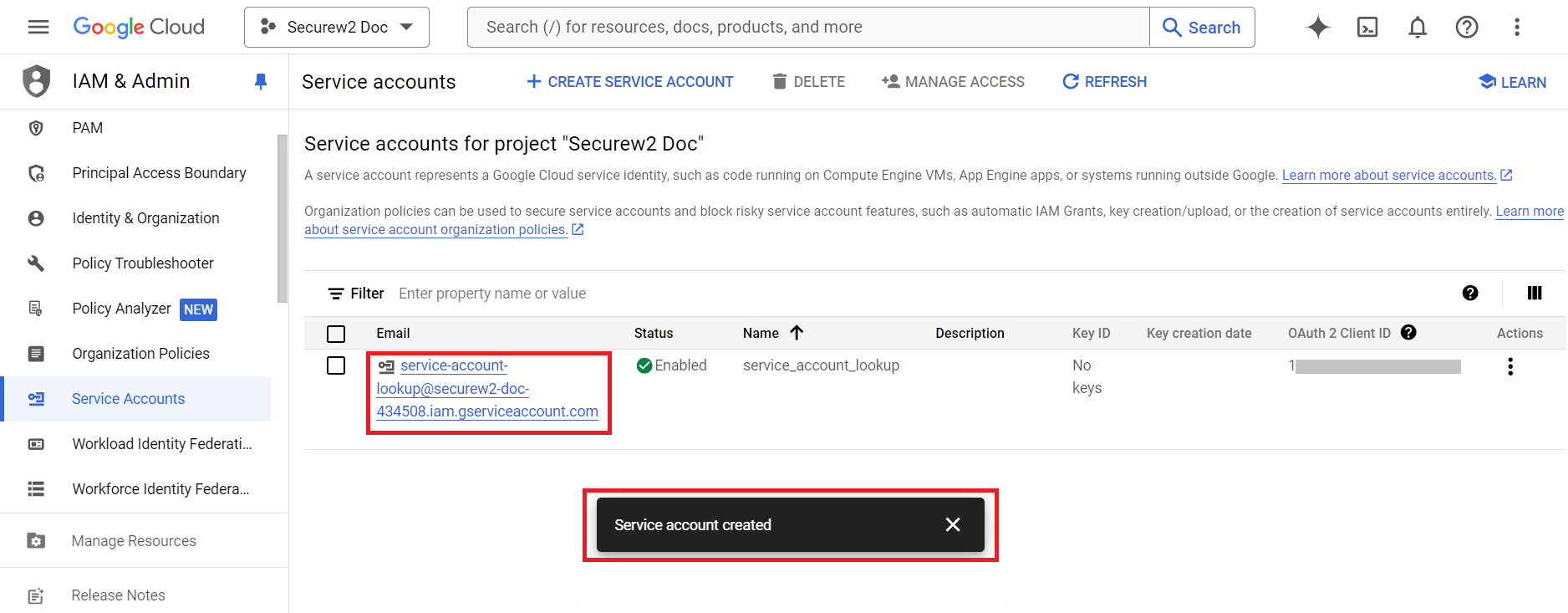
- On the service_account_lookup page, click the KEYS tab.
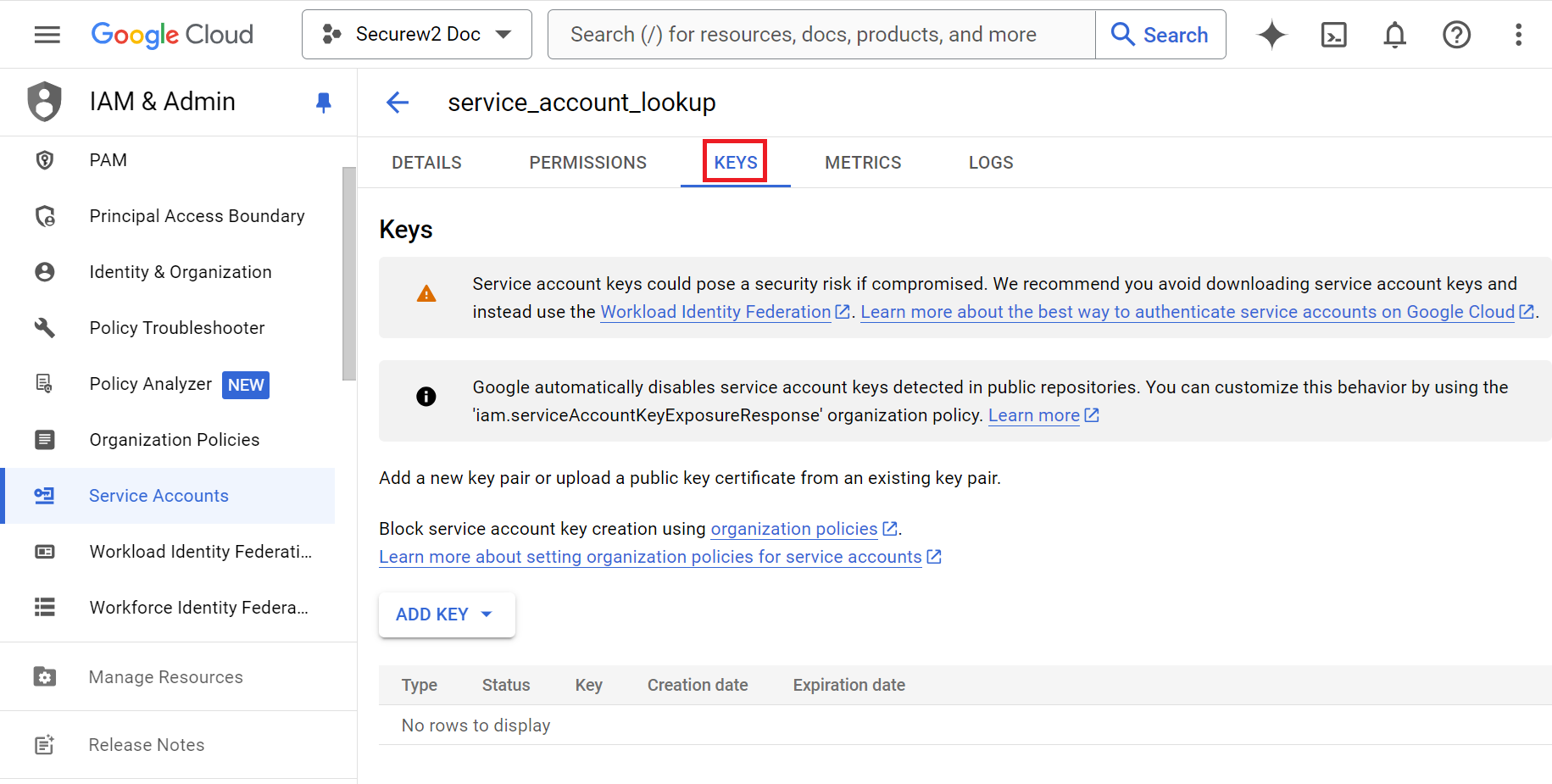
- From the ADD KEY drop-down list, select Create new Key.
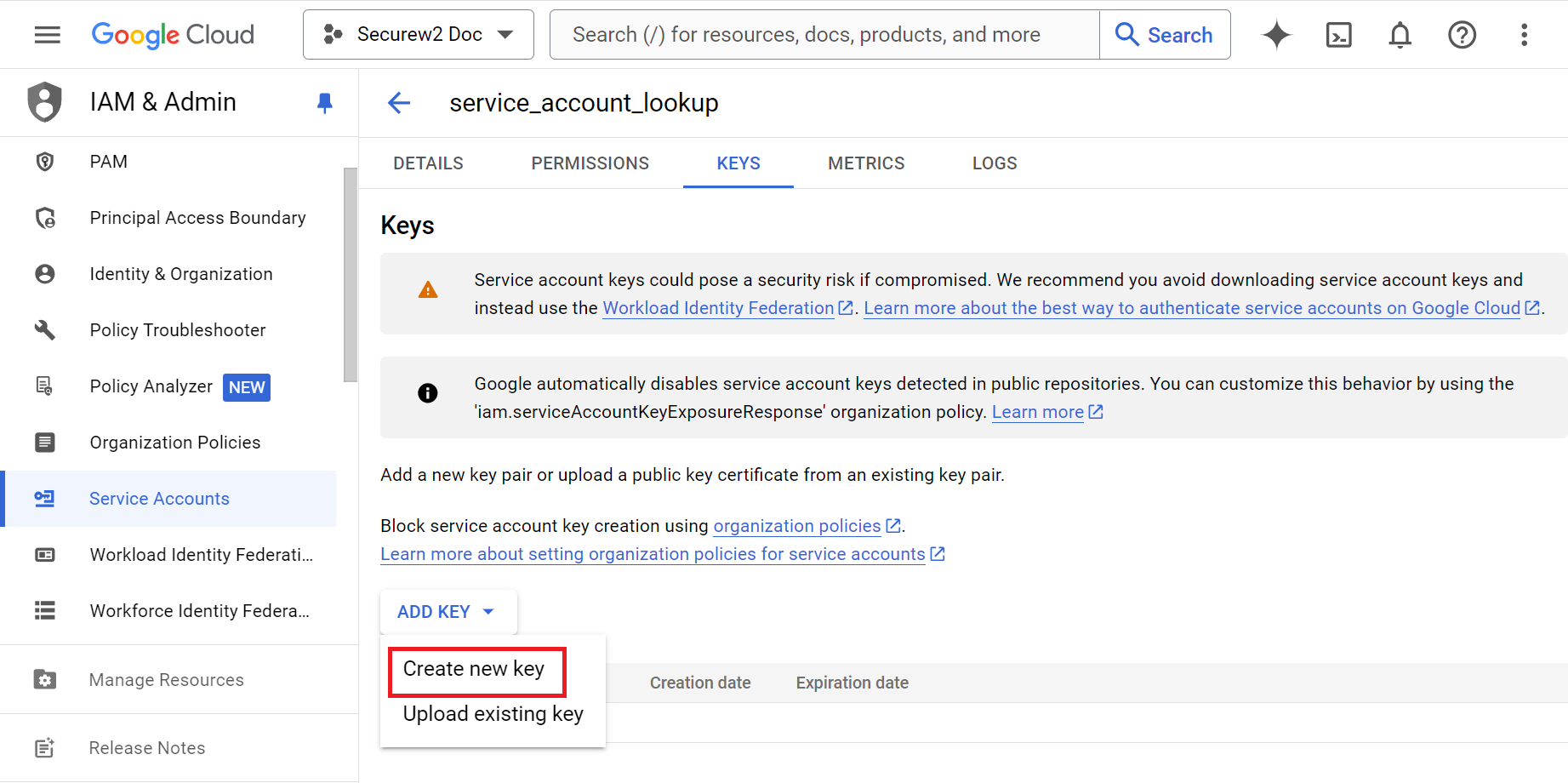
- In the Create private key pop-up, select Key type as JSON.

- Click CREATE. The JSON file will be downloaded to the device.
- Click CLOSE.
Delegating Domain Wide Authority to Service Account from Google Admin Console
Delegating domain wide authority helps administrators of the organization to authorize the service account to access user data required for lookup. Admins can delegate access to a service account from their Google Admin console.
To delegate domain wide authority:
- Log in to the Google admin console.
- Navigate to Security > Access and data controls > API controls.
- In the Domain wide delegation section, click MANAGE DOMAIN WIDE DELEGATION.
