Key Points
- EAP-TLS provides strong security through mutual authentication with client and server certificates, but it requires setting up a Public Key Infrastructure, which can be complicated.
- EAP-TTLS/PAP offers flexibility with password-based authentication within a secure tunnel, making it easier to deploy but less secure against specific threats.
- SecureW2's managed PKI simplifies EAP-TLS implementation by reducing the complexity of certificate management and improving network security.
Choosing the right authentication protocol is more than a matter of security. Authentication is the critical check ensuring only rightful users can access certain data or networks. The decision between implementing EAP-TLS or EAP-TTLS/PAP is more than a technical dilemma—it’s about balancing security, compatibility, and implementation challenges. These choices affect everything from user experience to the robustness of defense against cyber threats.
This article aims to dissect and compare two prominent players in the authentication arena: EAP-TLS and EAP-TTLS/PAP. We will dive into the technicalities that define these protocols, weighing their strengths, vulnerabilities, and applications in network security.
What is Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP)?
EAP protocols serve as a foundational framework for enforcing various authentication methods across network security landscapes. Distinctively modular, EAP is designed to operate within both the authentication phase of a network connection and the PPP (Point-to-Point Protocol) negotiation phase, making it uniquely adaptable to varying network requirements and security policies. At its core, EAP functions by encapsulating the mechanics of authentication methodologies, allowing for their use over a common interface.
This encapsulation supports multiple authentication mechanisms—ranging from certificate-based authentication, such as EAP-TLS, to simpler, password-based methods like EAP-TTLS/PAP—without necessitating changes to the underlying network transport layer. Thus, EAP’s versatility enhances its applicability across different network types (e.g., LANs, WLANs, cellular networks), enabling a cohesive, secure authentication framework that can be tailored to meet the specific security demands of each context.
What is EAP-TLS?
EAP-Transport Layer Security (EAP-TLS) stands out among authentication protocols for its rigorous security measures, anchored in the utilization of digital certificates for both server and client authentication. This protocol elevates EAP-TLS above simpler authentication mechanisms by embedding mutual authentication and encrypted communication as its core principles. It uses two main components to achieve this:
- Server Certificates: A server certificate validates the server’s identity to the client, ensuring that the entity on the other end of the connection is legitimate. A server certificate establishes a trust relationship from the outset of the communication, safeguarding against man-in-the-middle attacks.
- Client Certificates: A client certificate confirms the client’s identity to the server, enabling a two-way authentication street. It provides a higher degree of security by ensuring that only authorized clients can gain access to the network.
This dual-layer certificate approach ensures that EAP-TLS not only secures the authentication process against unauthorized access through rigorous validation but also encrypts the information exchange, thus protecting the data integrity against potential cyber threats.
The critical advantage of EAP-TLS lies in its unmatched security, leveraging full TLS to mitigate risks associated with identity theft and data breaches. Its security is based upon the concept of asymmetric cryptography, which uses both a public key and a private key to encrypt and decrypt data. However, this level of security comes with notable disadvantages, primarily the operational complexity and administrative burden of managing a comprehensive Public Key Infrastructure (PKI). This includes the overhead of distributing, renewing, and revoking digital certificates, which requires significant resources and expertise.
Furthermore, the necessity for client certificates can present additional deployment challenges, particularly in heterogeneous network environments where device compatibility and certificate management become logistical hurdles.
Organizations looking to deploy a PKI of their own may not have the ability or expertise to build their own network access control based on certificate-driven security. Thankfully, there are managed PKI solutions, such as SecureW2’s managed PKI, which are cloud-based and can be deployed rapidly. These solutions empower organizations to use passwordless authentication without needing to build complex infrastructure of their own.
EAP-TLS process
What is EAP-TTLS/PAP?
For those seeking a more adaptable authentication protocol, EAP-TTLS/PAP offers a compelling solution. It combines the secure tunneling of EAP-TTLS with the password-based authentication of PAP, offering a blend of security and flexibility. EAP-TTLS operates by creating a secure, encrypted tunnel between the client and the authentication server. Within this secure tunnel, user authentication can happen, where user credentials can be safely exchanged, even if those credentials are not inherently secure.
How Does EAP-TTLS/PAP Work?
EAP-TTLS establishes a secure communication channel, protecting the data integrity and confidentiality between the end users and the authentication server.
Password Authentication Protocol (PAP) Within EAP-TTLS
Once the secure tunnel is established, Password Authentication Protocol (PAP) is used to transmit the user’s credentials for validation. This method allows for the use of legacy password-based systems within a modern, secure framework.
EAP-TTLS process
The Benefits of EAP-TTLS/PAP
EAP-TTLS/PAP offers significant advantages, particularly in terms of flexibility and ease of deployment. It does not require client-side certificates, simplifying the setup process for end users and reducing the administrative overhead of managing a certificate infrastructure.
EAP-TTLS Vulnerabilities
However, this protocol is not without its weaknesses. The reliance on password-based authentication within the secure tunnel can be a potential vulnerability if not managed properly. Passwords, unlike digital certificates, are susceptible to various attacks such as phishing or brute force.
Efficient security measures, including strong password policies and regular user education, can mitigate the risks associated with password-based authentication. Additionally, implementing layers of security measures like multi-factor authentication can further enhance protection without compromising the flexibility that makes EAP-TTLS/PAP attractive. The issue with policies like these, though, is that they make the end-user experience more inconvenient than it has to be.
EAP-TLS vs. EAP-TTLS/PAP: How Do These Authentication Methods Compare?
