Key Points
- Apple Managed Device Attestation (MDA) allows organizations to confirm a device is authentic by communicating with Apple servers.
- This process allows PKI services such as SecureW2’s JoinNow to more securely issue digital certificates to managed Apple devices.
- At the time of certificate enrollment, our PKI can work with your MDM to verify an Apple device is legitimate before issuing a certificate.
Apple introduced Managed Device Attestation (MDA) to give organizations stronger assurance about the devices they authorize for access. Device Trust, which identifies devices managed by your organization and ensures they comply with security policies, is a foundational part of Zero Trust security.
Many blogs discuss what Apple Managed Device Attestation is, but we don’t feel that they explain it in a way everyone can understand. So we met with one of the Security Engineers at Apple, who has been helping organizations adopt Apple MDA to help us understand and develop our support for the feature.
What is Apple Managed Device Attestation?
In the simplest way, Apple MDM is a combination of a protocol and Apple Servers that give macOS and iOS devices the ability to accurately identify themselves, such as stating, “I am an authentic Apple Device” or “My unique ID is 1123XYZ, and that exists in your Jamf MDM.” The level of Device Trust this enables is incredibly valuable for organizations, allowing them to enforce robust security policies across a wide range of use cases.
During WWDC 2022 Apple announced that it created a process for its devices to use, allowing third parties to have their legitimate Apple devices validate their identity by communicating with Apple Servers.
Essentially, Apple devices when prompted can use their Secure Enclave to securely communicate with Apple’s servers. The Secure Enclave is a critical component, as it keeps a unique identifier and certificates hardware-locked to the device. It can use this to securely communicate with Apple Servers, and the servers can attest to the authenticity and identity of the device. According to Apple’s own documentation, you can get the following data using Managed Device Attestation:
- The device is a genuine Apple device
- The device is a specific device
- The device has certain properties (for example, the serial number)
- The private key is hardware bound to the device
As a Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) vendor, we are working with Apple so we can use the Device Trust that is gained using Apple MDA to enroll devices for certificates that can be used to prove to other systems (Wi-Fi, VPNs, Application Firewalls), that the device that is requesting access is in fact a trusted device. To do that, we use the Automated Certificate Management Environment (ACME) protocol, and we will explain how that works with MDA in the next section.
ACME + MDA = Super Secure Certificate Management
Automated Certificate Management Environment (ACME) is a protocol, with a pretty self-explanatory name. It allows a PKI to automate the management of certificates. In this case, our JoinNow Connector PKI can use it to create unique certificate enrollment policies that factor in the information received from Apple MDA. The diagram below outlines how the JoinNow Connector PKI works with an MDM to distribute the ACME Payload, which will use Managed Device Attestation during the certificate enrollment process.
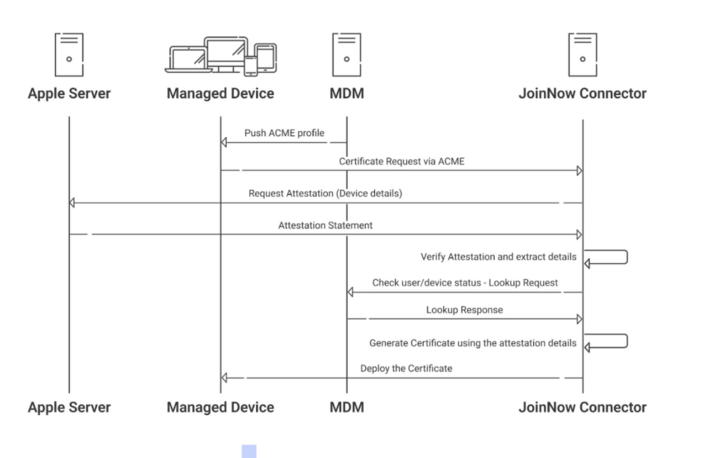
Using Managed Device Attestation during the certificate enrollment process ensures that only trusted and authentic devices can receive a certificate. These certificates can then be used across systems to prove device trust and authorize secure access to sensitive resources. While Wi-Fi authentication is a key application, MDA-backed certificates support multiple high-security use cases beyond just network access.
Organizations can also use these certificates to secure VPN access, enforce device trust policies for SaaS and internal applications, and validate device compliance before granting access to sensitive resources. By ensuring only attested, trusted devices receive certificates, IT teams can effectively segment access, reduce risk, and protect against threats from unverified or compromised endpoints.