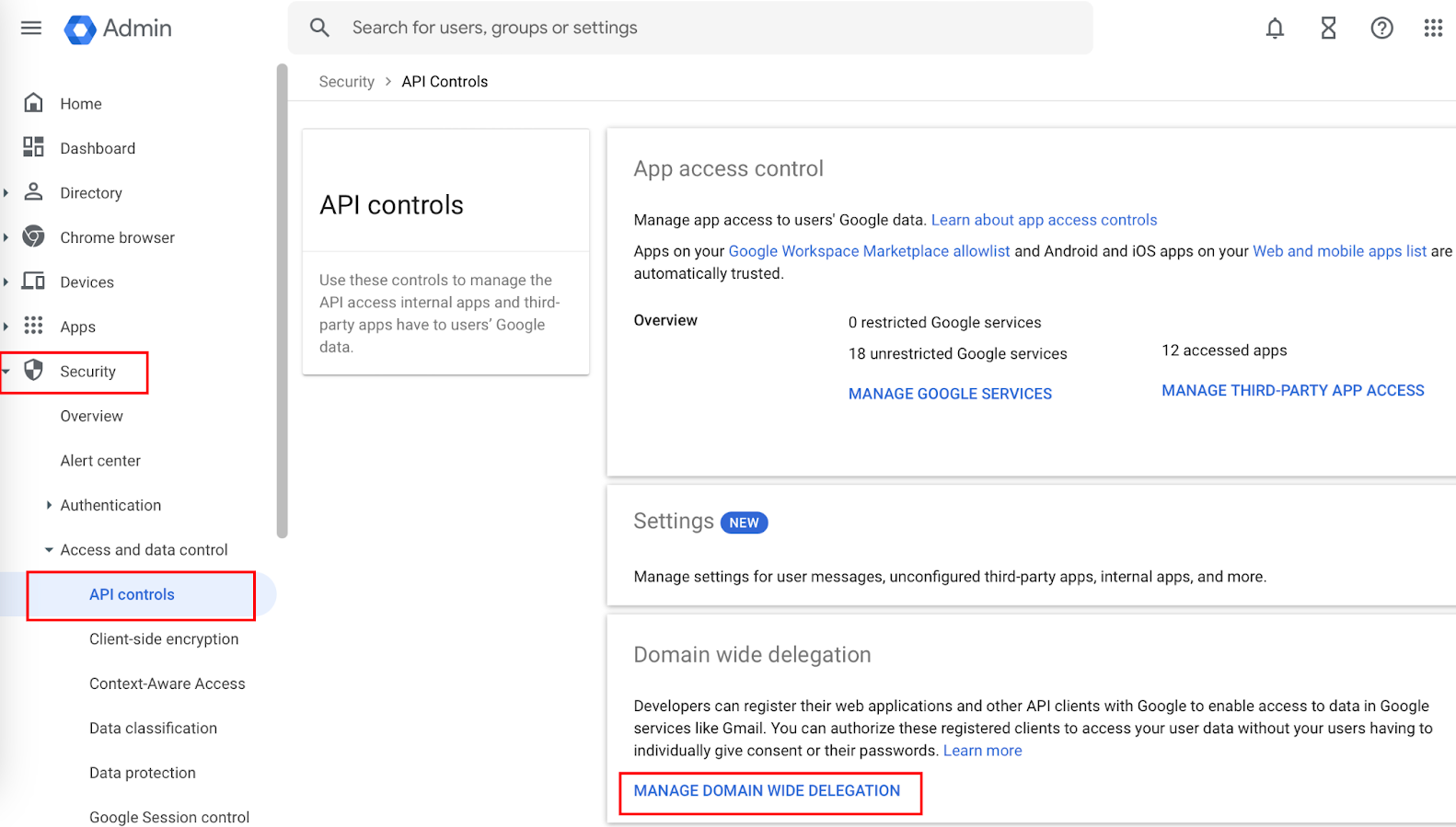
- Click Add new. A pop-up to add client ID will appear.
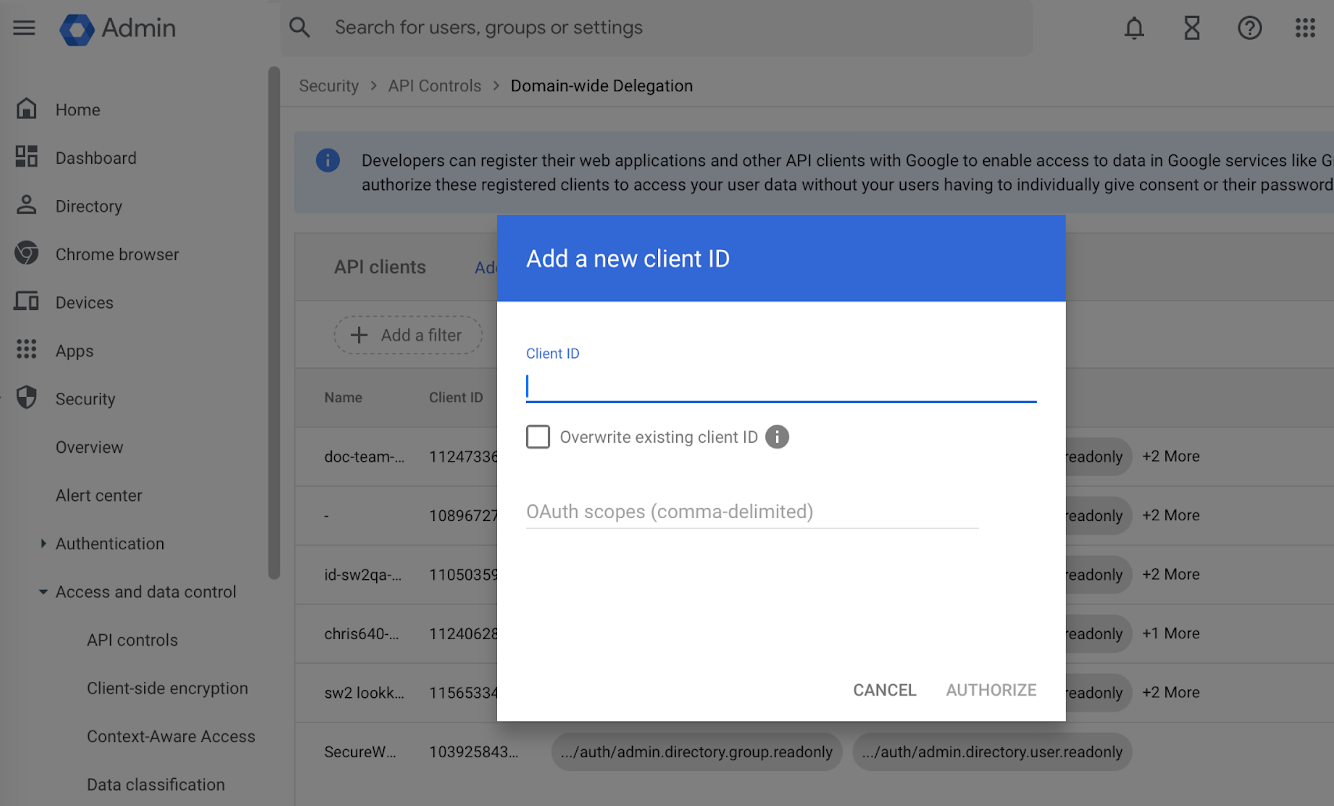
- Navigate back to your Google Service Account. Go to the Service Accounts tab and click on the service account created in Creating A Service Account and a JSON Key File section. Copy the Unique ID displayed under the DETAILS tab.
Paste the value in the Client ID field. - In the OAuth scopes field, enter “https://www.googleapis.com/auth/admin.directory.user.readonly,https://www.googleapis.com/auth/admin.directory.group.readonly,https://www.googleapis.com/auth/admin.directory.device.chromeos.readonly,openid”.
- Click Authorize.
Creating a User in Google Admin Console
Google mandates the creation of a user for the access of information from the service account. To create a user in the Google Admin console:
- Navigate to Directory > Users.
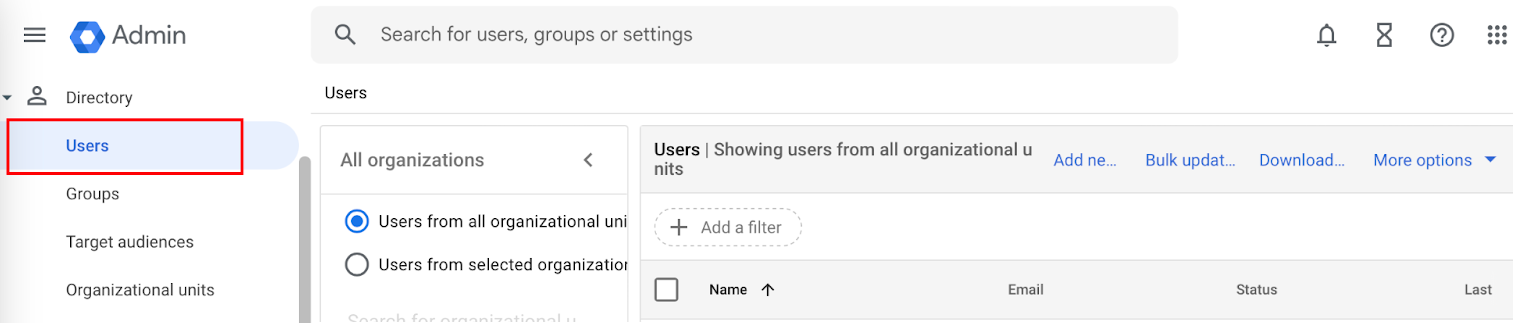
- Click Add new user. The Add new user form opens.
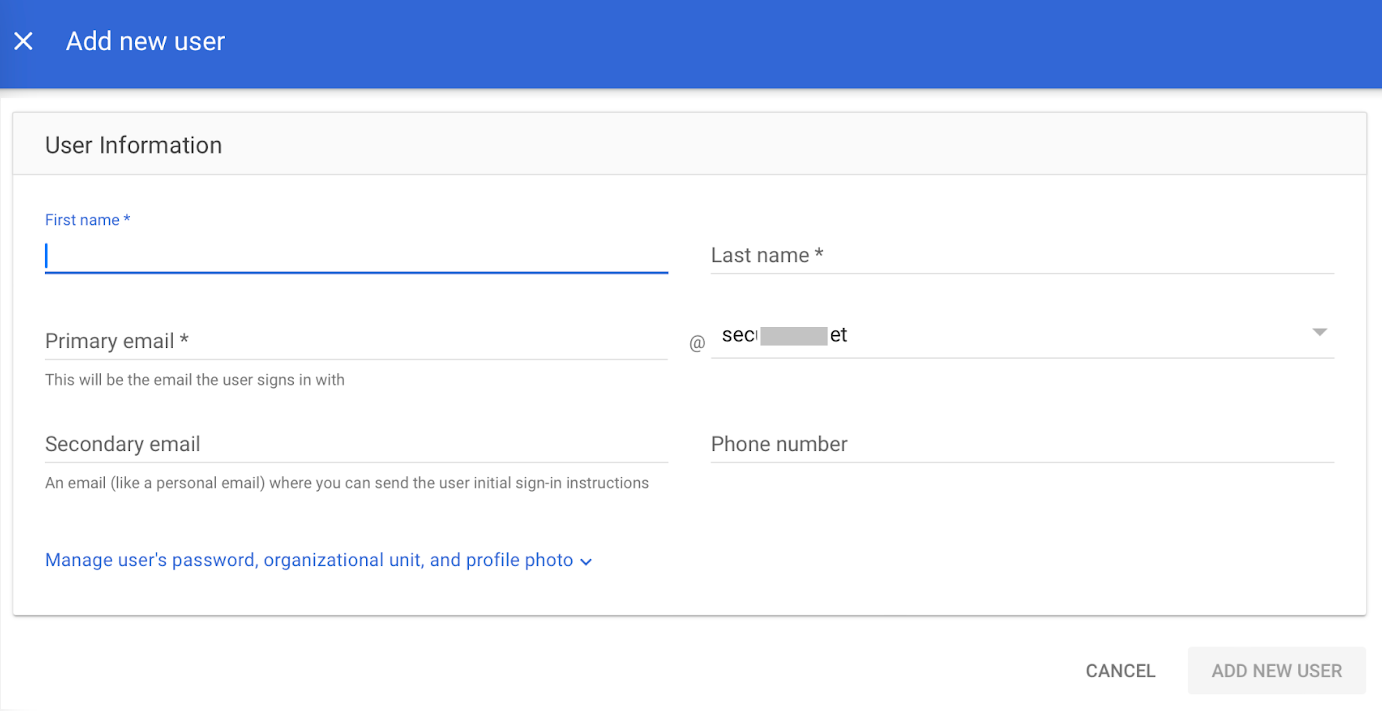
- In the First name field, enter the first name of the user.
- In the Last name field, enter the last name of the user.
- In the Primary email field, enter the organizational email of the user.
- Click ADD NEW USER.
