Key Points
- MITM is one of the most common attacks in which attackers exploit the communication channel between a user and an application by creating a rogue access point.
- You can minimize the risk of MITM attacks by using and migrating to 802.1x EAP-TLS.
- EAP-TLS authentication protocol is the best way to eliminate the risk of MITM attacks, as it performs mutual server certificate validation and does not require sending credentials over the air.
A MITM happens when attackers hijack a communication channel to intercept and steal data. In this type of attack, they position themselves between a user and an application, silently capturing or altering the data by deploying a rogue access point or malicious hardware. Attackers can launch MITM attacks by spoofing websites, intercepting network traffic, setting up rogue Wi-Fi hotspots, hijacking emails, and taking over active sessions to steal data.
Read here to learn more about various prominent ways for Wi-Fi hacks and ways to prevent them.
Stages of MITM Attacks
MITM attacks take place in six distinct stages:
- First, attackers position themselves between the two entities and intercept their targeted data without creating suspicion using methods like ARP spoofing.
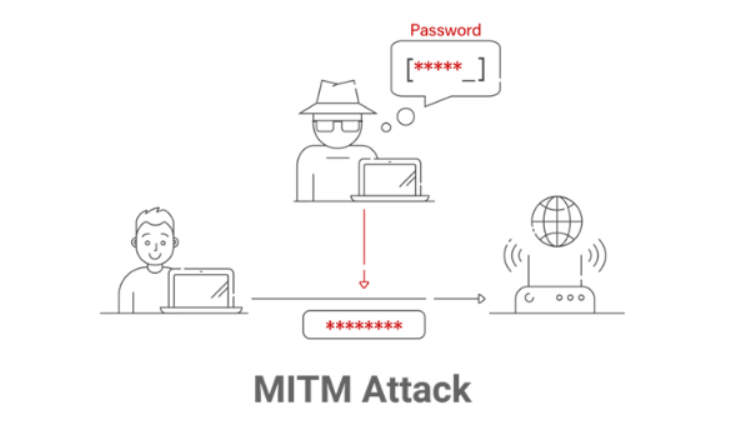
- Secondly, the intercepted data is decrypted using methods like SSL stripping or other phishing and social engineering.
- Then, criminals will look for valuable and usable information, like login credentials.
- Next, attackers modify the data they have intercepted, altering codes or injecting fraudulent responses before reaching the recipient.
- With enough stolen data, attackers are able to take over an active session by impersonating a legitimate user to gain unauthorized access.
- Finally, to maintain control, attackers typically deploy techniques like backdoors and rootkits. Wi-Fi Eavesdropping and MITM Attacks.
Wi-Fi Eavesdropping and MITM Attacks
In Wi-Fi eavesdropping, attackers intercept unencrypted data transmitted over a compromised, misconfigured, or open Wi-Fi network. This can happen in two ways: passively, by simply capturing network traffic on an insecure connection, or actively, by setting up a rogue Wi-Fi hotspot that mimics a legitimate network. In both cases, attackers can steal sensitive data such as login credentials, financial information, and personal communications without the user realizing their connection is compromised.
Wi-Fi eavesdropping often serves as the first step in a broader MITM attack. Once attackers gain access to network traffic, they can move beyond passive monitoring to actively intercepting and manipulating data. They leverage techniques like ARP spoofing, DNS spoofing, and Evil Twin attacks to position themselves between users and legitimate services.
This allows them to steal credentials, redirect users to malicious sites, or inject harmful payloads into communications. Exploiting unencrypted or poorly secured networks, attackers can escalate from simple eavesdropping to a full-scale MITM attack, compromising sensitive data in real-time.
Preventing MITM Attacks with EAP-TLS
Migrating to the 802.1X framework with digital certificates significantly reduces exposure to cyberattacks like MITM attacks. Unlike credential-based authentication, EAP-TLS eliminates the need to transmit passwords over the air, preventing credential theft.
With EAP-TLS, both the client and server authenticate each other using mutual certificate validation, ensuring a secure connection. This prevents devices from mistakenly connecting to rogue access points, as authentication requires both sides to present valid digital certificates. By removing reliance on passwords and enabling certificate-based trust, organizations strengthen their security posture against MITM threats.
See how a university eliminated the risk of cyberattacks and network insecurity by shifting to the EAP-TLS authentication protocol.