When comparing EAP-TLS with EAP-TTLS/PAP, organizations must weigh several critical factors, including the desired level of security, the complexity and resources available for configuration and management, and the range of devices needing access. This is how they compare:
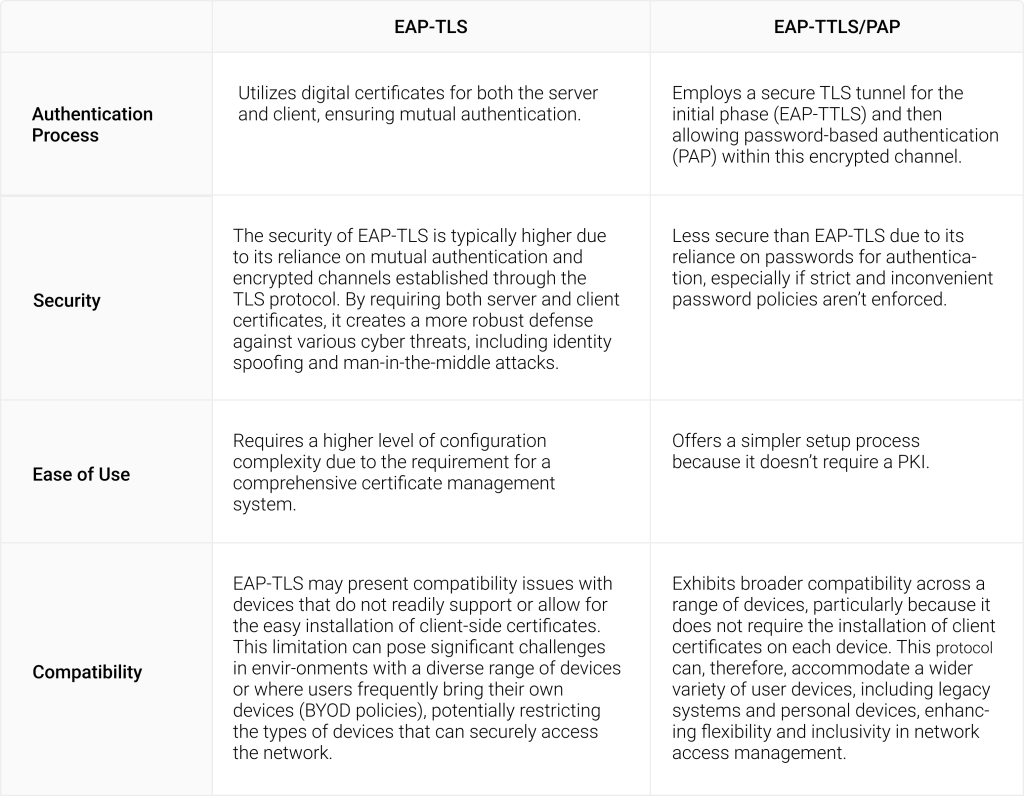
Beyond EAP-TLS and EAP-TTLS/PAP
EAP authentication methods extend far beyond these two. The continuous evolution of EAP methods is driven by a perpetual arms race against cyber threats and the diverse needs of modern network infrastructures. For instance, EAP-FAST (Flexible Authentication via Secure Tunneling) introduces an alternative that aims to balance the rigorous security measures of EAP-TLS with the deployment simplicity of EAP-TTLS/PAP, leveraging a Protected Access Credential (PAC) to facilitate a simplified setup process while maintaining a secure tunnel for authentication.
This adaptability underscores the importance of selecting an authentication protocol not just on its current capabilities but its ability to evolve and integrate within a dynamic security landscape, ensuring compatibility with emerging technologies and the increasing sophistication of cyber threats.
EAP-TTLS Versus PEAP (Protected Extensible Authentication Protocol) Authentication Method
Comparing EAP-TTLS with PEAP reveals nuanced distinctions significant to network security professionals. Both authentication methods establish an encrypted TLS tunnel for secure authentication; however, their approaches to client authentication diverge markedly. EAP-TTLS allows for a variety of authentication methods, including PAP, within its secure tunnel, thus offering flexibility in handling client credentials. Conversely, PEAP encapsulates EAP communication within a secure channel, typically using MS-CHAPv2 (Microsoft Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol version 2) for client authentication. This difference highlights PEAP’s tighter integration with Microsoft environments, providing a streamlined setup for networks predominantly relying on Microsoft infrastructure.
PEAP’s reliance on MS-CHAPv2, while facilitating a smoother deployment in certain settings, may not offer the same level of flexibility in client authentication methods as EAP-TTLS. Critical assessment of the specific network environment, including device ecosystem and infrastructure, is essential when determining the optimal EAP method, underscoring the necessity of a protocol that not only enhances security but also aligns with the operational and technological frameworks of the organization.
Making EAP-TLS Security Accessible & Easy with SecureW2’s Managed PKI
The security benefits of EAP-TLS are significantly amplified when coupled with SecureW2’s managed Public Key Infrastructure (PKI). SecureW2’s managed PKI solution offers a comprehensive, user-friendly platform that simplifies the complexities associated with certificate management, addressing one of the primary challenges of implementing EAP-TLS.
SecureW2’s managed PKI streamlines the entire lifecycle of digital certificates — from issuance to renewal and revocation — without requiring organizations to invest in extensive in-house PKI expertise. With SecureW2, the administrative burden of deploying and maintaining a secure, certificate-based authentication method such as EAP-TLS is dramatically reduced.
We also provide a vendor-neutral RADIUS server that was designed for passwordless authentication. Our PKI and RADIUS can integrate seamlessly with all major Identity Providers and MDMs, allowing you to leverage your existing infrastructure for a robust authentication system. This integration ensures that organizations can leverage the robust security advantages of EAP-TLS — including mutual authentication and encrypted data transmission — while minimizing the operational complexities, making SecureW2’s managed PKI an invaluable asset in securing network access. Click here to see our pricing.