Hackers have been constantly upgrading their attack methodologies and have infiltrated practically every business imaginable thanks to the surge in cutting-edge techniques. The Australian cyber-security chief confessed that one hack occurs every seven minutes, accounting for a 13% increase in these crimes in a single year.
To prevent these sophisticated breaches, you must regularly upgrade your network security infrastructure. In doing so, you must examine the existing access privileges of your organization’s users and devices. Sometimes admins overlook Device Trust due to placing more emphasis on individual users and their access privileges, which can compromise the security within a network.
In this article, we will discuss the concepts of device trust and cryptographic principles of attestation and also explain the role device trust plays in assuring a high degree of protection for organizations.
What is Device Trust?
Device trust, as the name implies, is a process for determining if the devices present in a network can be trusted to authenticate and authorize the enterprise’s resources.
Device trust is crucial when it comes to categorizing devices for specialized decision-making within an organization. In device trust, each endpoint of the organization is examined, and trust is granted based on the needs of the specific device.
For example, the access granted to a managed device like a laptop used exclusively by a unique user will be different compared to a public desktop system which many users handle simultaneously. In a similar manner, the level of trustworthiness of the different devices will vary based on the access levels of users operating them.
Generally, establishing user trust accompanies device trust by verifying the identity of users before allowing them access to the device. But this can sometimes be challenging, especially when using an unmanaged device that must be registered with users.
What is the ACME Protocol?
As the name implies, ACME (Automated Certificate Management Environment) protocol is a recent protocol that automates the entire lifecycle of digital certificates from issuance to renewal/revocation by eliminating human interventions.
The ACME protocol was created by the Internet Security Research Group (ISRG) for its public certificate service, Lets Encrypt. ACME was recently published as an Internet Standard in RFC 8555 by ISRG IETF working members. Since then, it has received widespread usage, particularly in the networking arena, where it now supports several CAs (Certificate Authority).
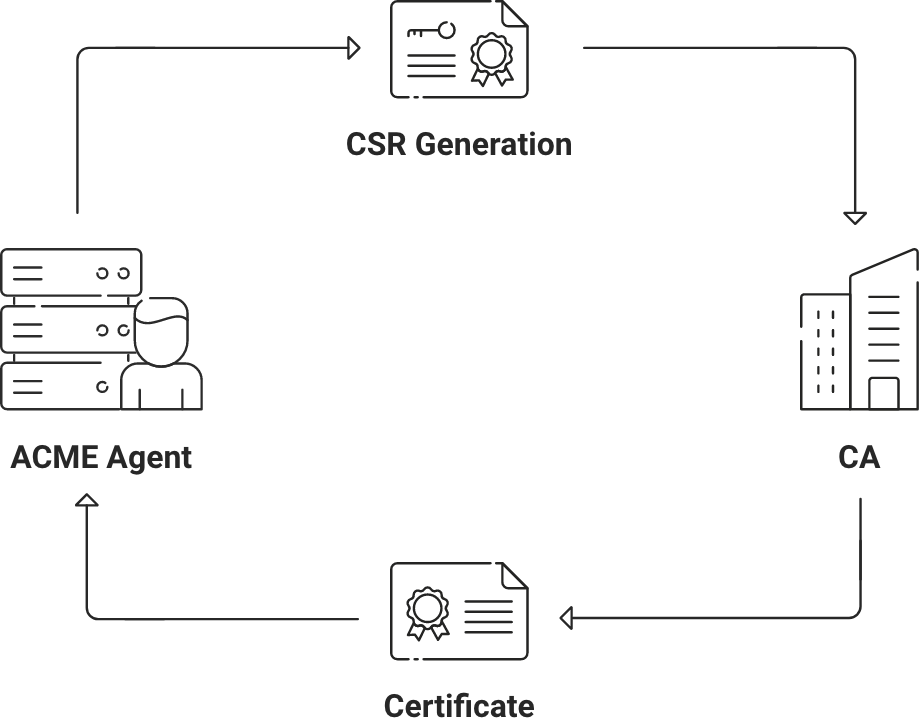
ACME has emerged as the talk of the town, owing to its ability to revolutionize certificate issuance by automating the entire process. Previously, this task was primarily handled by SCEP (Simple Certificate Enrollment Protocol), which we have previously described extensively in many of our blogs.
What is Device Attestation?
Device attestation is the method that allows a device to make status assertions that are helpful to designers and cloud-based service providers that seek reassurance before trusting the devices.
These assertions contain a device ID, installed software, and hardware variant and are supplied in a way that can be independently confirmed. The attestation results are processed by a particular recipient in order to make policy choices, such as providing device access to specific resources.
ACME’s presence in the root store also enables organizations to employ Managed Device Attestation, which gives a high level of assurance of device attributes, which can subsequently be reviewed as part of a client certificate identity authorization request.
Zero Trust Device Attestation in Apple Devices
Attestation in Apple devices is cryptographic proof of the validity of device attributes based on the Secure Enclave’s and Apple’s attestation servers’ security. These high-assurance IDs may be used to authenticate Wi-Fi, MDMs, VPNs, Kerberos, and other services.
For example, an enterprise issuing certificates using ACME may seek an attestation of the enrolled device’s properties during the initial stages of MDM (Mobile Device Management) enrollment. The issuing ACME can cryptographically validate the verified device characteristics and cross-reference them against the enterprise’s device catalog. Finally, only after the final verification is the device validated as the enterprise’s device.
In addition, Apple has recently introduced a new API framework for the support of ACME in iOS 16, iPadOS 16.1, and tvOS 16. The presence of ACME in the Apple root store certainly gives ACME the upper hand over SCEP for managing these devices, mainly because SCEP enrollment usually stores the private keys in the URL, making it potentially vulnerable to interception.
Also, In iOS 16, iPadOS 16.1, and tvOS 16, managed device attestation offers solid evidence about a device’s identity that may be employed as part of a trust assessment, especially as part of a zero trust architecture.
Advantages of Device Attestation in Apple Devices
Device attestations in Apple devices/gadgets enable the MDM to enroll a client certificate identity via the ACME protocol, which can establish the following cryptographically:
- The gadget is a genuine Apple product.
- The gadget in use is a specific gadget.
- The gadget possesses specific characteristics, such as the serial number.
- The gadget’s private key is hardware-bound.
Device attestations also help to curb the following vulnerabilities in Apple devices:
- A compromised device delivering an out-of-date attestation that might be vulnerable.
- A corrupt device that lies about its features and attributes.
- A corrupt device communicates the identifiers of a different device.
- An attacker forges a certificate request in order to deceive the CA into granting the attacker a certificate.
- Extraction of a private key for use on a malicious device.
Easy Device Attestation with any MDM
We at SecureW2 have been practicing the concept of device trust from our very inception. In addition to practicing device trust, device attestation has been a significant part of our core value in certificate management. We can guarantee the legitimacy of certification generation and its entire lifecycle from inception to revocation.
Our certificate solutions ensure that a user’s certificate cannot be stolen or intercepted after it is issued. Only authorized network users may be recognized in the IDP, and no outside agent can acquire the certificate.
Apart from that, we can seamlessly integrate with almost all the major MDM solutions, such as Jamf, Intune, Mosyle, etc. Also, we can extend the Apple device attestation feature to other OS MDMs if need be.
Even for unmanaged devices, we have JoinNow MultiOS that vastly reduces the burden of admins by enabling end-users to self-configure their unmanaged devices/BYODs with just a few clicks.
You can book a call with us or check out our pricing page to see if SecureW2’s onboarding solutions fit the authentication needs of your organization.
