Key Points
- Windows RADIUS servers like NPS are vendor-locked with Active Directory and lack support for cloud directories. They cannot directly communicate with cloud-based directories to transfer your existing environment to a CloudRADIUS, requiring hours of manual configuration.
- NPS (Network Policy Server) is configured by adding the Roles through the server manager and configuring it as a RADIUS server.
- A Cloud RADIUS is compatible with almost all cloud IDPs, such as Entra ID, Okta, Google, etc. Thus, it enables using digital certificates, which can be extrapolated with attributes from Entra ID, for network segmentation.
Anytime there’s a discussion about a wired or wireless authentication, it’s probable that the word “RADIUS server” will come up sooner or later. RADIUS, also known as a “AAA server,” carries out the essential functions of Authentication, Accounting, and Authorization within a WPA-2 Enterprise network. As you might expect, Microsoft has improved its RADIUS server over time to meet the authentication needs of its vast customer base.
Just like Windows 2008 server, the 2012 edition has long been used by organizations across the globe until the latest versions in the form of 2016/2019/22 came into existence. Unlike its latest cloud counterparts, Windows 2012 servers are on-premise in nature and catch a great deal of attention from hackers.
Here’s a recent incident of an update causing authentication to fail, affecting primarily the on-premise setups. On-premise servers, however, are not the subject of our attention here; let’s get back to configuring the Windows 2012 server.
Before configuring the Windows Server 2012, ensure that you met the following requirements for successfully configuring the Windows 2012 server.
Prerequisites for Windows RADIUS Server 2012:
System Requirements:
- Processor: You need a processor with at least 1.4 GHz for x64 processors. But Microsoft recommends using 2GHz for smooth functioning.
- RAM: The minimum requirement for RAM is 512 MB, but Microsoft recommends having at least 2GB of RAM.
- Disk space: You need a minimum disk space of 32 GB or more, but Microsoft usually recommends using 40 GB or more disk space. Also, the disk space requirements vary with the processor and RAM used in the system.
Active Directory Setup:
You must update the Active Directory environment before adding the domain controller.
Server Core Installation:
Unlike Windows Server 2008 version, the admin need not select the Full Installation or Server Core Installation option beforehand in Windows Server 2012.
These features are merged in the 2012 version to give three optional features which the admin can install or uninstall at his will.
Miscellaneous Requirements:
- Ensure that your Windows Server 2012 kernel-mode drivers are up to date and digitally signed for x64-based operating systems.
- Turn off your antivirus software, as the installation process can be hampered by virus protection software. For instance, checking each file that is copied locally to your computer might significantly slow down the installation.
- Ensure that the Windows Firewall is enabled by default.
- Ensure that all the relevant data and information are appropriately backed up before the configuration.
Overview of Windows RADIUS Server 2012 Configuration:
- Install and set up Windows Server 2012/Windows Server 2012 R2.
- Install Active Directory Domain Services (ADDS) to configure the new domain.
- Install Certificate Authorities (CA) with Active Directory Certificate Services (ADCS).
- Install NPS ( Network Policy Server).
- Configure Certificate Authorities (CA), i.e., Active Directory Certificate Services (ADCS) for Certificates.
- Configure NPS ( Network Policy Server) for the authentication protocol.
- Configure RADIUS.
- Define Network policies for users/devices.
- Configure Access Point.
- Set up zero clients, and select 802.1x authentication.
- Configure Wireless Connection Request.
Configure Windows 2012 RADIUS Server:
Now we will see each step involved in configuring Windows 2012 server in detail:
Install and Configure AD DS:
For configuring ADDS, follow the given instructions:
- Navigate to Windows Server 2012.
- Click Start.
- Click Server Manager.
- Navigate to Role Summary.
- Click Add Roles and Features.
- Select Role-based or Feature-based installation.
- Navigate to the Before You Begin page and click Next.
- Navigate to the Select Server Roles page.
- Select the Active Directory Domain Services.
- Click Next.
- Click Install on the Confirm Installation Selections
- Navigate to the Installation Results page and click Close.
- ADDS is installed.
Install AD CS and NPS :
- Navigate to Server Manager.
