Wireless network security is of the utmost importance in the rapidly evolving digital world. Wi-Fi certificate authentication has become a vital option that not only makes networks safer but also makes using them more accessible.
Wi-Fi certificate authentication uses digital certificates to set up safe and reliable links between devices and wireless networks. This approach goes beyond the limits of traditional password-based systems. It provides a robust and smooth access experience that keeps private data safe and reduces the risks of unauthorized access.
This article explores the intricacies of Wi-Fi certificate authentication windows 10, explaining how it operates and illuminating its benefits to modern network environments. We will discover the relevance of this authentication mechanism and its essential role in redefining wireless security paradigms as we follow the process from initial client connection requests to the final setup of devices.
Click here to learn how SecureW2 helped a private university graduate with Certificate-Based Authentication.
The Significance of Wi-Fi Certificate Authentication Windows 10
Wi-Fi certificate authentication windows 10 is based on digital certificates, like virtual ID cards for devices that want to connect to a network. These certificates, given out by trusted Certificate Authorities (CAs), give each device a unique and secure name and set the stage for strong connections. Certificates are more secure than passwords because they use secret keys and encryption. Passwords are easy to guess. This method allows network managers to control access in a specific way based on things like a user’s job or department. This kind of focused authorization makes the network environment more robust and structured.
Eliminating the Hassle of Password Resets
Password-based systems make it annoying to have to change passwords often. This chaos affects the user experience and makes IT teams work harder. This problem is solved by Wi-Fi certificate authentication, which makes certificates last longer. Users are relieved of the burden of frequent password changes, resulting in uninterrupted connectivity and increased user satisfaction. This makes Wi-Fi certificate authentication a good choice for work settings where things change quickly and users have different access needs.
Foiling Credential Theft Attempts
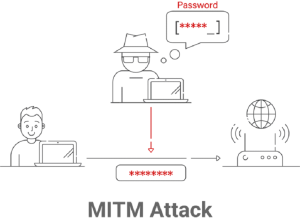
In a world of threats like Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) and Evil Twin attacks, the weaknesses of standard passwords become clear. Passwords are still vulnerable to hackers, brute-force attacks, and other evil methods, which is a big problem for network security. Unauthorized access becomes a major risk when a password is compromised. Wi-Fi certificate authentication guards against these risks using a strong two-factor verification process based on public and private keys.
The private key, an important part of the certificate authentication process, is safely stored on the device, making it hard to steal or acquire. This important security step makes it less likely that credentials will be stolen, which stops these attempts.
Obtaining Certificates on Devices
Mobile Device Management (MDM) solutions efficiently facilitate the transition to certificate-enabled security for corporate environments’ managed devices. This centralized approach guarantees a secure and seamless procedure. With meticulous integration between MDM systems and the organization’s chosen Certificate Authority (CA) infrastructure, certificate enrollment for managed devices is automated. This may involve trusted public CAs or private CAs, like SecureW2, ensuring a seamless certificate issuance process for managed devices. The coordination process includes generating a Certificate Signing Request (CSR) and submitting it to the CA to issue the necessary certificate.
Click here to read our blog on the Best Private CA / PKI Service.
The challenge of integrating certificates on Bring Your Own Devices (BYODs) is handled using a user-centric technique. Self-service portals act as gateways for network access for personal devices. This method allows users to initiate the certificate enrollment procedure and acquire certificates quickly.
In addition, enrollment communications contain personalized links that guide users through the registration process. This method prioritizes security without increasing its complexity. As users enroll effectively, their devices receive unique certificates, establishing a secure and trustworthy connection to the network.
JoinNow MultiOS by SecureW2 makes it easy to set up your device. Our user-friendly solution ensures error-free configuration of unmanaged devices, removing the possibility of misconfiguration. It works with all major operating systems, has guided user flows, and gives end-users the power to set up their devices easily. With JoinNow MultiOS, you can make onboarding both secure and easy.