How MDA Confirms Device Legitimacy
The device’s Secure Enclave initiates attestation by generating a hardware-bound private key and contacting Apple’s servers. The response, a signed attestation certificate, contains immutable device properties, such as:
- Serial Number (excluding user-enrolled privacy scenarios)
- UDID (Unique Device ID)
- Secure Enclave firmware version
- Secure Boot / SIP status on Apple Silicon Macs
- A freshness code to verify the timeliness of the attestation.
These properties are cryptographically signed and rooted in Apple’s Enterprise Attestation Root CA. The issuing system, such as ACME-based PKI, validates these fields to confirm the device is genuine, hardware-secure, and unique to your managed device.
How MDA Confirms Secure Enclave Presence
The Secure Enclave is a dedicated hardware module used for secure key operations. Apple MDA attestation confirms:
- A hardware-backed private key was generated inside the Secure Enclave, preventing export.
- Apple refuses to issue an attestation certificate if the Secure Enclave hardware, firmware, or private key extraction is compromised.
This ensures private keys cannot be duplicated or used on unauthorized hardware, making attestation-backed certificates strongly tamper-resistant.
What Problem Does Apple MDA Solve?
Apple’s documentation states that MDA provides cryptographically verifiable evidence of a device’s properties, enabling enterprises to validate that devices are not spoofed, compromised, or misconfigured. It protects against threats such as:
- Devices providing false information about their attributes.
- Impersonating another device’s identifiers.
- Extracting private keys for misuse on rogue devices.
- Using stale or outdated attestations.
- Hijacking certificate requests to trick certificate authorities into issuing certs to attackers.
MDA stops attackers from exploiting cloned, jailbroken, or spoofed hardware by ensuring that certificate issuance or device-based access occurs only on verified endpoints.
Does Jamf Support Apple Managed Device Attestation?
In theory, any MDM can support Managed Device Attestation. This is because Apple designed the attestation to go through the device. All authentic Apple devices are capable of using its Secure Enclave to request and receive an official attestation from Apple’s servers, it’s just up to the MDMs to prompt the device to perform an Attestation check and store the data.
Jamf has created a new blog about Apple Managed Device Attestation, along with new Features and Enhancements in November 2024, in response to Apple’s announcement at WWDC22. In this blog, they generally explain what Apple MDA is and how it relates to Jamf, but there are no details of how it would be implemented. However, in this video published in April 2023, Jamf stated the following:
“The device performs a check-in with Apple attestation servers, and ultimately returns a certificate that is signed by Apple that attests that the device is genuine. The certificate is validated by Jamf Pro, and stored with other inventory data. The results will be shared with Jamf’s security tools, and available for consumption for other third-party systems and tools via the Jamf Pro API.”
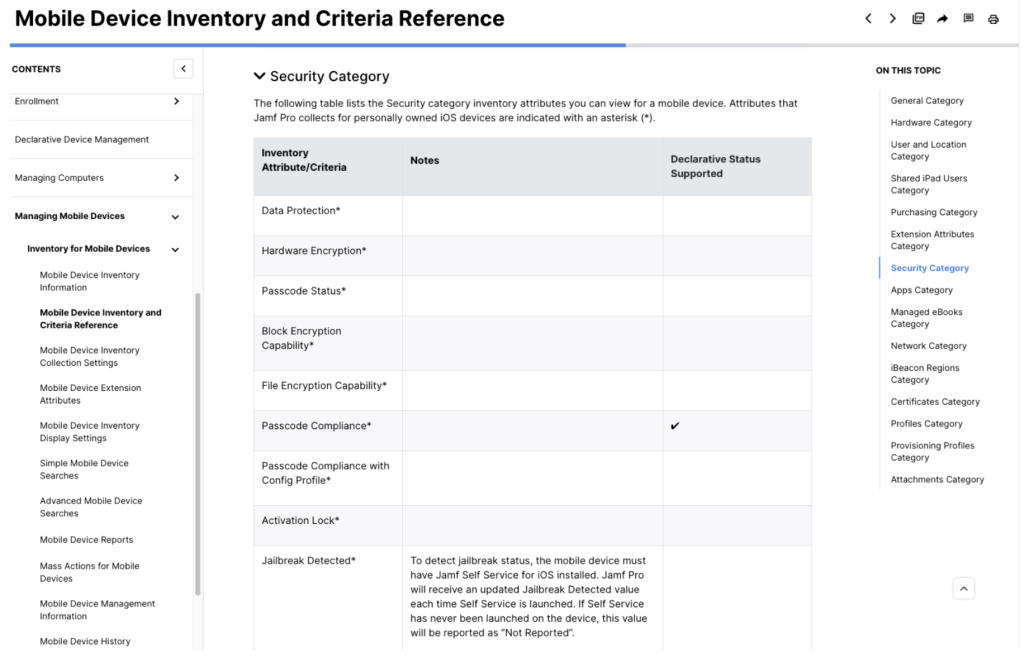
In the Security Category of Jamf’s Inventory Data, updated in April 2025, we can see that the ‘Last Successful Attestation’ attribute displays the time that Jamf Pro received and validated an attestation from a device. This ensures that the unique hardware properties in the attestation match Jamf Pro’s inventory data. Similarly, the “Last Command Sent” attribute displays the time when Jamf Pro successfully sent a DeviceInformation MDM command to a device that included a DevicePropertiesAttestation request.