Creating a Role with Read-only Access
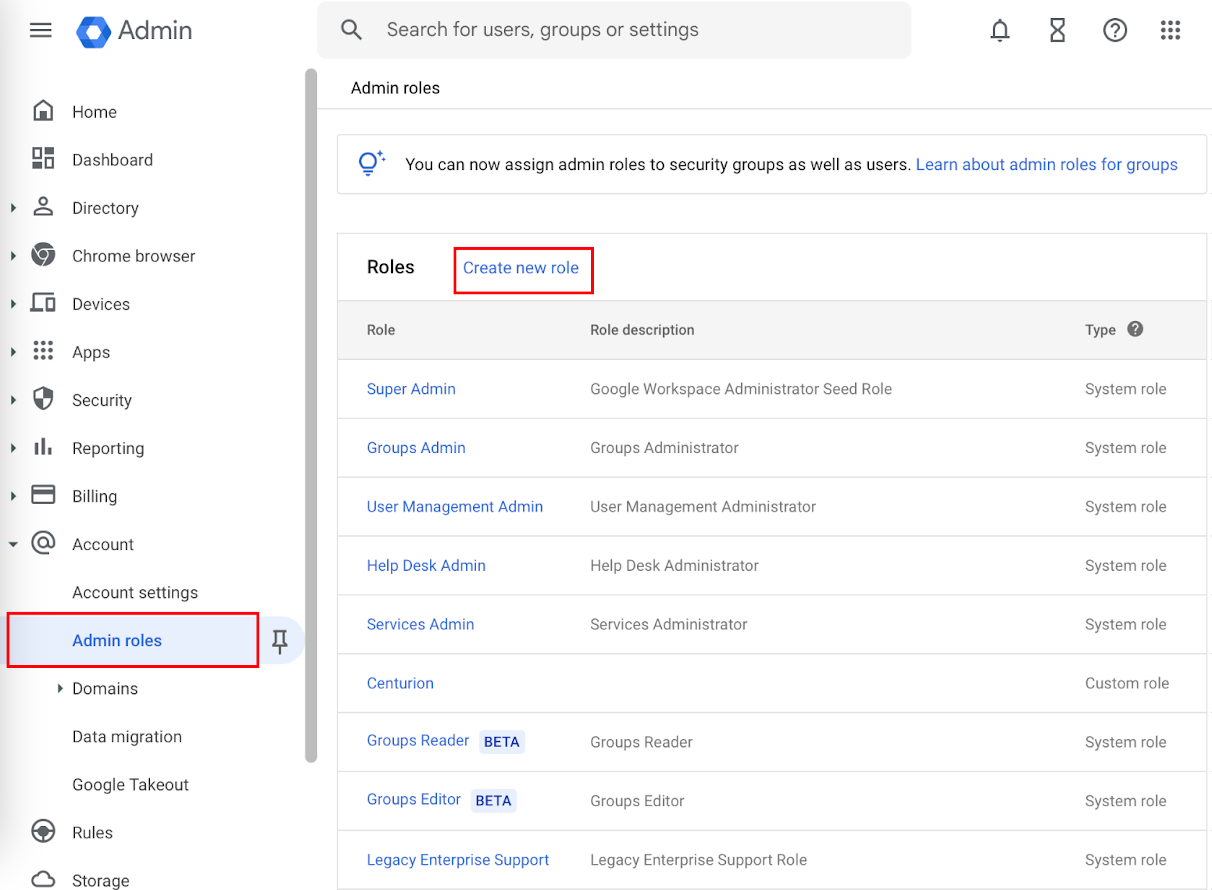
A role with read-only access privileges should be assigned to the created user. To create a role:
- Navigate to Accounts > Admin Roles.
- Click Create new role. The Create role page opens.
- In the Role info tab, for the Name field, enter a name for the role.
- In the Description field, enter a description for the role.
- Click Continue.
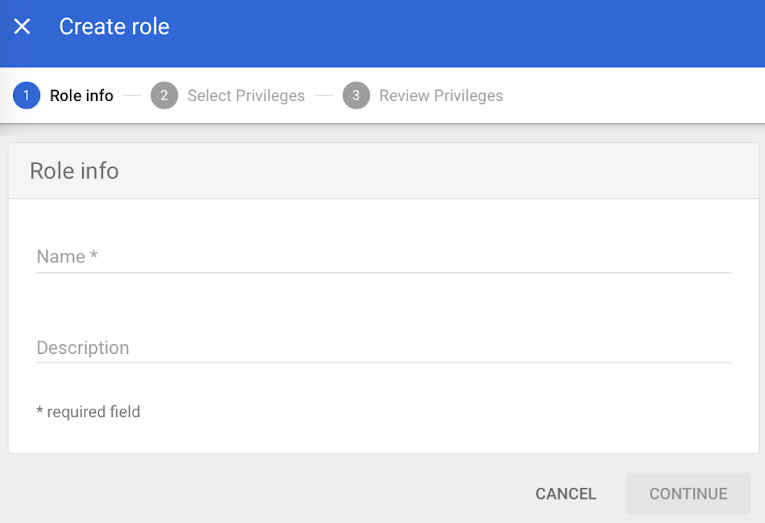
- In the Select Privileges tab, select the following access privileges;
- Admin console privileges:
- Chrome Management > Settings > Manage ChromeOS Devices > Read
- Admin API privileges:
- Users > Read
- Groups > Read
- Admin console privileges:
- Click CONTINUE. Review the privileges assigned and click DONE.
- Navigate to Users and select the user created in Creating a User in Google Admin Console section.
- Click ASSIGN ROLES.
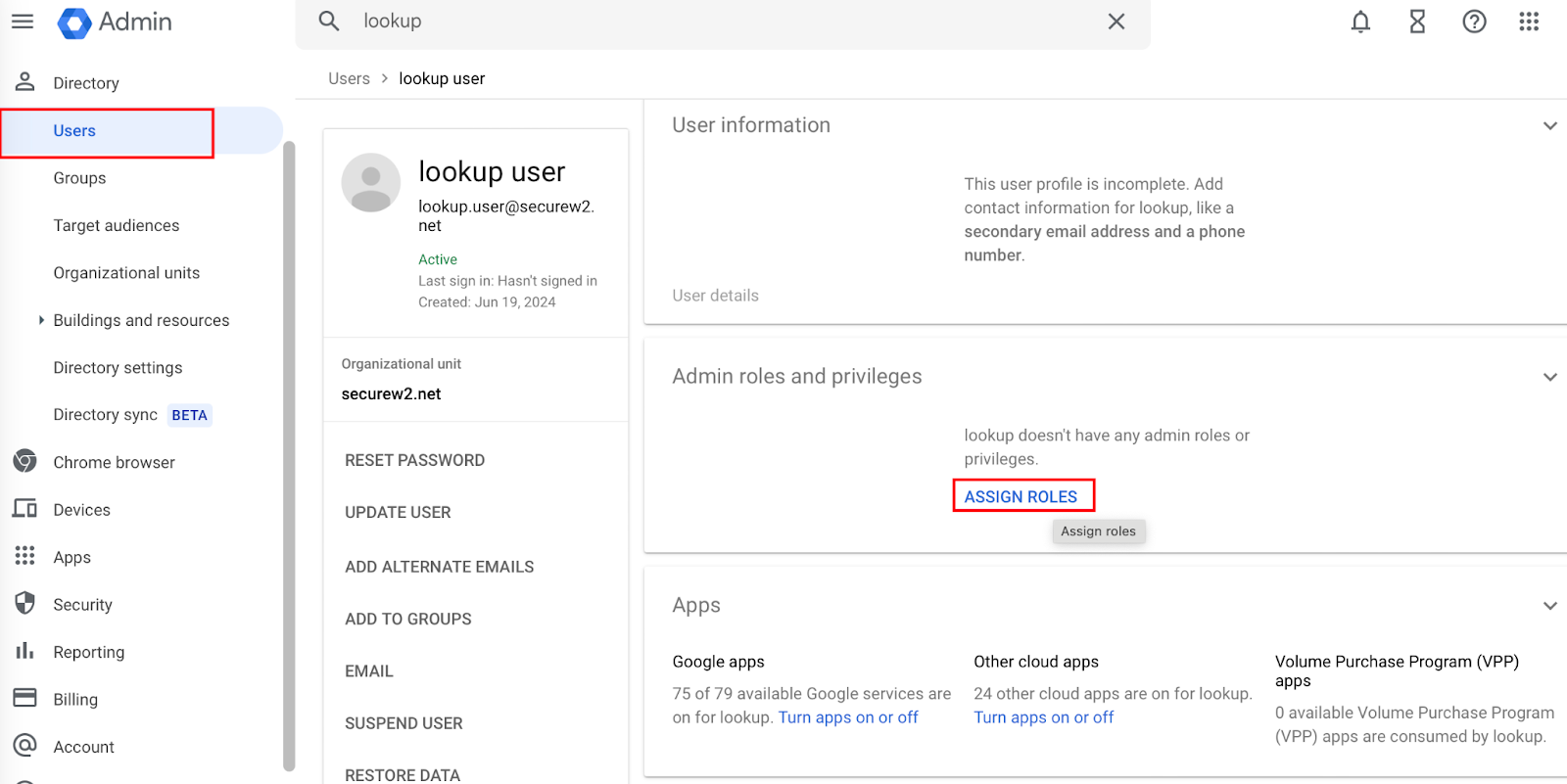
- Assign the created role with read-only privileges to the user.
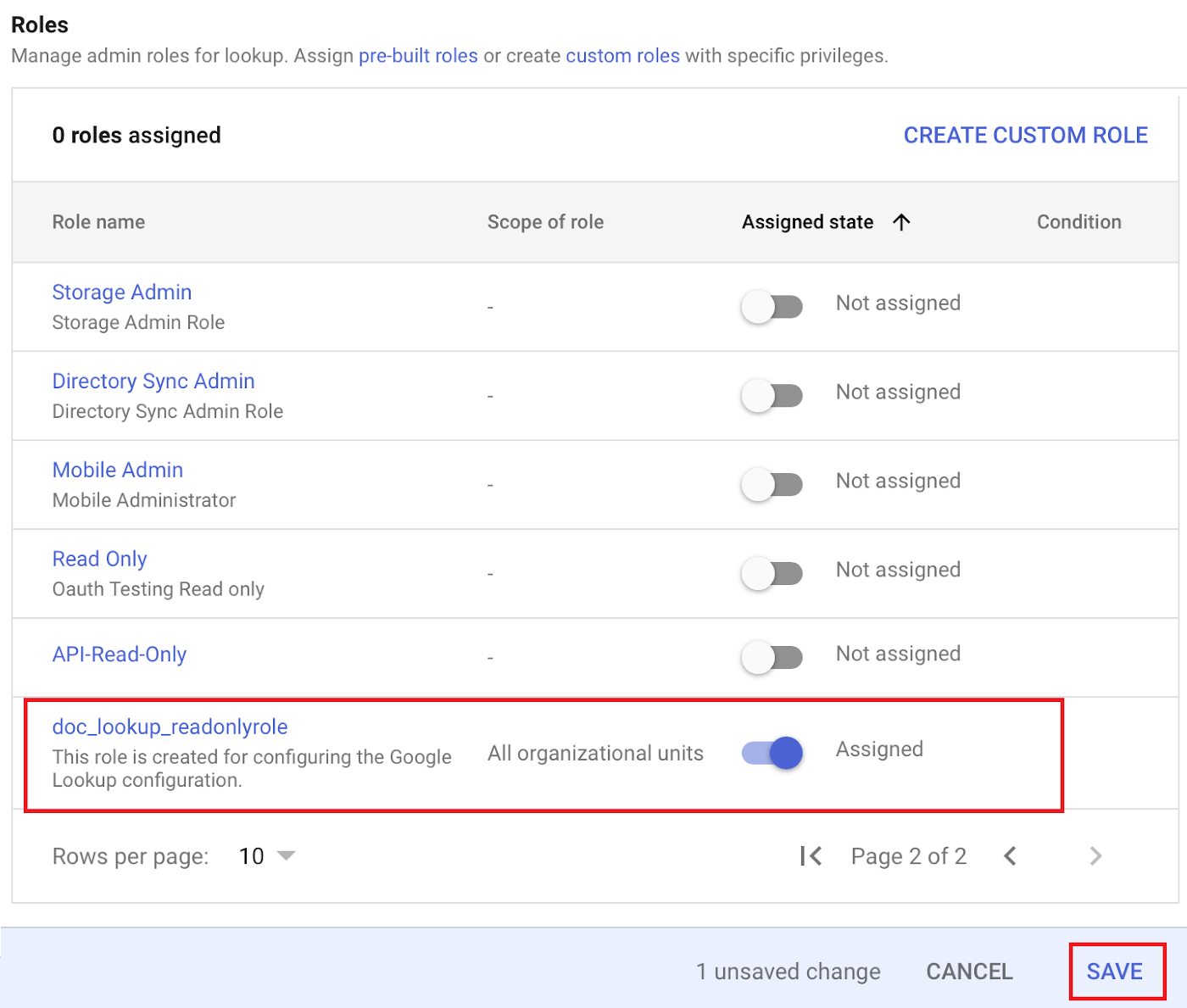
- Click SAVE.
Configuring JoinNow
The following are the high-level steps to configure JoinNow for Google Identity Lookup.
Creating an Intermediate CA for Google Workspace Integration
SecureW2 recommends the use of an Intermediate CA for Google lookup as a best practice for easy identification and management of your CAs
To create a new intermediate CA:
- Log in to the JoinNow Management Portal.
- Navigate to Dynamic PKI > Certificate Authorities.
- Click Add Certificate Authority.
- In the Basic section, from the Generate CA For drop-down list, select the Device and User Authentication option to authenticate devices and users.
- From the Type drop-down list, select Intermediate CA.
