Key Points
- Certificate pinning binds specific certificates or public keys to services, ensuring only trusted certificates are accepted, but requires ongoing management to prevent service disruptions.
- Pinning requires significant upkeep, and key compromise can expose systems to vulnerabilities, highlighting the need for backup strategies.
- Cryptographic agility, certificate transparency, and automated lifecycle management offer robust, flexible alternatives to certificate pinning.
- SecureW2’s automated certificate lifecycle management simplifies security, reducing reliance on certificate pinning while ensuring network integrity.
While digital certificates undoubtedly provide a more secure authentication method than passwords, some organizations still fear the possibility that certificates can be issued to unauthorized parties. Certificate pinning is a security strategy designed to prevent this from occurring by creating an approved list of “pinned” certificates – much like pinning a message in a chat.
Certificate pinning has played a vital role in ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of data exchanged over networks. But what exactly is certificate pinning, why does it matter in secure connections, and is it a viable practice today?
What is Certificate Pinning?
Certificate pinning, also referred to as SSL pinning, is a mechanism that strengthens the authentication process between a client (such as a web browser or mobile app) and a server. In essence, it involves associating a specific cryptographic identity (usually a digital certificate or its public key) with a particular service or domain. However, it’s not without its drawbacks.
While it mandates the acceptance of only predefined certificates, it also presents additional overhead in maintaining this predefined list, ensuring their validity, and the possible risk of service disruption if the pinned certificates expire or are compromised.
What is The Role of Certificate Authorities (CAs) in Certificate Pinning?
CAs play a critical role in the certificate issuance process. While certificate pinning reduces reliance on a certificate authority for establishing trust, CAs are still responsible for issuing the initial certificates. However, with pinning, organizations gain more control over which certificates are trusted, minimizing the risk of fraudulent or compromised certificates slipping through undetected.
How Does Certificate Pinning Work?
Certificate pinning operates at the application layer, where developers embed a list of authorized certificates or public keys within their applications. When establishing a secure connection, the client verifies that the server’s presented certificate matches one of the pinned certificates. If no match is found, the connection is terminated, preventing unauthorized access. To delve deeper into how certificate pinning works, let’s break down the process into several key steps:
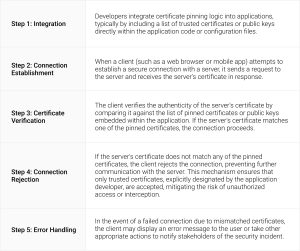
Importance of Key Pinning in Network Security Configuration
Key pinning associates specific public keys with a particular service or domain, somewhat like certificate pinning. However, it focuses on validating the authenticity of public keys presented by servers during the Transport Layer Security handshake process, rather than solely validating certificates issued by a trusted certificate authority. It brings about several benefits, including:
Enhances Authentication
By pinning specific public keys, organizations can enhance the authentication process between clients and servers, reducing the risk of man-in-the-middle attacks and unauthorized access. Key pinning ensures that only servers possessing the predefined public keys are accepted, thereby strengthening the trust model and mitigating the risk of certificate-based attacks.
Mitigates Certificate Vulnerabilities
Key pinning mitigates vulnerabilities associated with the reliance on certificates issued by CAs, such as certificate mis-issuance, compromise, or revocation. By pinning public keys directly, organizations can reduce their exposure to such risks and maintain greater control over the trustworthiness of their communication channels.
Offers Granular Control
Key pinning offers granular control over the trust model, allowing organizations to specify which public keys are trusted for specific services or domains. This level of control enables organizations to tailor their security posture to meet their unique requirements and effectively defend against targeted attacks.
Choosing the Right Approach: Public Key Pinning or Certificate Pinning?
The choice between public key and certificate pinning depends on factors such as the complexity of the environment, the level of control desired, and the resources available for maintenance. Organizations must weigh the trade-offs and select the approach that best aligns with their security requirements and operational capabilities.
Securing HTTPS Connections with SSL Pinning
Certificate pinning, also known as SSL pinning in the context of HTTPS connections, serves several crucial purposes in the realm of network security. By enforcing the use of specific certificates, SSL pinning mitigates the risk of unauthorized access and data interception, bolstering the overall confidentiality and integrity of communication channels.
Preventing Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) Attacks with SSL Pinning
Man-in-the-middle attacks pose a significant threat to the confidentiality and integrity of data exchanged over networks. SSL pinning acts as a barrier against such attacks by ensuring that only a trusted certificate is accepted, thereby thwarting attempts by malicious actors to intercept or manipulate communication between clients and servers.
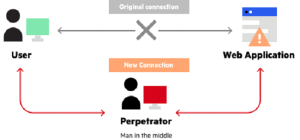
Source: Imperva,Inc.
Ensuring Data Integrity and Confidentiality with SSL Pinning
In addition to thwarting man-in-the-middle attacks, SSL pinning also safeguards data integrity and confidentiality. By verifying the authenticity of the server’s certificate, clients can be assured that they are communicating with the intended endpoint and that their data remains encrypted and protected from eavesdroppers.
The Importance of Pinning More Than One Certificate
Application developers considering this technique should think about pinning more than one or all certificates in the certificate chain, including:
Root Certificates
Root certificates are issued by a trusted certificate authority based on a defined certificate validation method with public and private key combinations. These are created by complex cryptographic algorithms and hashing algorithms and are carefully monitored and protected by the root certificate authority.
Intermediate Certificates
Intermediate certificates, also known as intermediate certs, are issued by root CAs and are used to issue end-entity certificates, such as SSL/TLS certificates, code signing certificates, or client certificates. An intermediate CA helps manage the certificate issuance process while preserving the integrity of the root CA.