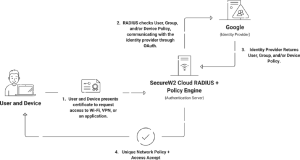
The Role of RADIUS Servers in Certificate Authentication
RADIUS servers serve as network security guardians, intermediaries between wireless devices requesting access, and the central authentication infrastructure. This essential function ensures that only authorized devices with valid certificates can establish secure network connections. RADIUS servers form the backbone of certificate-based authentication by facilitating seamless communication between access points and authentication servers.
Leveraging EAP-TLS
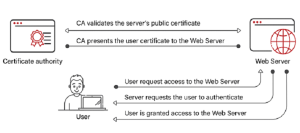
EAP-TLS uses a certificate-based authentication process that is highly secure. When a client device seeks to connect to a network, it presents its digital certificate, which contains a public key, to the authentication server, which is usually a RADIUS server. The RADIUS server then verifies the certificate’s authenticity by examining its digital signature and ensuring that it hasn’t expired or been revoked by an approved Certificate Authority (CA). The server generates a session-specific encryption key if the certificate successfully completes these validation tests. The encryption key is then encrypted with the client’s public key from the certificate and returned to the client. The client decrypts this key, which holds its private key and returns it to the server. The client and server share a secret encryption key for secure data transmission throughout the session.
This rigorous certificate validation and key exchange process ensures that only authenticated, authorized devices with valid certificates are granted access to the network, thereby substantially enhancing the overall security of the network.
Server Certificates and Issuing CAs
RADIUS servers require certificates in addition to validating client certificates to secure the communication channel between devices and the server. This procedure ensures that the exchange of sensitive information remains encrypted and secure against eavesdropping. The RADIUS server certificate and the certificate of the issuing CA support this secure communication channel. As devices and servers engage in mutual certificate-based authentication, the network ecosystem is strengthened against potential threats.
Navigating Security and Granularity by Managing Access
Wi-Fi certificate authentication extends beyond the initial connection phase and into the specifics of access management. This section explores the advanced techniques that enable RADIUS servers to control access precisely. This multifaceted management process ensures a robust and secure network environment through attribute-based authorization, real-time lookup, and efficient certificate revocation techniques.
Authorization Based on Attributes
Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC) is a sophisticated access control method that surpasses traditional Role-Based Access Control (RBAC). ABAC bases access decisions on several attributes associated with users, resources, and the surrounding environment. This method enables organizations to dynamically grant or deny access based on user roles, resource types, location, time of day, and other variables. ABAC provides a robust framework for customizing access permissions based on specific user scenarios, enhancing security and adaptability. ABAC allows administrators to construct fine-grained policies that adapt to changing attributes, facilitating enrollment and enhancing the user experience. It also provides real-time evaluation, which enables access decisions to be made dynamically, thereby enhancing security by preventing unauthorized access in specific situations, such as when users are outside the organization’s secure network.
SecureW2’s Cloud RADIUS with ABAC support leverages these features to provide a robust access control solution. Referencing cloud directory attributes during authentication ensures real-time, context-based access decisions, reducing administrative burden and enhancing security in SaaS-based environments. ABAC is a flexible and granular method for regulating user access while maintaining a robust security posture.
Real-Time Lookup
Wi-Fi certificate authentication differs from before it because it can look up information in real time. RADIUS servers do immediate certificate validation to ensure the certificates are valid and up-to-date. This dynamic method stops unauthorized access attempts caused by certificates that have been canceled or have been hacked. As devices join the network, RADIUS servers quickly check Certificate Revocation Lists (CRLs) or the Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP) to make real-time access decisions. This makes the network faster and more secure.