- From the Certificate Authority drop-down list, select the default Root CA that comes with your organization.
- In the Common Name field, enter a common name for the CA certificate. SecureW2 recommends a name that includes “SCEP.”
- From the Key Size drop-down list, select 2048 for the CA certificate key pair.
- From the Signature Algorithm drop-down list, select the signature algorithm for the certificate signing request. The option available is SHA-256.
- In the Validity Period (in years) field, enter the validity period of the CA certificate.
- In the Notifications section:
- From the Expiry Notification Frequency (in days) drop-down list, select the frequency interval for which a certificate expiration notification should be sent to users.
- Select the Notify user on successful Enrollment check box to notify users after a successful enrollment.
- In the Revocation section:
- In the Revoke Certificate if unused for field, select the number of days after which an unused certificate can be revoked.
- From the Reason Code drop-down list, select any one of the following reasons for which the certificate is revoked.
- Certificate Hold
- AA Compromise
- Privilege Withdrawn
- Unspecified
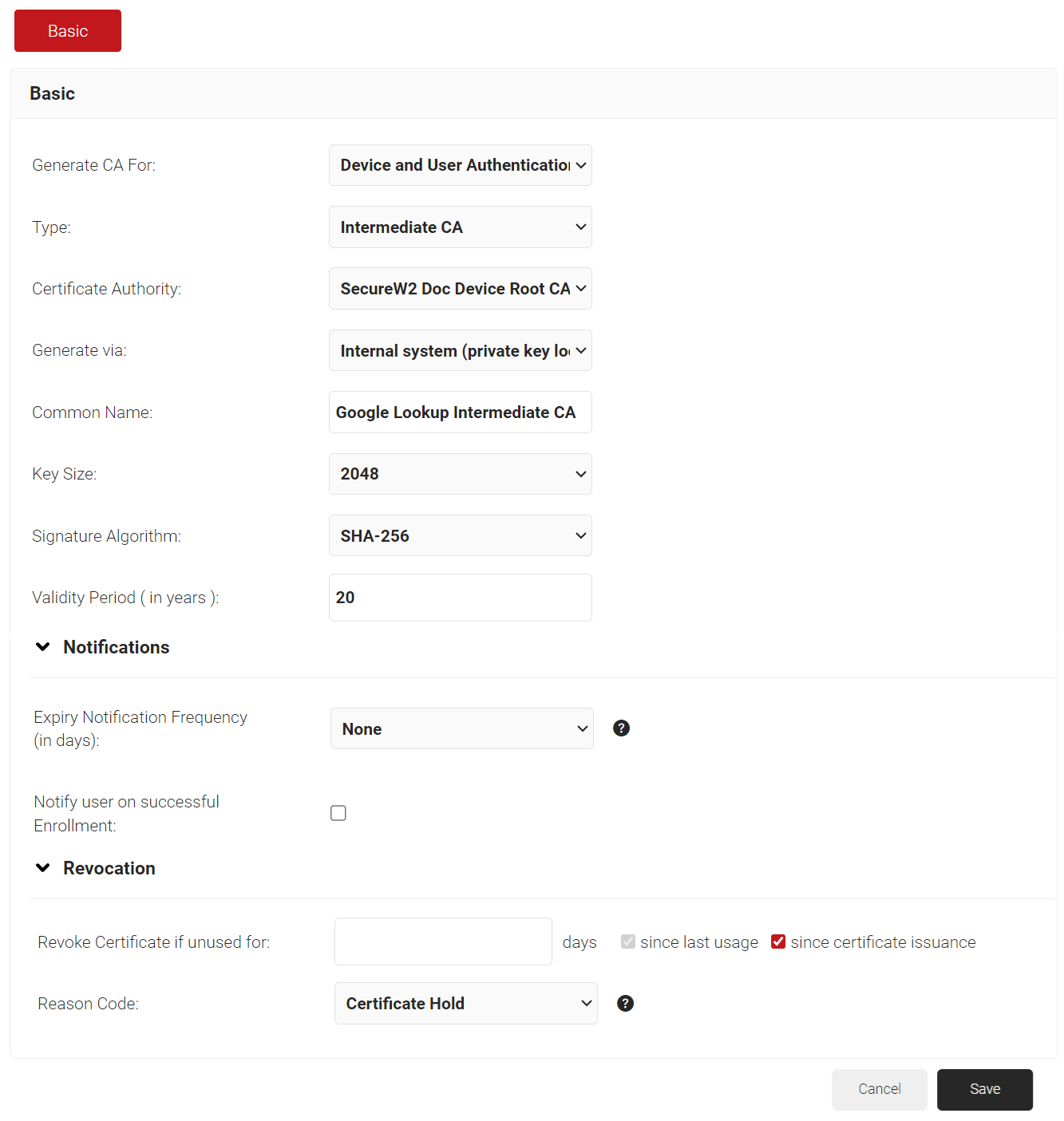
- Click Save.
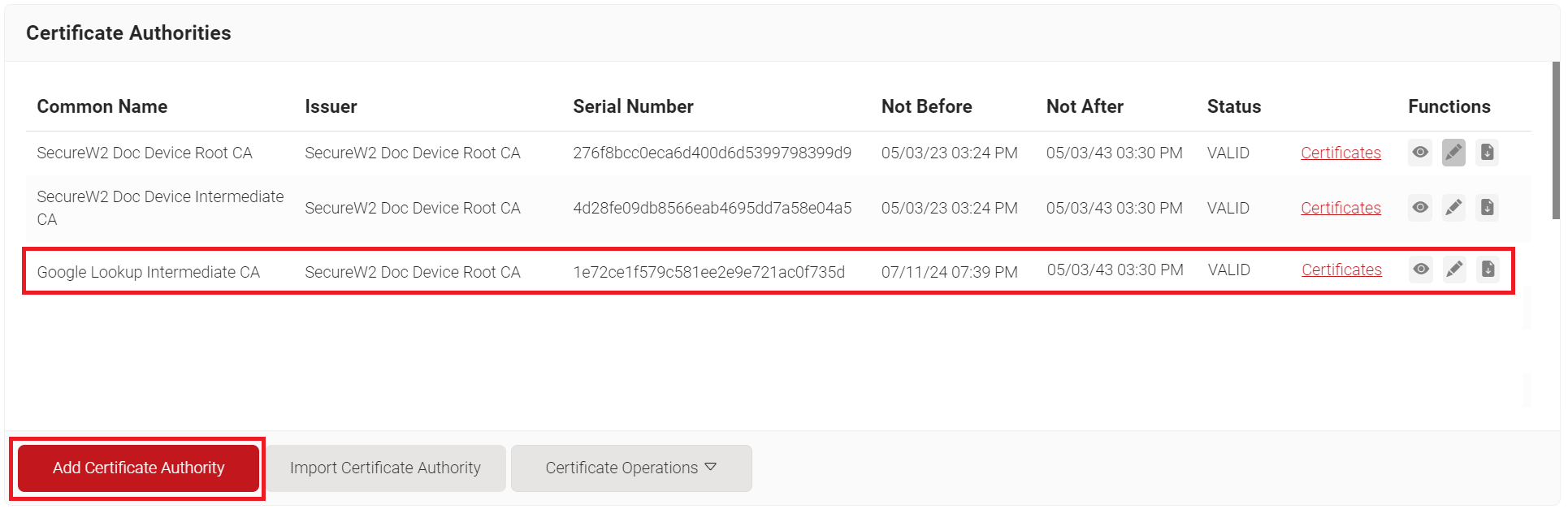
Creating a Certificate Template
A certificate template determines how information is encoded in the certificate to be issued by the Certificate Authority. It will consist of a list of certificate attributes and how the information must be encoded in the attribute values. This information is provided by the organization administrator using the JoinNow Management Portal.
SecureW2 recommends creating multiple templates based on your business requirements to easily identify the different values being passed.
To create a Certificate Template for Google lookup:
- Navigate to PKI > Certificate Authorities.
- Scroll to the Certificate Templates section and click Add Certificate Template.
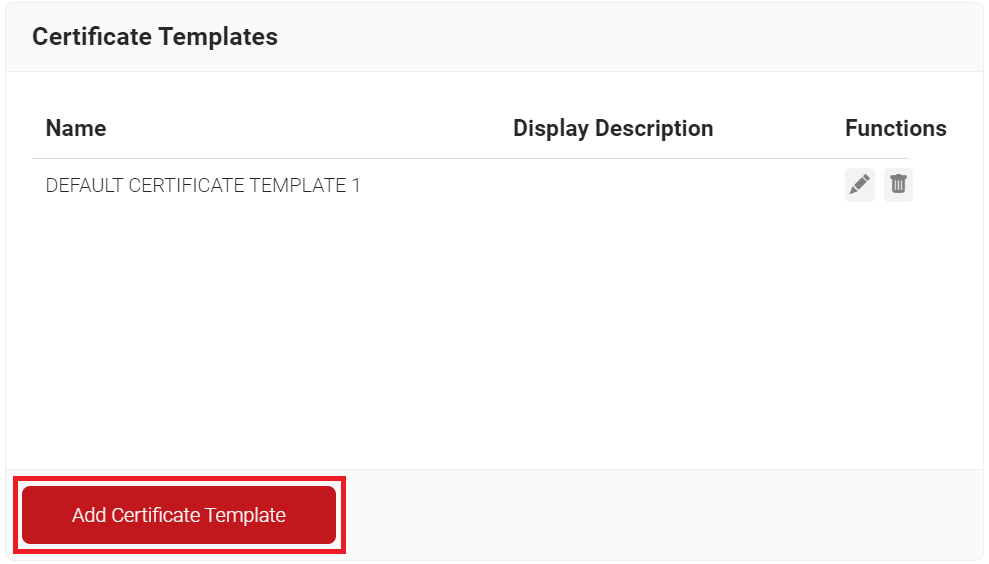
- In the Basic section, for the Name field, enter the name of the certificate template.
- In the Subject field, retain the default values hardcoded in the certificate template.
- In the Display Description field, enter a suitable description for the certificate template.
- In the Validity Period field, type the validity period of the certificate (based on the requirement).
- From the Signature Algorithm drop-down list, select the signature algorithm for the certificate signing request. The option available is SHA-256.
- In the SAN section, for Other Name, RFC822, DNS, and URI fields, retain the default values provided in the certificate.
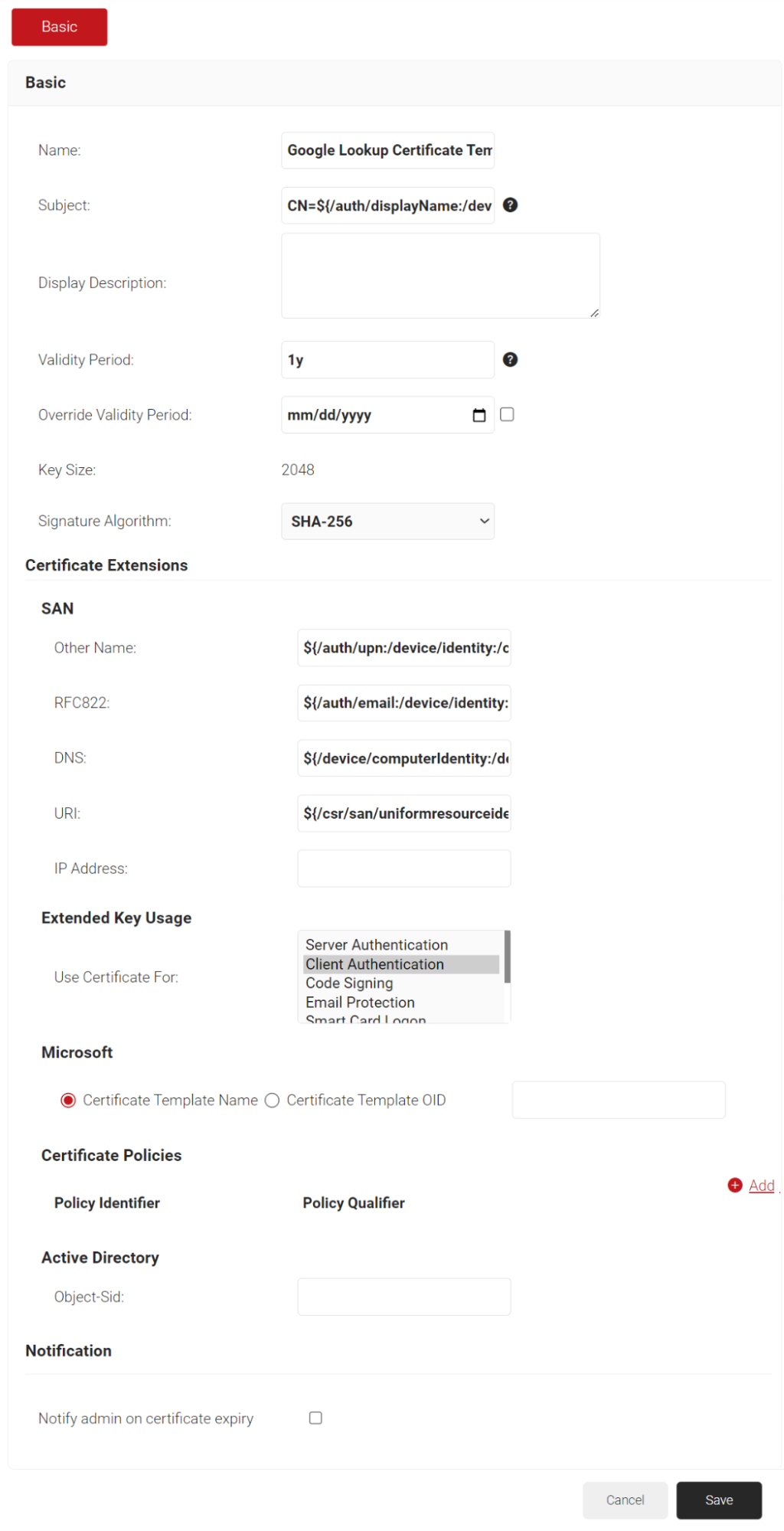
- Click Save.
