Key Points
- 802.1x authentication is widely supported by modern devices, ensuring secure network access through protocols like EAP.
- Operating systems like Windows, macOS, Android, and Linux support 802.1x, while lower-end IoT devices may lack sufficient processing power.
- Devices that don’t support 802.1x typically lack necessary hardware resources, like gaming systems and older IoT models.
- SecureW2 offers streamlined 802.1x onboarding solutions, reducing misconfigurations and improving network security for all major operating systems.
It is hard to imagine life without Wi-Fi, both in personal or professional spaces but we can not deny that it has parallelly caused the transmission of more and more sensitive information over the air. The evolution of WPA2-Enterprise has ensured the safety and security of networking to a different level altogether. A significant component of WPA2-Enterprise is IEEE 802.1x, a subset of the standard IEEE 802.1 group networking protocol.
802.1x has been the real game-changer in modern-day authentication protocols such that it has almost become synonymous with the WPA2-Enterprise. Also, with the evolution of modern-day devices with advanced processing power and operating systems, it is hard to imagine a network without the support of 802.1x.
In this blog, we want to narrate the evolution of devices supporting 802.1x so that you can better understand the nature of networking protocols best suited for your organization.
Which Devices Support 802.1x?
Most modern devices used for WiFi connectivity usually support the 802.1x authentication protocol. When we say that a device does not support 802.1x, the chances are that it does support 802.1x, but it doesn’t know if the SSID in use is configured for 802.1x. Such devices need external configurations to push the infrastructure required for 802.1x to the existing network.
Also, processing power plays a pivotal role in determining whether a device is capable of supporting 802.1x or not. Many lower-end IoT devices that do not have sufficient RAM might not support the 802.1x as their processing power is not sufficient to do so.
With that being said, let’s look at some major 802.1x-compatible devices and discuss them by the operating system.
- Windows Devices
- Windows 8 and above
- Windows XP
- Apple Devices
- Mac OS X Panther and above
- iOS 2 and above
- Android Devices
- Android 2.0 and above
- Linux Devices
- By using the configuration tool
- Modern or High-End IoTs
- Modern Wired and Wireless Infrastructure
Windows Devices
The versions of Windows prior to Windows 7 had a tough time supporting 802.1x, and most of them needed external support from Microsoft to do so. Both Windows XP and Windows Vista have issues related to VLAN and IP address which can be resolved only with the help of external addons like Hotfix by Microsoft.
Windows 7 requires a manual configuration on its premise, or it needs to be informed manually that it’s making a Wi-Fi connection, which has the 802.1x protocol enabled.
From Windows 8 onwards, that wasn’t the case because, as soon as you click on the SSID, it can detect the authentication protocol enabled for that SSID. After that, it usually asks for credentials whether you do EAP-TLS or EAP-PEAP because the authentication protocol is configured on the RADIUS server and not on the controller.
So the client has information about only 802.1x authentication, while the RADIUS server decides the EAP protocol that’s going to be used in the authentication.
Apple Devices
Most Apple devices working on the macOS operating system have been supporting 802.1x natively, long before Windows started the same.
For macOS, the processor has started supporting the 802.1x natively from Mac OS X Panther (version 10.3). For iOS, the processor has been supporting the 802.1x from the iOS 2 version and above.
Linux Devices
Linux has been supporting 802.1X with the help of wpa_supplicant and other third-party integration apps like NetworkManager. NetworkManager is the most standard Linux networking tool that natively integrates with all the major desktop and mobile environments in Linux and is widely used by network admins.
Android Devices
Android has supported 802.1x since the release of Android 2.0. The other requirements for 802.1X Authentication on Android devices are similar to other major operating systems, including a RADIUS Server, Identity Provider / Directory, and enterprise-grade Access Points and Switches.
IoT Devices
In IoT devices, the hardware, and the RAM play a significant role in determining whether or not the device supports 802.1x. If the processing power permits the device to store certificates, it can efficiently perform the TLS handshake and supports 802.1x.
Some common examples of the high-end IoTs that support 802.1x include smart home appliances, high-end printers, scanners, smart TVs, and so on.
So, in a nutshell, the processing power or RAM is the deciding factor for deciding the authentication protocol for these devices.
Which Devices do not Support 802.1x?