Leaf Certificates
Also known as end-entity certificates, leaf certificates are issued to entities such as websites, email servers, software applications, or individuals. They are signed by intermediate CAs and are used to secure communications, authenticate users, or verify the authenticity of digital documents.
What is Wrong With Certificate Pinning?
While certificate pinning comes with undeniable security benefits, it also presents challenges. Notably, certificate pinning can introduce significant complexities into the certificate management process. An organization opting for certificate pinning must meticulously manage and maintain its list of trusted certificates, mandating a significant commitment of resources and expertise.
Risk of Key Compromise
In certificate pinning, the primary risk lies in key compromise. Should a key become compromised, all applications or systems relying on the pinned certificate are vulnerable. This scenario underscores the need for a robust key management process and, in most cases, necessitates the complexity of maintaining backup keys.
The Challenge of Frequent Updates
Certificate pinning also requires frequent updates, as certificates come with finite lifetimes and are routinely replaced or renewed. This necessitates a proactive approach to maintain the pinned certificates and ensure they remain current, an effort that can impose a significant administrative burden for organizations.
Cryptographic Agility and Certificate Pinning
Cryptographic agility plays a pivotal role in the effectiveness and long-term security of certificate pinning implementations. It refers to a system’s ability to adapt and evolve in response to emerging cryptographic threats and vulnerabilities. In the context of certificate pinning, cryptographic agility ensures that a pinned certificate remains resilient against evolving attack vectors and cryptographic weaknesses. Cryptographic agility intersects with certificate pinning in various ways including:
Updating Pinned Certificates
As cryptographic algorithms and standards evolve, organizations must update their pinned certificates to maintain the integrity and security of their pinning implementations. Cryptographic agility enables organizations to seamlessly transition to newer, more secure algorithms and key lengths without compromising the trustworthiness of their communication channels.
Addressing Algorithm Deprecation
Cryptographic agility is particularly important in scenarios where cryptographic algorithms or key lengths are deprecated due to security vulnerabilities or weaknesses. Organizations must promptly update their pinned certificates to align with industry best practices and mitigate the risk of exploitation by adversaries.
Future-Proofing Security Controls
By incorporating cryptographic agility into certificate pinning implementations, organizations future-proof their security controls against emerging threats and regulatory requirements. This proactive approach enables organizations to maintain compliance with evolving security standards and adapt to changes in the threat landscape without significant disruption.
Evaluating Cryptographic Strength
When selecting and updating pinned certificates, organizations should evaluate the cryptographic strength of the chosen algorithms and key lengths. Cryptographic agility allows organizations to assess the security posture of their pinning implementations and make informed decisions about the suitability of their cryptographic choices.
Implementing Key Rotation Policies
Cryptographic agility facilitates the implementation of key rotation, allowing organizations to regularly update pinned public keys to mitigate the risk of key compromise or obsolescence. By rotating keys in accordance with established policies, organizations ensure the continued effectiveness and resilience of their pinning controls.
Proactively Monitoring Security Landscape
Cryptographic agility enables organizations to proactively monitor the security landscape for emerging threats and vulnerabilities that may impact their pinning implementations. By staying abreast of developments in cryptographic research and industry trends, organizations can adapt their security controls accordingly and maintain a robust defense posture.
What Are The Alternatives to Certificate Pinning?
While certificate pinning offers effective protection against many common threats, it is not the only approach to enhancing security in network communication. Two prominent solutions are certificate transparency and HTTP strict transport security (HSTS), which can provide robust security controls while avoiding the complexities associated with manual certificate management.
Certificate Transparency
Certificate transparency is an open framework used to monitor and audit digital certificates. It provides a public, append-only log of issued certificates, which organizations can query to check the legitimacy of their certificates. By leveraging certificate transparency, organizations gain greater visibility into their certificate operations, enabling them to detect mis-issued or rogue certificates more quickly.
HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS)
HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS) is a security feature that forces all connections to be made over HTTPS. This policy prevents protocol downgrade attacks and cookie hijacking by requiring that all communication with the server happens over a secure connection.
Automated Certificate Lifecycle Management
Automated certificate lifecycle management is also a feasible and cryptographically agile alternative to certificate pinning. This approach leverages automation technology for different parts of the certificate lifecycle, including issuance, revocation, and renewal.
Automated certificate lifecycle management provides a robust defense against threats like Man-in-the-Middle attacks without the complexities associated with certificate pinning. It reduces reliance on a single certificate or public key and provides greater flexibility to adapt to changes in the cryptographic space.
SecureW2’s certificate lifecycle automation solution includes zero-touch certificate enrollment for managed devices and a self-service, dissolvable onboarding application for unmanaged ones. Our managed device gateway APIs even have advanced integrations with Intune and Jamf to enable automatic revocation in addition to automatic issuance.
The Security of Digital Certificates Made Simple with SecureW2
Pinning certificates and keys may sound like an easy way to prevent unauthorized access, but in reality, it’s inflexible and doesn’t keep up with the regular changes to certificate status. Certificates need to be revoked and renewed periodically for effectiveness. Thankfully, a managed PKI solution like SecureW2’s JoinNow Connector PKI simplifies management of the certificate lifecycle.
Our PKI offers a comprehensive suite of features and capabilities aimed at helping organizations build networks based on device trust. We provide everything you need to issue and manage certificates, including onboarding technology for both managed and unmanaged devices, as well as a streamlined portal for certificate management.
Whether deploying certificates for Wi-Fi authentication, VPN access, or other network services, SecureW2 empowers organizations to strengthen their security posture and ensure the integrity and confidentiality of their network communication. To learn more, contact us today and see our comprehensive offerings.