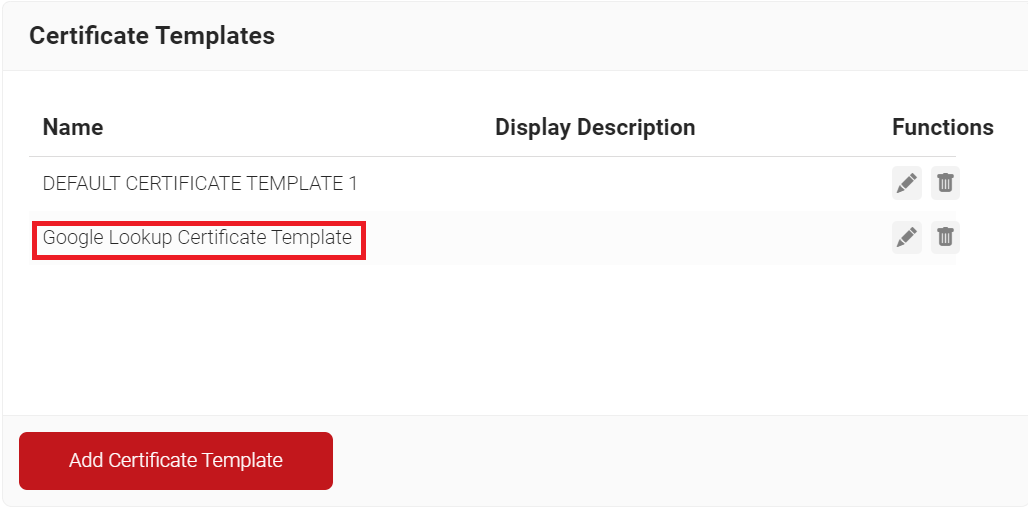
Creating a Google Workspace Identity Lookup Provider
Before the certificate issuance and during the RADIUS authentication process, the Identity Lookup feature validates that a device/user is active within the organization by checking the identifying information against the existing accounts in the Identity Provider.
To create an Identity Lookup Provider:
- Navigate to Identity Management > Identity Providers.
- Click Add Identity Provider.
- In the Basic section, enter the name of the IDP in the Name field.
- In the Description field, enter a suitable description for the IDP.
- From the Type drop-down list, select Google Workspace Identity Lookup.
- Click Save.
- The page refreshes, and the Configuration, Attribute Mapping, and Groups tabs appear.
- Under the Configuration tab, provide the following information:
- In the Service Account Key File field, click Choose file. Select the JSON Key file created in the Creating A Service Account and a JSON Key File section and upload the file.
- In the Delegated Domain Authority Email field, enter the primary email for the user in the Creating a User in the Google Admin Console section.
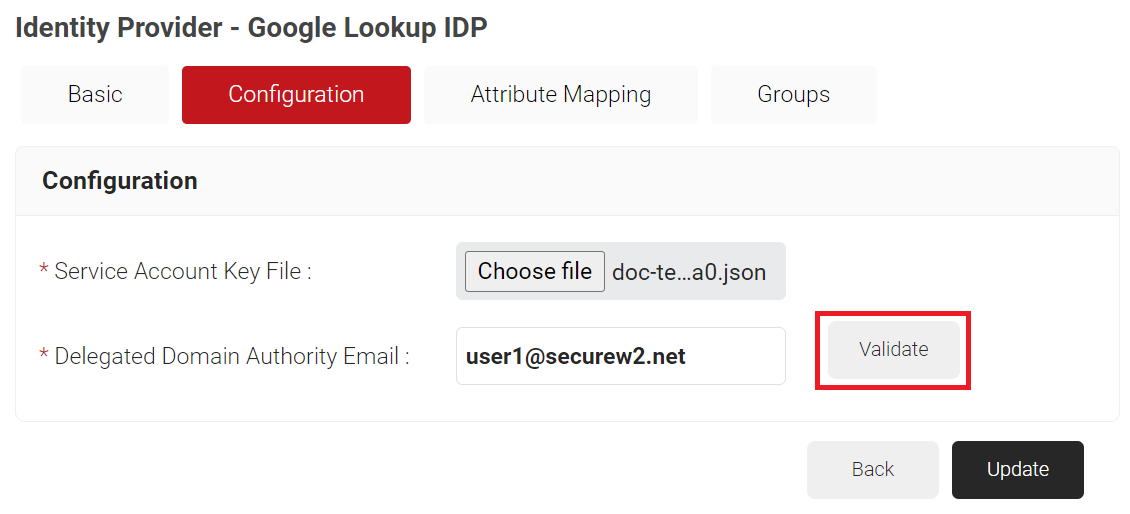
- Click Validate to check the validity of the primary email entered.
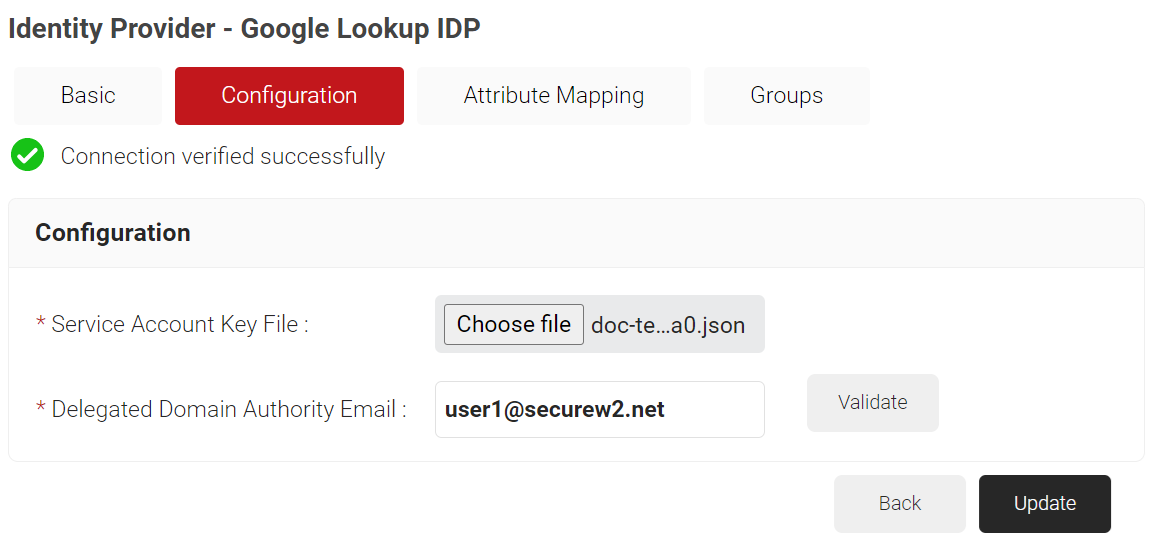
- Under the Attribute Mapping tab:
- Click Add.
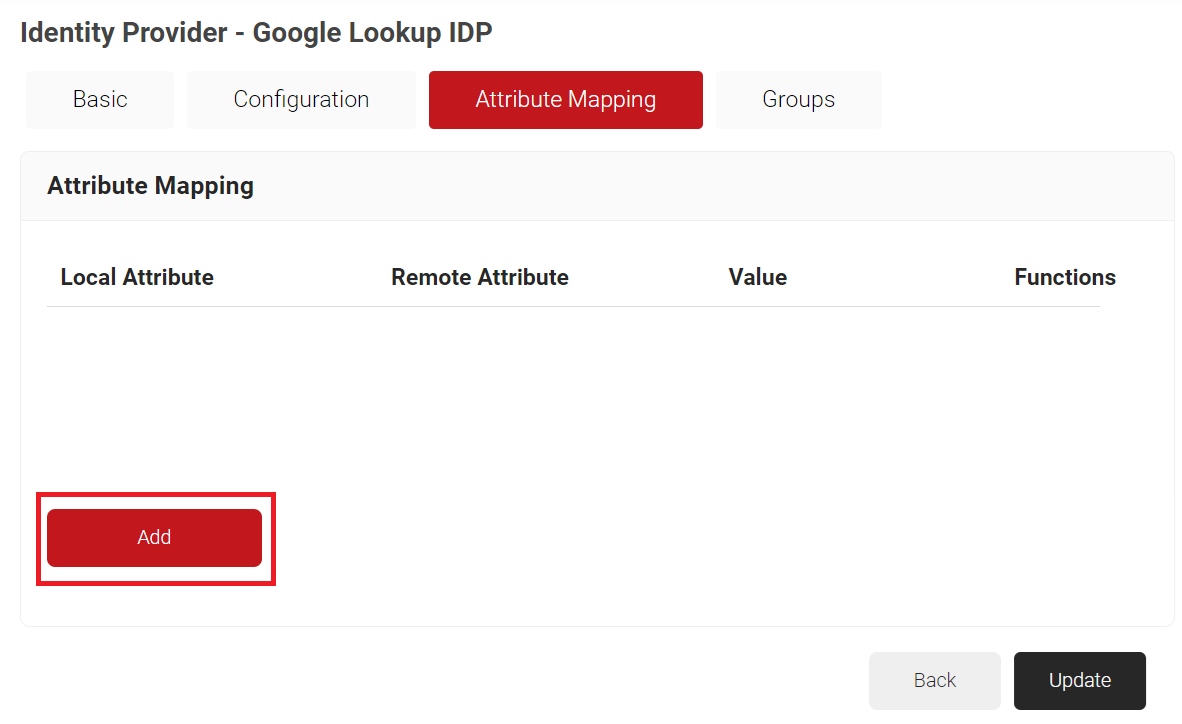
- In the Local Attribute field, enter the name of the attribute that corresponds with the Remote Attribute. This is used during Policy Configuration.
- In the Remote Attribute drop-down list, select the Google attributes configured for user and group attributes. If the Google attributes are unavailable in the default values, select the User Defined option and enter the exact attribute name configured in Google.

- Click Next.
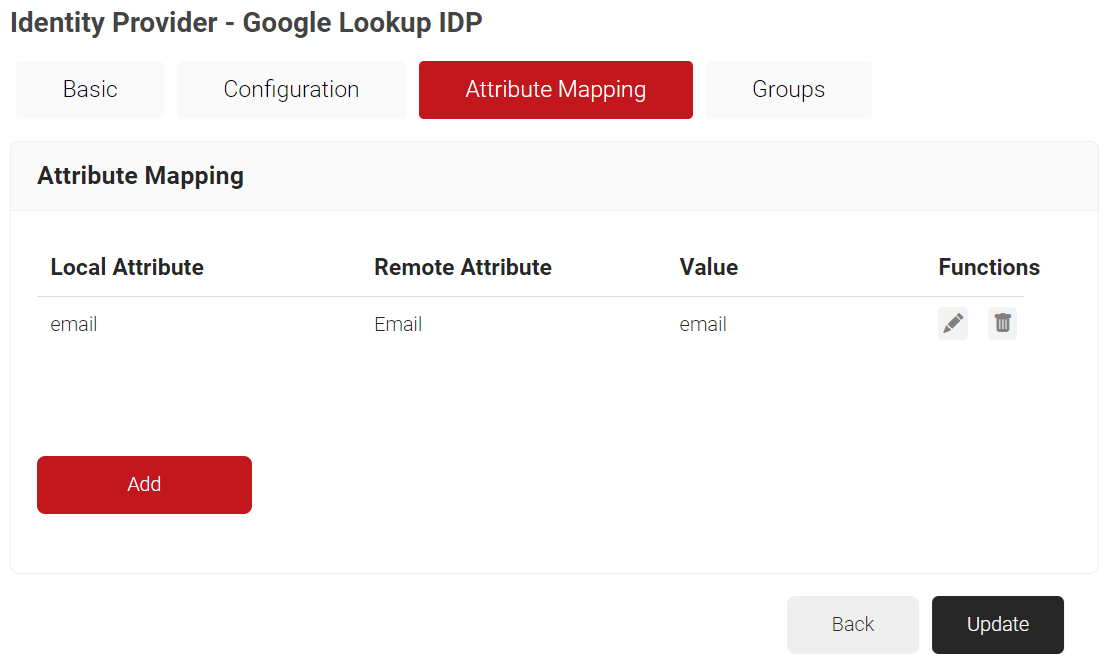
- Repeat steps a – d to add the required attributes.