As per our earlier discussion, the processing power or RAM and the storage capacity or ROM play an essential role in determining the 802.1x support in a device. So most gaming systems that do not require such advanced WiFi capabilities do not support 802.1x, such as –
- Nintendo Wii
- Xbox 360
- Playstation 3
- PSP
- Nintendo Switch
- Xbox One
- Playstation.
Also, the lower-end IoTs with minimal processing power do not support 802.1x, such as Kindle Reader, Sony Reader, Roku, Apple TV (1st and 2nd generation), and many more.
How Does 802.1x Work?
802.1x is the standard protocol defined by IEEE for Port-Based Network Access Control (PNAC). It is the most common protocol used by network admins for authenticating the users/clients to the server via an access point.
The standard authentication protocol practiced on encrypted networks is Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) in 802.1x. The EAP authentication method utilizes an encrypted EAP tunnel to provide a safer path for communication between client and server. The EAP tunnel prevents external users from intercepting information in the local network, thus adding an extra layer of security.
The 802.1x mainly consists of 3 main components:
- Supplicant
- Authenticator
- Authentication Server
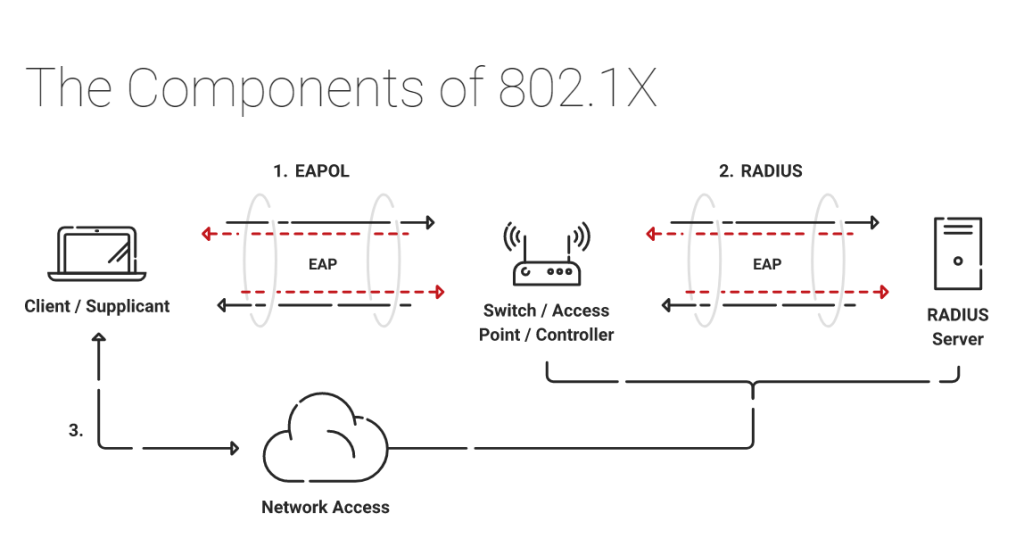 Supplicant
Supplicant
The user/client at the endpoint has a built-in supplicant for initiating a request to the server for network access via authenticator. It participates in the initial EAP transaction with the authenticator to send the request to the authentication server in a protocol compliant with the 802.1x network.
Authenticator
The authenticator is the access points or controllers/switches that act as a medium for initiating the communication between the endpoint supplicants and the authentication server. It forwards the request by the supplicants to connect to the network to the correct RADIUS server based on the configuration in the Wireless Security Settings.
Authentication Server
This is basically the RADIUS server which helps in the authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) of the end-users or clients. Whenever a user attempts to access the network, the RADIUS server validates the identity of the users by confirming it with the Identity provider before permitting access to the users.
SecureW2: The Best 802.1x Onboarding Solution
As we have seen, the evolution of devices with operating systems and networking protocols has significantly shaped how we use WiFi today. Most modern devices support 802.1x, but they need to be properly configured to do so.
You can manually attempt to configure 802.1x for your organization, but it will be a humongous task, especially for mid or large-sized enterprises. Alternatively, you could rely on end-users to configure their own devices, but this exposes you to the risk of misconfiguration, since technical proficiency may vary. The solution is an onboarding application that safeguards end-users from misconfiguration while also saving your IT department time.
SecureW2 offers a wide- variety of onboarding solutions for different devices working on all the leading operating systems such as Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, and many more. We have the leverage of both natively integrating with your existing infrastructure or providing a full-fledged network security solution, and our ever-expanding customer base is a testimony to that. We have affordable options for organizations of any size. Check out our pricing to learn more.