- Select Roles and Click Add Roles.
- Click Next on the Before you Begin page.
- Select Active Directory Certificate Services (AD CS) and Network Policy and Access Services.
- Click Next.
- Click Next on Network Policy and Access Services
- Navigate to Role Services and select Network Policy Server.
- Click Next.
- Select Create a self-signed certificate for SSL encryption and click Next.
- Click Next on the Introduction to Active Directory Certificate Services
- Select Certification Authority on the Select Role Services page and click Next.
- Select Enterprise on Specify Setup Page and Click Next.
- Select Root CA on Specify CA Type Page and Click Next.
- Select Create a new private key on the Set Up Private Key Page and Click Next.
- Click Next on Configure Cryptography for CA.
- Enter details on Configure CA Name page and click Next.
- Enter the validity period on the Set Validity Period page and click Next.
- Click Next on Configure Certificate Database
- Click Next on the Web Server (IIS).
- Click Next on the Select Role Services.
- Click Install on the Confirm Installation Selection
- Click Close.
Now the AD CS (Active Directory Certificate Services), Web Server (IIS), and NPS are installed successfully.
Configure NPS ( Network Policy Server) and RADIUS authentication.
- Click on the Start button and select Administrative tools.
- Click NPS on the Network Policy Server.
- Select Register Server in Active Directory and click OK.
- Click OK.
- On the NPS (Local) page, select RADIUS server for 802.1x Wireless or Wired Connections.
- Click Configure 802.1x.
- Select Secure Wireless connections on the Configure 802.1x page.
- Type Name and click Next.
- Add RADIUS clients on the Configure 802.1x page and click Next.
- Type the following details on the New RADIUS Client page.
- Name
- IP Address
- Shared Secret (Manual)
- Click OK and click Next.
- Select Microsoft Protected EAP (PEAP) on the Configure 802.1x
- Click Configure.
- Select Secured password on the Edit Protected EAP Properties page and click Edit.
- Enter the Number of authentication retries and click OK and click Next.
- Select Groups and click Next.
- Click Next again and click Finish.
- Restart NPS again.
Define Network Policies for users/devices.
You can follow the given steps for Defining the network policies.
- Navigate to the NPS console and click NPS (local).
- Click and expand Policies.
- Select Network Policies.
- Click New.
- Enter a Policy Name.
- Select the Type of Network Access Server to Unspecified while using Netscaler or RCdevs OpenLDAP while using OTP.
- Click Add in Specify Conditions
- Select Windows Groups and click Add.
- Click Add Groups and click OK.
- Select NAS Identifier in the Select Conditions
- Enter a Name and select Next to continue.
- Select Access Granted in Specify Access Permission
- Under Configure Authentication Method, select MS-CHAP v2 for maximum security.
- Click Next.
- Select RADIUS attributes as Standard in Configure Settings.
- Click Add.
- Enter the attribute value in String and click OK.
- Click Next and click Finish.
You can use the Network Policy Wizard to create and add new conditions, constraints, and setting to the network policies.
Administrators can define and implement a wide range of policies using our Cloud RADIUS, including lookup policies applied at the moment of authentication. For instance, depending on the time of day, you can decide whether to accept or reject people and devices. You may also restrict access to devices running a specific operating system.
Set up Zero Clients, and Select 802.1x Authentication
- Navigate to the Control panel and open the Network and Sharing center.
- Click Change adapter settings.
- Select Local Area Connection and click Properties.
- Select Authentication and click Enable IEEE 802.1x authentication.
- Select the desired protocol in the dropdown button.
Configure Wireless Connection Request
- Navigate to the Control panel and open the Network and Sharing center.
- Click Manage Wireless Networks.
- Select Manually Create a network profile.
- Enter your SSID in Network Name and click Next.
- Click Change Connection settings.
- Select Security and click Settings.
- Select the Trusted Root CA and click OK.
- Navigate to Advanced Settings.
- Select Specify Authentication Mode and click OK.
Is On-Premise Windows RADIUS a Good Idea?