- Click Update.
- Click Add.
- Navigate to the Groups tab.
- Click Add.
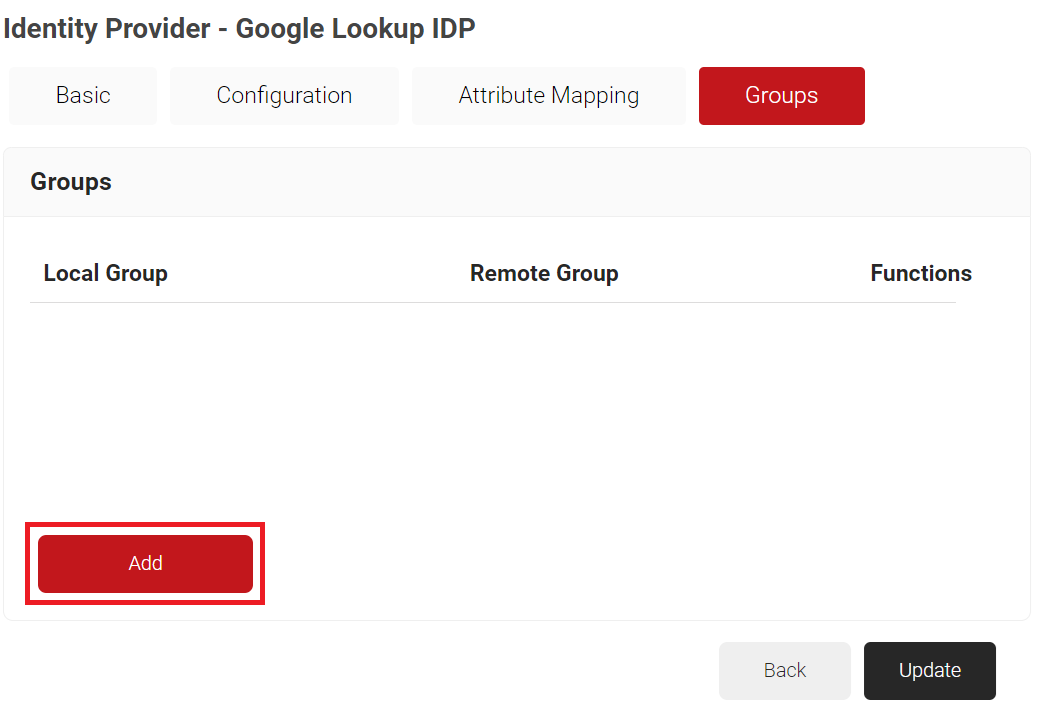
- In the Local Group field, enter a name for the group. This group name can be used to configure the Network Policies.
- In the Remote Group field, enter the name of your group as it is configured in the Google Workspace.
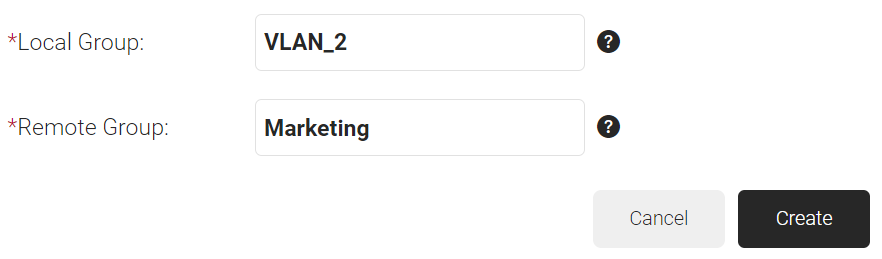
- Click Create.
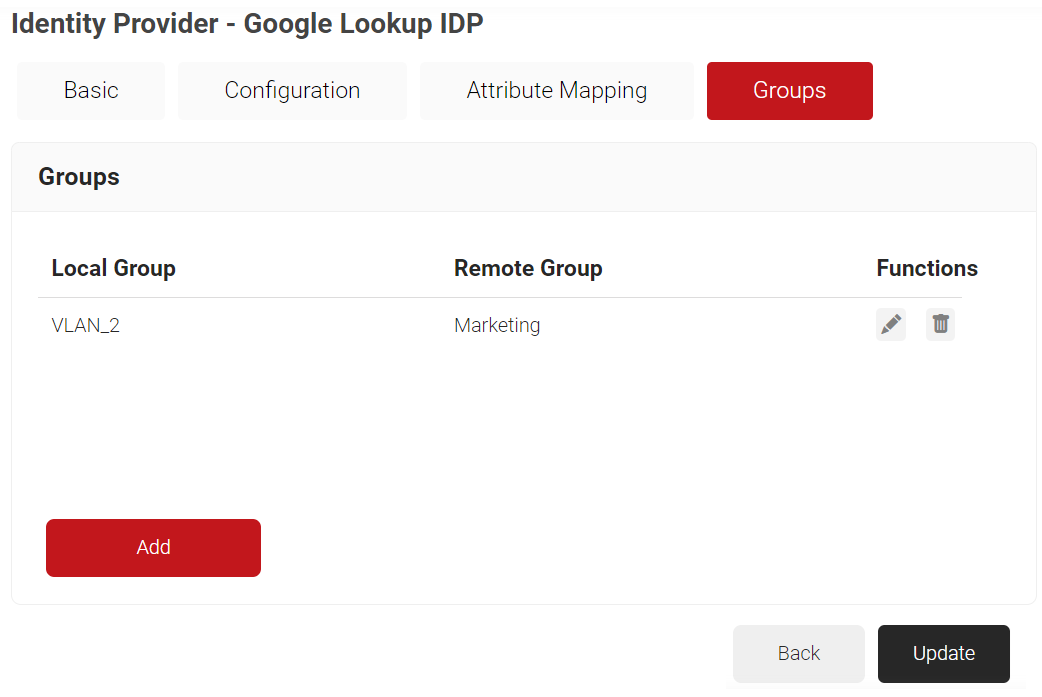
- Repeat as necessary for any group you wish to create Network Policies around.
- Click Update.
- Click Add.
Configuring Policies
SecureW2 policies allow the organization administrators to segment users and restrict/allow resources based on information stored in their directory entry. Since enforcement occurs at runtime, changes made to a user’s permissions are propagated immediately rather than a day or two later, as is typical with most RADIUS servers.
Creating an Account Lookup Policy
Lookup Policies are how we tie the new Identity Lookup Provider to domains. Here, you create a condition that ties your domain to the new Identity Lookup Provider you created in the previous section.
- Navigate to Policy Management > Account Lookup Policies.
- Click Add Account Lookup Policy.

- In the Basic section, enter the name of the Account Lookup Policy in the Name field.
- In the Display Description field, enter a suitable description for the Account Lookup Policy.
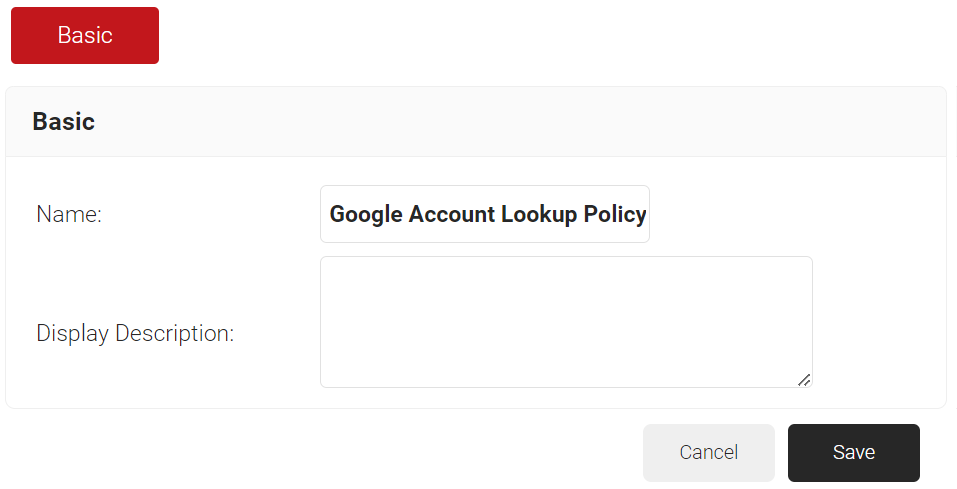
- Click Save.
- The page refreshes, and the Conditions and Settings tabs appear.
- Click the Conditions tab.
- From the Identity drop-down list, select an option from the following:
- Username
- Certificate-CommonName
- Certificate-SAN-UPN
- Certificate-SAN-Email
- In the Regex field, enter the value you want to match.
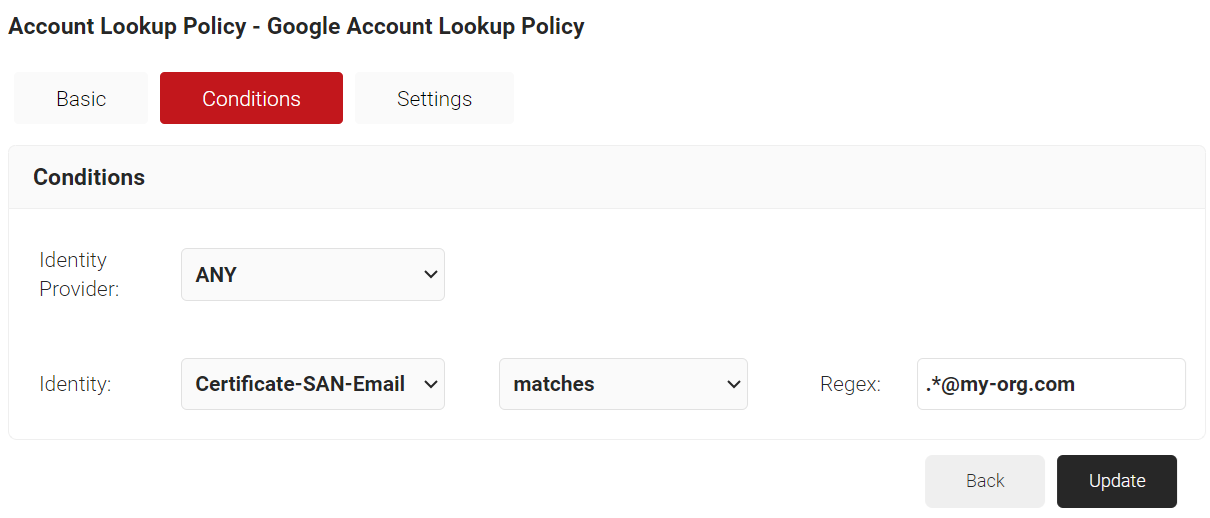
- Under the Settings tab, from the Identity Provider Lookup drop-down list, select the Google Workspace Identity Lookup you created in the Creating a Google Workspace Identity Lookup Provider section.
- From the Lookup Type drop-down, select the lookup type:
- Auto – The system automatically uses identity as the Lookup attribute.
- Custom – The Identity drop-down list is displayed. Select a device or user identity for lookup.
- The user identities are:
- Username
- Certificate-CommonName
- Certificate-SAN-UPN
- Certificate-SAN-Email
- The device identities are:
- Certificate-SAN-DNS
- Client ID
- Computer Identity
- The user identities are:
- From the Identity drop-down, select the Identity attribute mapped for lookup.
- Lookup Purpose – Purpose of Account Lookup
- Certificate Issuance – To lookup the user/device account during Enrollment.
- RADIUS Authentication – To lookup the user/device account during RADIUS Authentication
- Select the Revoke On Failure checkbox to automatically revoke a certificate if an account lookup fails, if necessary.
- Click the Validate Configuration button to check if the lookup is valid.
- On the Validate Configuration pop-up window, in the Enter a valid identity field, enter the identity (user/device) to validate the lookup, and click Validate.
