Key Points
- WPA2 is far more secure than WPA, using AES-CCMP encryption and offering enterprise-grade protection.
- Digital certificates with RADIUS eliminate password risks, ensuring unique credentials for every user and device.
- Upgrade your network today with WPA2 and certificate-based authentication to safeguard against modern Wi-Fi threats.
Wireless networks are omnipresent. You may have access to many wireless networks, whether in a neighborhood coffee shop, a school, or home. However, it’s hard to tell which ones are secure. Looking closely at Wi Fi security settings can often determine which ones you can trust. Wireless network security solutions are continually changing. They have had to adapt and improve since hackers and cybercriminals are likewise becoming more sophisticated with every technological innovation.
While Wi-Fi has altered how we work, there are threats and obstacles, too. The two most prevalent security protocols for safeguarding your unsecured wireless networks are WPA and WPA2. Organizations and their employees must become more knowledgeable about the distinctions between the two and the varying degrees of security they provide. We compare WPA vs. WPA2 and review the background of the security protocols to help you understand your alternatives.
Click here to learn how SecureW2 partnered with an Engineering firm for their network authentication.
What is WPA (Wi Fi Protected Access)?
Introduced in 2003, Wi Fi Protected Access WPA is a secure encryption protocol created to address and replace the weaknesses of the Wired Equivalent Privacy WEP method. WPA implements stronger encryption features, such as:
Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP)
The static WEP encryption keys were replaced with the dynamic 128-bit TKIP key. Furthermore, the TKIP algorithm was developed to enable TKIP upgrades without requiring hardware replacement for users of outdated WLAN equipment.
Message Integrity Check (MIC)
MIC stops attacks on encrypted packets sent over the network. In this instance, an encrypted message delivered across the network is intercepted, changed, and retransmitted by an attacker. By using MIC, these packets become impenetrable to tampering.
Pre-shared key (PSK)
Encrypted communication delivered across the network is unlocked using PSK. By intercepting transmitted wireless data packets, hackers attempt to crack the encryption using brute force assaults, which PSK helps to thwart. Even with these advantages, WPA still has several security flaws.
What are the Vulnerabilities in WPA?
While WPA’s encryption method is more secure than its predecessor, WEP protocol, the new TKIP encryption scheme, must consider backward compatibility with older WEP devices. As a result, the WPA protocol reused some components of the previous, vulnerable WEP system, and naturally, the same flaws eventually surfaced in the upgraded WPA system.
Security flaws in the WPS standard
Many wireless routers that enable WPA come equipped with the network security standard Wi-Fi Protected Setup, or WPS. WPS, however, was designed with ease of use in mind. Therefore, using WPS to connect to the network usually entails a significant security trade-off. An attacker can quickly authenticate your network and retrieve your WiFi password if they can gain the WPS 8-digit PIN using brute force.
Why are digital certificates a safer option than PSK?
Regarding Wi-Fi network security, digital certificates provide a vital substitute for conventional password-based authentication. In contrast to passwords, which are easily lost, stolen, or used maliciously, digital certificates offer a more secure form of user authentication. Certificates protect sensitive data sent over the air using public/private key encryption, eliminating the necessity for Wi-Fi Pre-Shared Keys (PSKs). This implies that your Wi-Fi network is naturally more secure when passwords are not involved.
A significant benefit of digital certificates is the enhanced safety they provide. With certificates, every connection has more identification context, which makes it more difficult for hostile actors to eavesdrop or spoof conversations. SecureW2’s managed PKI platform is one example of a solution that makes managing and deploying certificates easy. With its user-friendly certificate management tools, this cloud-based public key infrastructure (PKI as a service) makes activities like network authentication, document signing, and code signing easier. Through contemporary automation technologies, establishments may guarantee the control and efficiency of each phase of the certificate lifecycle, therefore augmenting security and operational effectiveness.
For Wi-Fi network authentication, digital certificates provide a more secure option than passwords, to sum up. Organizations may benefit from improved security and streamlined certificate lifecycle management by simply deploying and managing certificates with SecureW2’s managed PKI platform. By implementing certificate-based authentication, businesses may improve their cybersecurity posture and reduce the dangers associated with password-based authentication.
What is WPA2?
The WiFi security protocol known as WPA2 – Wi Fi protected access 2 was released to fix the flaws in the WPA system. WPA2 replaced TKIP with more sophisticated encryption methods, such as
The Advanced Encryption Standard (AES)
AES is a block cipher that uses a formula and a fixed same key to operate on discrete data blocks. WPA uses the RC4 stream cipher, which is less secure than AES for wireless networks. AES provides more robust encryption and more resilient protection.
Counter Mode Cipher Block Chaining Message Authentication Code Protocol (CCMP)
The Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) encryption technique is the foundation for the CCMP encryption protocol. By comparison, CCMP provides more security than TKIP. However, CCMP’s improved security and privacy necessitate more processing power, frequently requiring new hardware.
WPA2 functions in two ways:
- WPA2 Personal (PSK): This mode is typically utilized in residences.
- WPA2 Enterprise (EAP): This mode is better suited for usage in businesses or organizations.
What is the difference between Personal (PSK) and Enterprise (EAP) WPA2?
The authentication methods used for users and endpoints are the main distinction between WPA2-Personal and WPA2-Enterprise.
Now, let’s discuss WPA2-Personal. As its name implies, this architecture is suitable for residential networks. Pre-shared keys, often known as passwords, are used by WPA2-Personal and must be entered by users to join the WiFi network.