Traditional RADIUS servers located on a company’s premises are prone to many security issues. Windows RADIUS servers—which are extensively used in on-premise infrastructure—are typically built around NPS and have a number of vulnerabilities that hackers routinely employ in zero-day attacks.
Also, because of its physical accessibility, an NPS server’s on-premise presence makes it vulnerable to various physical security threats, from intruders to disasters – or just power outages. Given the costs of maintaining highly-secure physical locations, there’s rarely a circumstance in which on-prem works out to be cheaper than cloud RADIUS.
Cloud integration of NPS, designed primarily for on-premise AD setups, has significant downsides even with other Microsoft-owned cloud-based solutions like Azure AD. If you want to use Azure with NPS, you will require a separate authentication server or proxy to simplify the process. These operations are not only challenging and time-consuming but also relatively expensive.
Cloud RADIUS: The Most Reliable RADIUS Server for Windows
Network administrators have relied on Windows Server 2012 edition for years, but it has seen most of the Microsoft ecosystem change since that time. It is difficult to overlook its flaws, which are more of a security liability than a strength in the present era.
The move to the cloud offers several benefits over remaining in an on-premises environment, and what could be better than utilizing our ground-breaking Cloud RADIUS? You can nearly wholly avoid these limitations by using a cloud-based server like Cloud RADIUS supported by SecureW2.
With our Cloud RADIUS’ advanced Policy Engine feature, you may restrict or enable user access depending on any number of attributes, including user/device characteristics, date/time of day, and more. Additionally, you may use our Cloud RADIUS with any IDP because it is built for vendor neutrality.
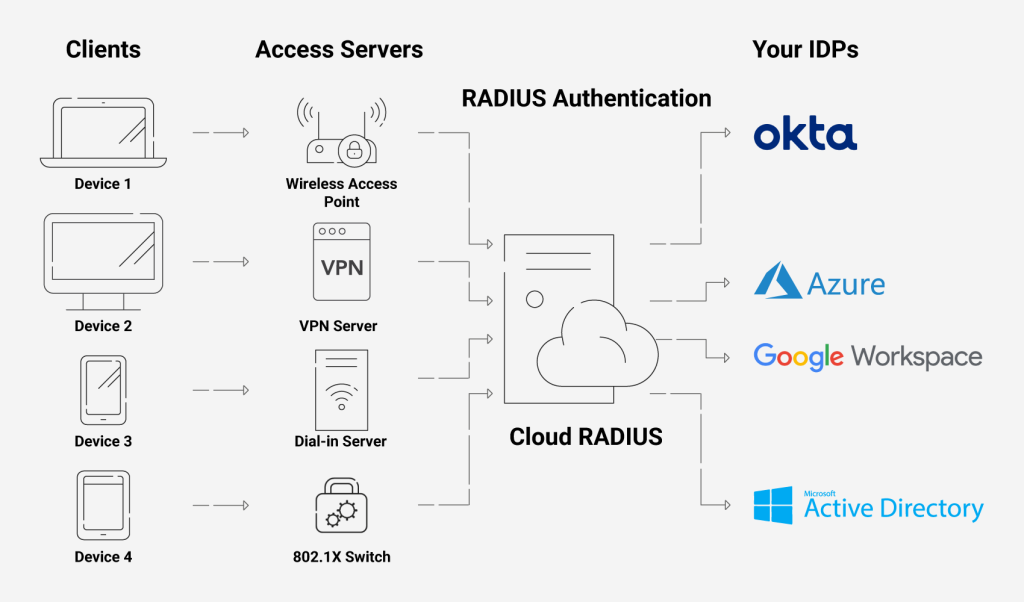
Using its servers, you may also enforce policies using real-time user lookups against Azure, Okta, and Google Workspace. You can also onboard users to Cloud RADIUS using their existing AD identities without the need to create an LDAP proxy.
Also, integrating with Securew2 gives you more customization for many innovative features like Azure MFA auth, Intune auto revocation, windows hello for business login, and many more. Our RADIUS services can be set up quickly, cost a fraction of what on-prem solutions do, and has no infrastructure costs because it is all in the cloud.
If you are interested in taking that first step towards security for your organization, look no further and click here to inquire about pricing.