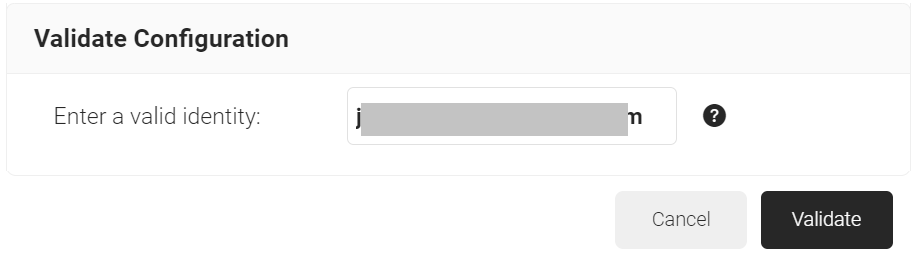
- After the successful validation, the associated attributes and groups of the Identity Provider Lookup are displayed on the Lookup Details prompt. The admin can use this information to configure the network policies and verify the user’s validity.NOTE: When the Admin enters an invalid identity on the Validate Configuration pop-up window, the following error message is displayed: “Account lookup failed.”
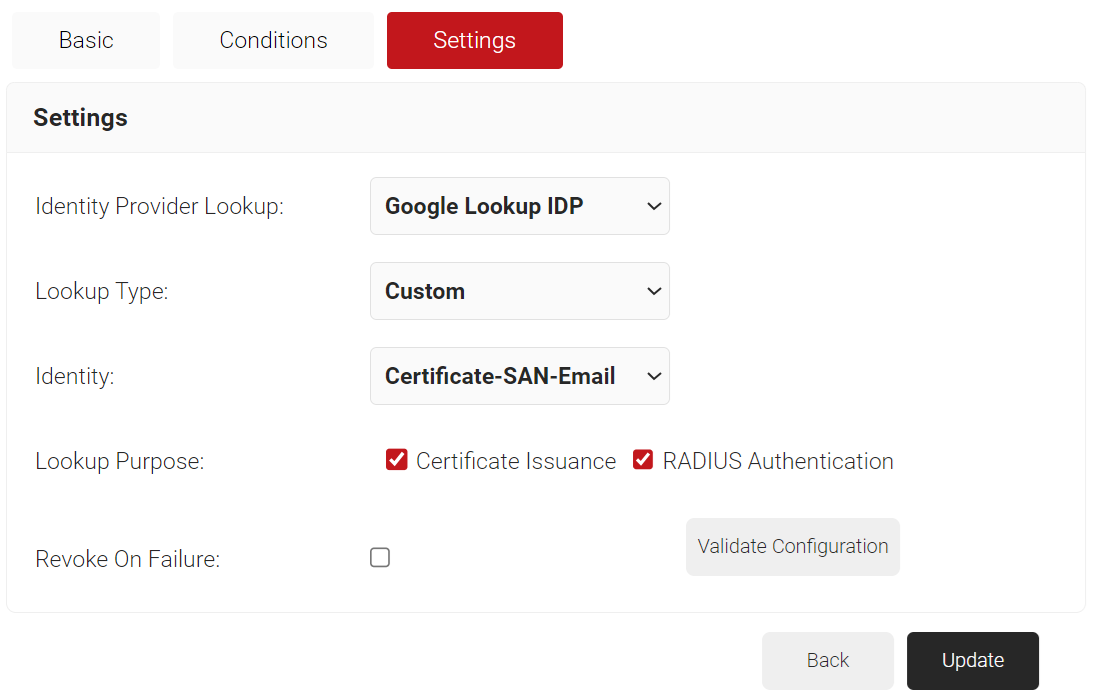
- Click Update.
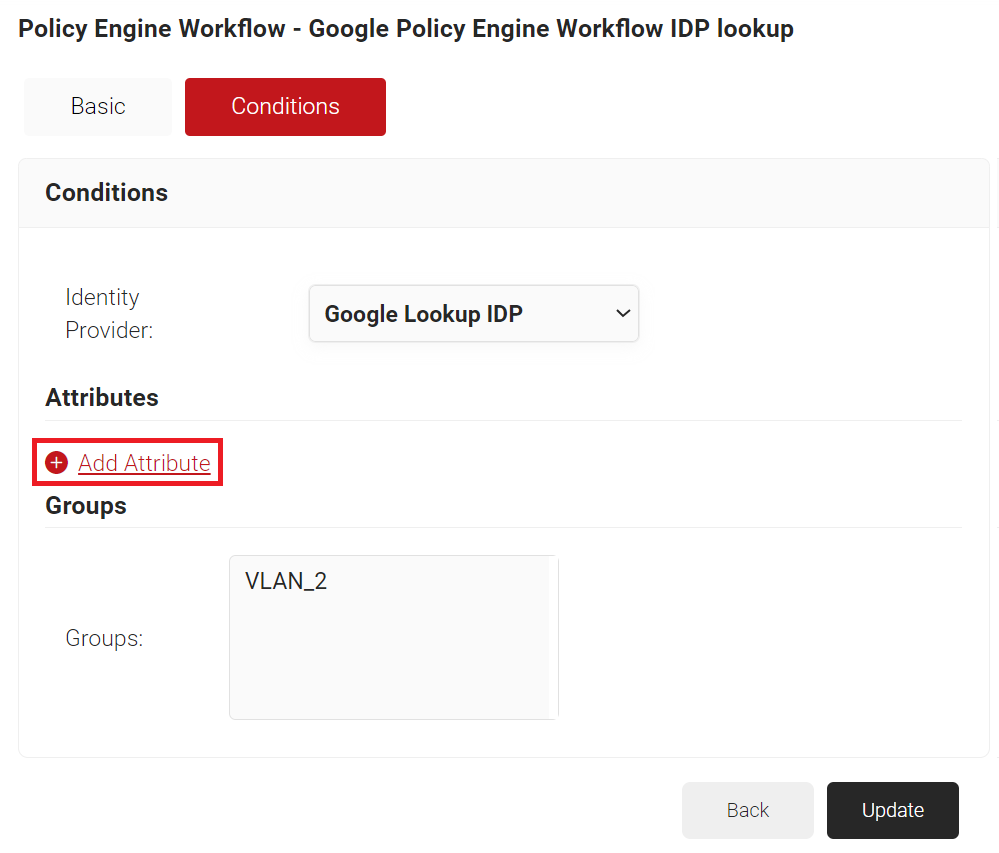
Creating a Policy Engine Workflow
To create a policy engine workflow, perform the following steps:
- Navigate to Policy Management > Policy Engine Workflows.
- Click Add Policy Engine Workflows.

- In the Basic section, enter the name of the Policy Engine Workflow in the Name field.
- In the Display Description field, enter a suitable description for the policy engine workflow.

- Click Save.
- The page refreshes, and the Conditions tab is displayed.
- Click the Conditions tab.
- From the Identity Provider drop-down list, select the Identity Provider you created in the Creating a Google Workspace Identity Lookup Provider section.
- In the Attributes section, click + Add Attribute.
- From the Attribute drop-down list, select the required attribute for Lookup.
- In the Groups box, select the required group to assign a network policy.
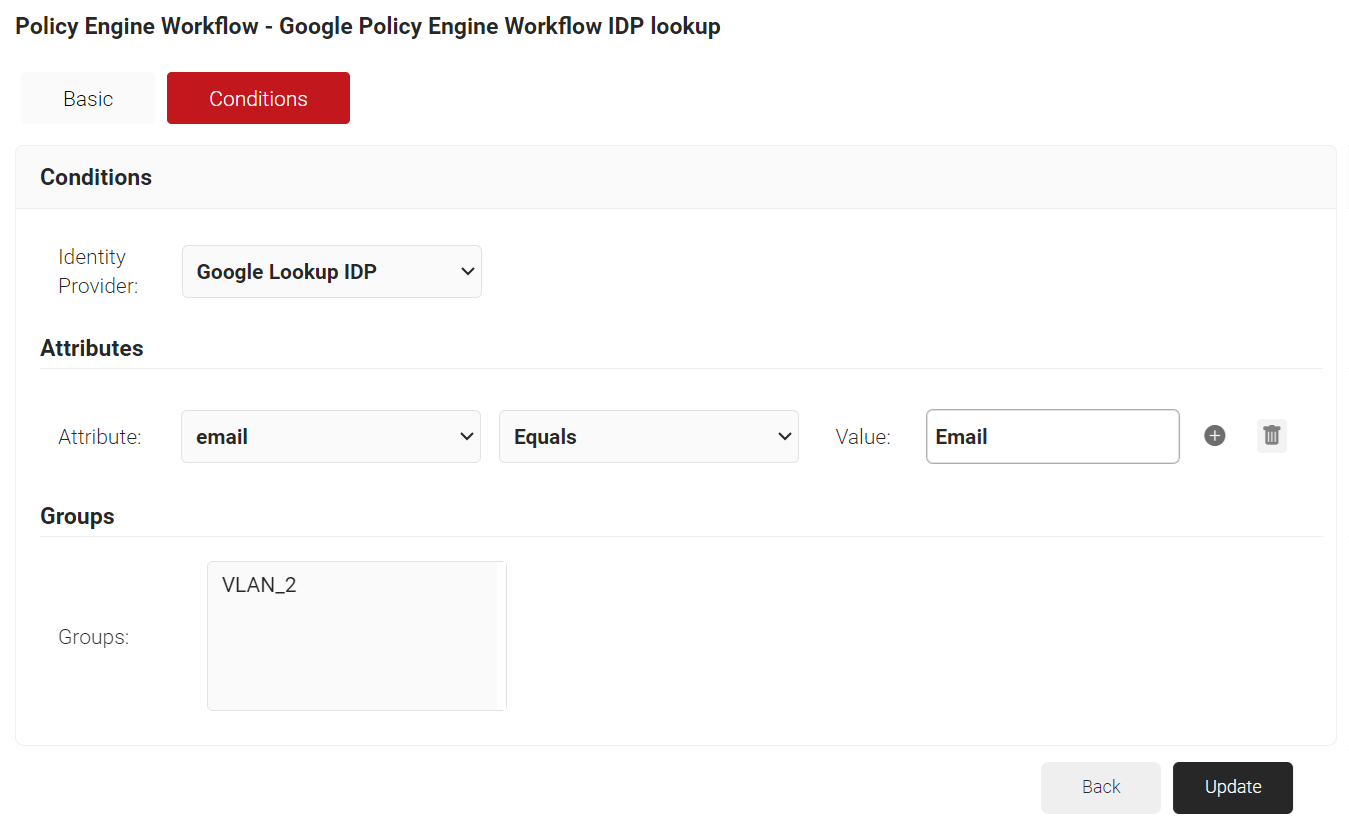
- Click Update.
Creating a Network Policy
Similar to the check during certificate issuance, Lookup can be used before the RADIUS Authentication as a dynamic check. To trigger the lookup during the RADIUS Authentication, map the policy engine workflow (created in the Creating a Policy Engine Workflow section) in the Network Policy created below:
- Navigate to Policy Management > Network Policies.
- On the Network Policies page, click Add Network Policy.
- Under the Basic section, in the Name field, enter the name of the network policy.
- In the Display Description field, enter a suitable description for the network policy.
- Click Save.
- Click the Conditions tab.
- Click Add rule and select the role you want to assign to this network policy. It is essential to select the appropriate role, as the network policy is triggered by the role policy. SecureW2 offers various rules that you can select based on your business requirements.