However, since only one password must be entered, everyone using the computer linked to the network may view the password. Using this approach on a corporate network is not advised.
On the other hand, WPA2-Enterprise offers the necessary privacy and security to protect wireless networks in a corporate setting. It is more difficult to set up, though. WPA2-Enterprise only applies when an 802.1x RADIUS server is connected for client authentication.
It provides centralized management of WiFi network access. Users must provide their login information (password and username) when attempting to join the network.
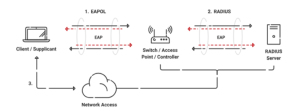
Because every device is verified before connecting, enterprise-grade security is ensured. A private, encrypted tunnel is also established between the device and the secure network.
WPA2-PSK vs WPA2-EAP – Comparison table
| PSK | EAP |
| Unmanaged authentication. The pre-shared key is common to all users. | Centrally controlled authentication. Every user has a distinct set of login credentials. |
| Authentication server is not required. | An authentication server (RADIUS) supporting the EAP 802.1x policy is required. |
| Used when there are few, trustworthy devices on the network. | Used in networks with many connected devices, such as those seen in business settings. |
How can a RADIUS Server Help Eliminate Vulnerabilities in Wireless Networks?
Putting in place a RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service) server is a vital first step in strengthening the security framework of your wireless network. A RADIUS server is a gatekeeper, validating each network access request to ensure that only authorized people and devices are allowed admission. By providing a RADIUS platform created especially for passwordless authentication, SecureW2 is changing the way businesses authenticate people and devices on their networks.
The SecureW2 RADIUS solution was rigorously designed to eliminate the risks of standard password-based authentication techniques. SecureW2’s passwordless RADIUS solution uses certificate-driven solid security instead of passwords, which are prone to theft and compromise. This method, which links user and device identities to every connection, improves authentication security for various network services, including Wi-Fi, VPNs, and Single-Sign-on. Enterprises may benefit from comprehensive monitoring and division functionalities, augmenting their network’s security posture.
One of the best features of SecureW2’s passwordless RADIUS solution is its ability to simplify authentication procedures while enhancing security. Employees may access network resources without the hassle of keeping passwords since password complexity and reset procedures are gradually becoming obsolete. Furthermore, there is a far lower chance of credential thefts from cloud-based or over-the-air assaults. The solution also allows organizations to prevent untrusted devices from connecting to the network to strengthen security measures further.
Furthermore, SecureW2’s passwordless RADIUS solution provides managed company-owned devices with zero-touch configuration and enrollment via managed device gateway APIs and self-service certificate registration for unmanaged devices and BYODs. This smooth interaction with current network infrastructures streamlines the deployment and maintenance procedures, guaranteeing a hassle-free experience for administrators and end users. By utilizing SecureW2’s passwordless RADIUS solution, organizations may improve their network security, reduce vulnerabilities, and adopt a more effective and secure authentication paradigm.
WPA vs WPA2: The Difference
When released in 2004, WPA2 was presented as the updated and enhanced version of WPA. While this is undoubtedly true, there are some situations where one may be more appropriate. We must examine the differences between these security procedures to comprehend this.
The main distinction is between AES and TKIP encryption techniques. Moreover, WPA passwords are shorter than WPA2 passwords. Longer passwords are preferable in password etiquette as they are more challenging to crack.
Regarding WPA vs WPA2, WPA may handle older software, while WPA2 is intended for the newest systems. Crucially, WPA2 has an enterprise version specifically designed for use in businesses, much like its predecessor. This indicates that WPA2 comes in two versions: personal and enterprise. Each employee and corporate device is given unique credentials while using the enterprise version to improve security. Because of this, WPA2 is a straightforward option for companies and other organizations.
The sole drawback of WPA2 over its more traditional competitor is that it may require more power because of its higher speed, which might cause network performance to lag.
When to use WPA?
WPA’s encryption process could be more secure, and an enterprise solution cannot support commercial use. However, WPA could be a better alternative if you are ready to accept security compromises and have older hardware. It also consumes less processing resources.
When to use WPA2?
Wi-Fi encryption protocol WPA2 is suitable for both home and corporate use. AES-CCMP encryption provides enhanced security, and a dedicated corporate solution facilitates business network management. Since its launch, WPA2 has been the industry standard for wireless security protocols. The Wi-Fi Alliance mandated that WPA2 be used for security on any device wearing the Wi-Fi trademark.
Final Verdict – WPA2 is the Safest Choice
WPA2 is the safest option due to its enhanced security features, which include Enterprise settings, more extended password requirements, and an extra layer of protection. However, WPA provides some security if your connection is sluggish or you have outdated firmware.
Elevating Wi-Fi Security: The SecureW2 Advantage
The decision between the two encryption methods in the continuing conflict between WPA and WPA2 comes down to more than simply a taste for the newest hardware. It has to do with protecting your network against changing threats and weaknesses.
With its extensive solutions, SecureW2 is a game-changer in pursuing strong Wi-Fi security. Organizations can quickly implement and manage digital certificates with SecureW2’s Managed PKI, protecting their networks from new threats without having to deal with the headaches of complicated PKI setups. Furthermore, password-based system vulnerabilities are eliminated by SecureW2’s passwordless Cloud RADIUS, which also revolutionizes authentication by guaranteeing that only authorized users and devices can access network resources. With a dedication to innovation, security, and ease of use, SecureW2 enables businesses to strengthen their Wi-Fi security posture and keep one step ahead of emerging cyber threats.
Contact us to learn more about how we can defend the Wi-Fi network at your organization.