Is Managed Device Attestation Supported on iOS?
Yes, MDA is supported on iOS and macOS.. According to Apple’s own documentation (published on March 27th, 2023), Managed Device Attestation is available from the following operating system versions:
- iOS 16 +
- iPadOS 16.1 +
- macOS 14 +
- tvOS 16 +
- watchOS 9+
- visionOS 1.1+
Supported hardware for Managed Device Attestation
- iPhone, iPad, Apple TV devices with A11 Bionic or newer
- Mac computers with Apple silicon (M-series chips)
There are no changes to MDA for Apple Watch and Apple Vision Pro.
What MDMs support Apple Attestation?
Jamf Pro
Jamf has implemented support for Apple MDA. That attestation data is validated, stored in device inventory, and made available via API for consumption by third-party systems.
Microsoft Intune
Microsoft has officially announced that Intune will support Managed Device Attestation and ACME certificate issuance for Apple devices. Apple stated in its tech community blog post that it would make this capability generally available in the second half of 2024. Admins can view attestation status reports for enrolled iOS, iPadOS, and macOS devices.
VMware Workspace ONE
VMware’s Workspace ONE UEM supports device-level MDM management, including compliance, device remediation, and attestation capabilities. Workspace ONE may initiate attestation queries via the Apple API to verify device properties and compliance. While the product documentation doesn’t name MDA explicitly, it confirms support for attestation-based device trust workflows.
Can MDA be used with unmanaged devices?
No. Apple attestation explicitly confirms MDM enrollment, hardware legitimacy, and secure OS status. Providing device Attestation with missing or unverifiable data, such as hardware or enrollment, results in failure. Only devices managed by enterprise MDM calculate a trustworthy attestation token.
What happens if attestation fails?
Failed attestations can result from hardware issues, non-genuine Apple devices, network faults, or compromised firmware. In these cases, devices can still respond, but omit key attestation data, and Apple does not indicate why, as it cannot rely on potentially compromised sources. Secure systems interpret any failure as a trust risk, triggering policy actions such as denying access, revoking certificates, or quarantining devices altogether.
How do Organizations Adopt Apple MDA?
The most common way organizations will adopt Apple MDA is through their MDM and PKI providers. Storing the data that Apple Managed Device Attestation provides in your MDM, or in the form of a Digital Certificate gives organizations a way to tell all their systems that devices are trusted, legitimate, and corporate-owned.
Most organizations we talk to are eager to use Managed Device Attestation for the following use cases:
- Issuing unique certificates to trusted, managed devices, for Wi-Fi, VPN, and Application Security
- Segmenting untrusted and trusted devices on the network
- Making sure MDM-managed devices are legitimate and not rooted
SecureW2’s Added Value with MDA + Dynamic PKI
SecureW2 stands out by offering turnkey support for Apple MDA within our dynamic PKI and Cloud RADIUS platforms. Our system supports ACME workflows, integrates with all major MDMs, and provides granular policy controls that factor in attestation status, device type, OS version, and other relevant factors. This dual-protocol support ensures compatibility with a wide array of existing network infrastructures and certificate authorities, streamlining the certificate enrollment process for managed devices.
If your organization is interested in adopting Apple MDA, get a free demo of our platform, and one of our engineers will guide you through the functionality of the solution.