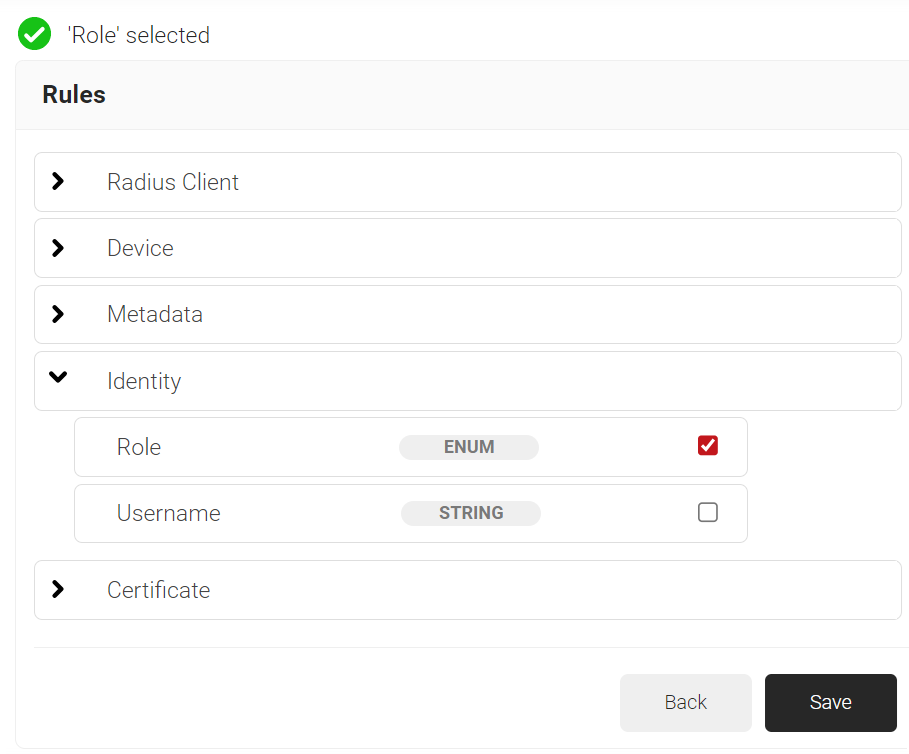
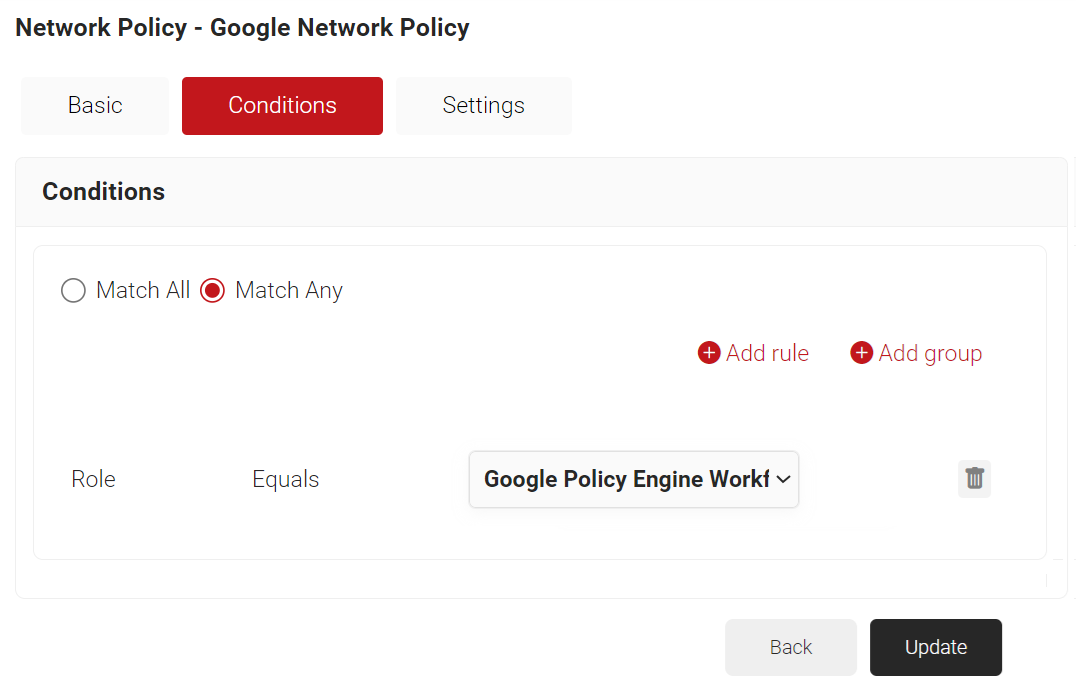
NOTE: You can assign a network policy to multiple user roles.
- Click the Settings tab.
- Click Add Attribute.
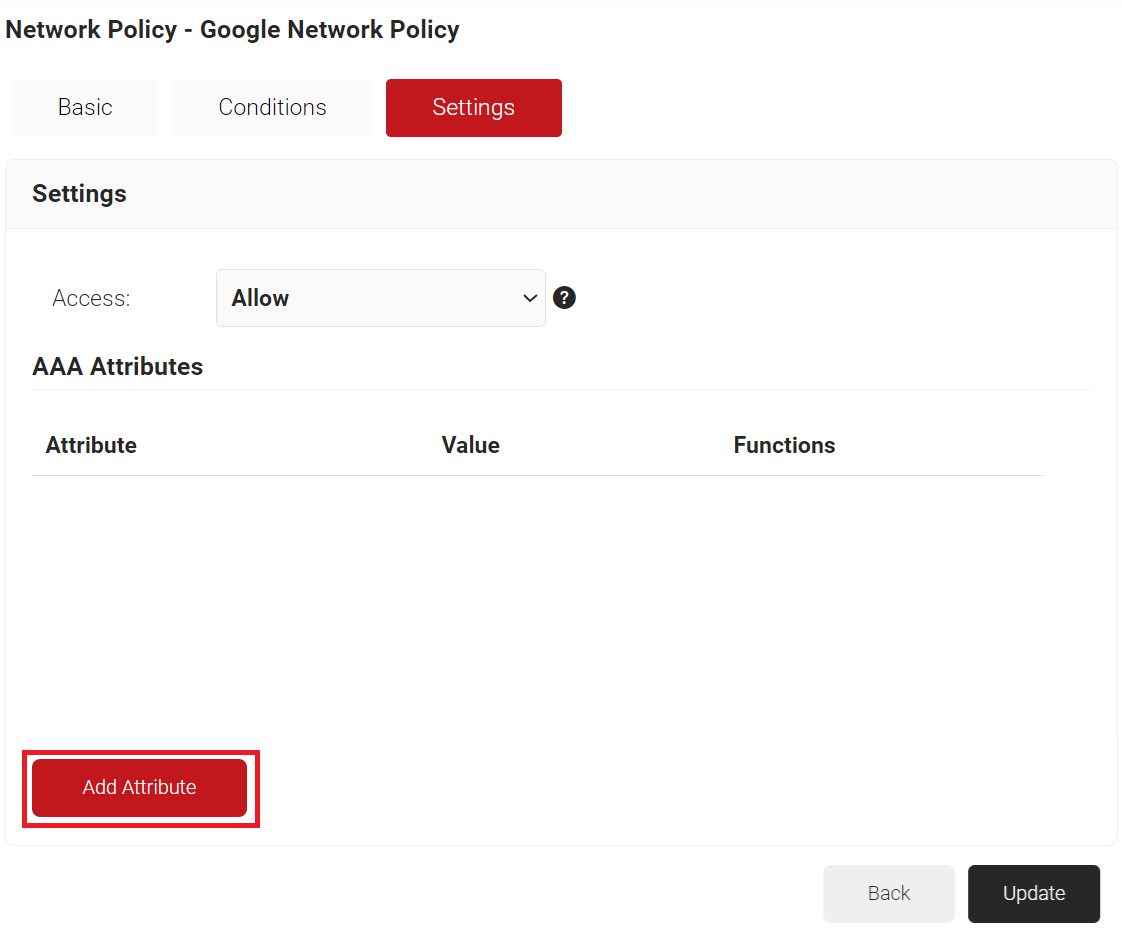
- From the Dictionary drop-down list, select an option: Radius: IETF or Custom.
- From the Attribute drop-down list, select an option.
- In the Value field, enter the appropriate value for the attribute.
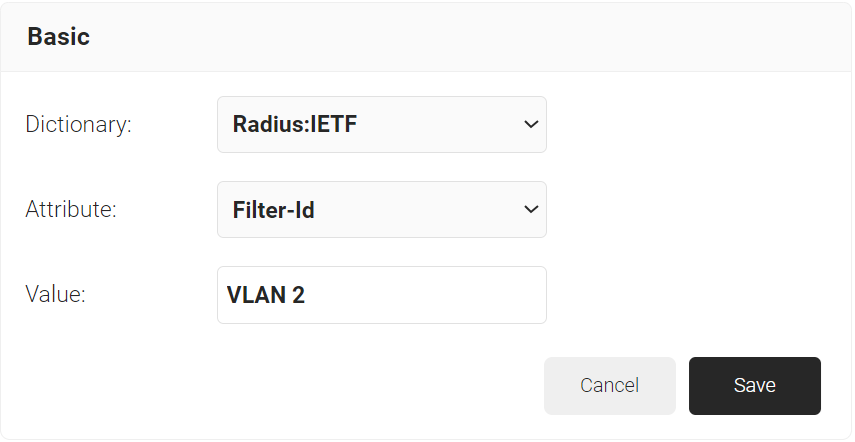
- Click Save.
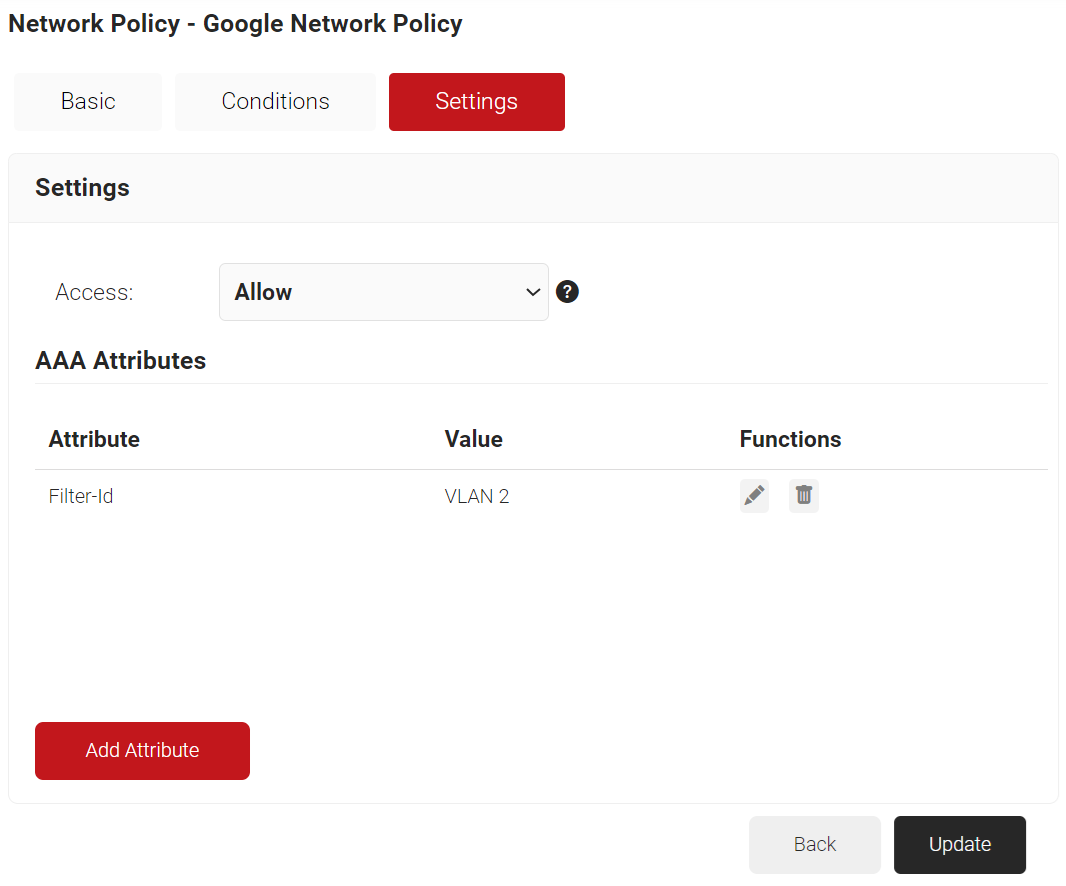
- Click Add Attribute.
- Click Update.
 After successful network authentication, the configured attributes are applied to the device via the controller, and the device is then assigned to the appropriate VLANs based on the configuration.
After successful network authentication, the configured attributes are applied to the device via the controller, and the device is then assigned to the appropriate VLANs based on the configuration.
Google Certificate Enrollment With Cloud RADIUS/Automate Certificate Enrollment With Cloud RADIUS
The connection of the SecureW2 network and a Google Workspace SAML application creates solutions for network administrators by achieving the goal of easily connecting users to the network and offering a higher level of control. Users have to complete the onboarding process once to automatically enroll for certificates for uninterrupted connection, whereas, in the past, it would be a manual effort that would divert countless resources. Administrators can also differentiate between groups and ensure that everyone in the organization has access to the connections they need.
The WPA2-enterprise network, with EAP-TLS authentication, uses PKI for certificate-based authentication using a pair of public and private keys. What makes it secure is that the private key is always stored in the device, and the public key is issued as a digital certificate with a reputed Certificate Authority signing the certificate. Authentication is considered complete only when the public and private key matches.
SecureW2’s Managed PKI (Public Key Infrastructure) solution simplifies certificate management that includes a Hardware Security Module (HSM) to protect the PKI and ensures that every certificate issued can be trusted. Create custom certificate templates and design certificate issuance and enrollment policies to improve network visibility and enhance network security. Our industry-best support team can assist you at anytime you need help with any assistance that you may need.
If you’re interested in learning more about the advantages your IT department can experience by using Google Cloud with SecureW2 solutions, contact us, and we’d be happy to set up a free trial. Click here to get a pricing estimate for this cost-effective solution.