Robust Revocation Methods
Revocation of a certificate is an integral part of Wi-Fi certificate authentication. RADIUS servers use vital ways to deal with certificates that have been hacked or are no longer valid. Certificate Revocation Lists (CRLs) contain a list of certificates that have been canceled. This lets RADIUS servers refuse connections from devices that use these banned certificates. On the other hand, the Online Certificate State Protocol (OCSP) checks the state of certificates in real time, so RADIUS servers can find out if a certificate is still good at any given time. These ways to revoke certificates keep network access safe from threats that could come from certificates that are not authorized or have been hacked.
Transitioning to Enhanced Security: Leaving Password-based Wi-Fi Behind
To move from standard Wi-Fi systems that use passwords to ones that use certificates for identity, you need to take a careful, well-planned, and well-communicated approach. This section details this change, its importance, and the main benefits for organizations that make the switch.
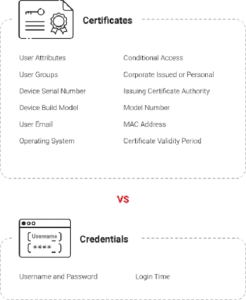
Advantages of Certificate Authentication
Using certificate authentication has many benefits that all involve making the network safer and improving the user experience.
Strong Encryption
Certificates use encryption keys to secure data between devices and the network. This level of security makes it much less likely that someone with malicious intent will be able to read the message.
Impenetrable Identification
Unlike passwords, which are easy to guess, certificates give each device a unique digital identity. This makes each device unique, which stops unauthorized access because only devices with proper certificates are allowed in.
Reduced Attack Surface
Wi-Fi certificate authentication eliminates the need for user-generated passwords, removing a popular attack method. This makes the network more secure by making it harder to attack.
Elimination of Credential Theft
Certificate verification eliminates the risk of stolen credentials because private keys stay safe on the device. With this precaution, unauthorized users can’t take over valid passwords.
Seamless User Experience
Since users don’t have to change or update their passwords often, the login process is smooth and easy. This makes things work better and makes users happier.
Supporting Legacy Devices Without 802.1X Certificates
The rise of cutting-edge network security solutions is accompanied by older devices that lack interoperability with advanced protocols such as 802.1X certificates. As organizations move to a more secure system of identity based on certificates, they will eventually run into devices that don’t support this advanced protocol. These devices, often old but still needed for daily tasks, could hinder the smooth user experience that certificate identification is supposed to provide.
Network managers use a dual-network approach to deal with this problem. This requires making a second SSID, which is a separate network channel. The primary SSID uses a certificate for identification, but this secondary SSID is only for devices that can’t use certificates. Instead, these devices gain entry to the network through a password. This new way keeps old devices connected without weakening the network’s security.
MAC authentication bypass (MAB) is a similar method that can be used with dual SSID configurations. MAB lets devices connect to the network based on their MAC addresses, unique identifiers for hardware assigned to network interfaces. When 802.1X certificates can’t be used, network managers can set up MAB to identify devices based on their MAC addresses. However, MAB has drawbacks because it does not give the same level of security as certificate-based authentication, and MAC addresses may be spoofed.
Even though dual SSIDs and MAB can help organizations support legacy devices, it’s important to consider the trade-offs between security and ease when using them. Also, network managers should be on the lookout and keep an eye on the security of their networks, especially when older devices with less secure login methods need to be connected.
Transforming Your Network Security Landscape With SecureW2
This article evaluated Wi-Fi certificate authentication, emphasizing its security over passwords, simplified access management, and compatibility with legacy devices.
SecureW2 is your trusted ally in bolstering the security of your digital environment by implementing robust Wi-Fi integrations. Our state-of-the-art solutions are designed to address the security needs of both managed and unmanaged devices, providing a comprehensive approach to safeguarding your network infrastructure.
As a pioneer in the cybersecurity realm, we have perfected the art of seamlessly integrating with a diverse range of cloud Identity Providers (IDPs). This unparalleled capability empowers you with the utmost flexibility and compatibility, enabling you to fortify your security ecosystem to its fullest potential.
To learn more, contact us today to delve into our comprehensive offerings.