Key Points
- Automated CLM increases speed but removes manual checkpoints, making continuous authentication critical to prevent unauthorized certificate actions.
- Unlike static methods, continuous authentication verifies identity throughout the session, which reduces the risk of credential theft and supports compliance.
- To protect your certificate workflows, implement continuous authentication as a core part of your CLM automation strategy.
Enterprises are relying more on automated solutions to manage the lifecycle of digital certificates. Certificate Lifecycle Management (CLM) has evolved from a manual, error-prone process to an automated, API-driven workflow optimized for speed and scalability. However, this shift introduces a critical risk: relying on automated systems without continuous identity validation can result in unauthorized certificate actions, especially when human oversight is minimal or nonexistent.
The solution is to implement continuous authentication, a security approach that verifies identity throughout the session or process lifecycle, rather than relying on a one-time check at login. It ensures that identity verification is an ongoing process rather than a one-time event.
The Shift Toward Automated CLM
CLM is critical because it manages the entire certificate lifecycle, enabling encrypted communication, authentication, and device trust. This includes the issuance, renewal, rotation, and revocation of certificates for users, computers, applications, and devices.
Organizations must integrate network security automation with certificate lifecycle management to ensure robust security and compliance. Automated systems must verify identities continuously to mitigate risks from compromised credentials and unauthorized access. Continuous authentication introduces a dynamic security layer that adapts to user behavior and real-time threats.
Zero-trust automation principles ensure that even automated certificate management activities are continuously verified, not just trusted by default. By implementing authentication workflow and RADIUS-based automation, organizations can streamline verification processes, improving both security and efficiency. Together, continuous authentication and certificate automation form the backbone of a resilient security infrastructure.
As cloud-native infrastructure, microservices, and DevOps practices gain traction, certificate volumes have surged. Manual certificate management is no longer a viable option. While automated CLM tools help manage certificate sprawl and improve availability, they also eliminate manual checkpoints, raising the risk of unverified actions without strong identity controls.
What Is Continuous Authentication
Continuous authentication is the ongoing verification of an entity’s identity throughout a session or process, not just at the point of login. The system assesses behavioral, contextual, and device-based signals to determine whether it should continue to trust the user or the system making the request.
With static authentication, the system verifies identity once at the start of a session and assumes that trust is continuous. The move to distributed systems means more services and endpoints, each needing its own certificate—making manual management unsustainable without automation.
Multi‑Factor vs. Continuous Authentication in Automated Workflows
Traditional Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) enhances initial login security by requiring multiple verification factors, such as a password and one-time password (OTP). In API-driven or automated environments like CLM, MFA typically relies on static credentials such as API keys or service account secrets, sometimes with a secondary check. Although this is stronger than single-factor authentication, the system seldom re-evaluates trust once it’s set.
This creates risk in automated workflows. For example, if a compromised device continues issuing certificate requests through an automated script, continuous authentication would detect the abnormal behavior, such as device non-compliance or unusual request patterns, and trigger certificate revocation in real time. Since MFA only protects the initial credential issuance, not each automated interaction, traditional MFA would not prevent ongoing misuse once access is gained.
Continuous authentication constantly reassesses trust based on dynamic factors such as behavior, device posture, and context. It extends verification beyond login and is ideal for securing ongoing, automated processes, such as certificate issuance or revocation. It provides a real-time, adaptive layer of trust that MFA alone cannot offer.
Adaptive and Risk‑Based Continuous Authentication
Risk-based authentication strengthens continuous authentication by adjusting response levels based on real-time context. Key methods include:
- Behavioral Analytics: Detects deviations from typical activity patterns, such as unexpected certificate volumes or access times
- Device Posture Assessment: Evaluates device health, patch status, and compliance posture before permitting certificate-related actions
- Geolocation and IP Reputation Analysis: Flags requests from high-risk regions or suspicious sources
These signals feed into a trust scoring engine. For example, if a script requests certificate revocation from an unrecognized IP address at an unusual hour, the system could assign a high-risk score and prompt additional verification or block the request. SecureW2 integrates with leading security platforms, including CrowdStrike for endpoint posture, Palo Alto Networks for network threat intelligence, and Microsoft Entra ID for identity risk signals. These integrations enhance adaptive authentication decisions by providing rich, real-time context across device, network, and user layers.
Integrating these signals through APIs with existing SIEMs or Identity Providers (IdPs) enhances context-awareness without introducing significant overhead.
Why Continuous Authentication Matters in CLM Automation
- Protects Against Unauthorized Access
Continuous authentication enforces identity checks for all automated interactions. This ensures that compromised credentials do not enable malicious activity. - Reduces the Impact of Credential Theft
Long-lived credentials are a common attack vector, but continuous authentication mitigates this by using certificates that require re-validation for each sensitive activity, limiting access and reducing risk. - Enables Real-Time Threat Detection
Continuous authentication monitors certificate activity in real time. If it detects unusual patterns—like a sudden spike in certificate requests, access from an unknown IP, or a change in device posture—it can trigger alerts, require additional verification, or block the request entirely. - Promotes Compliance and Audit Readiness
Every CLM action is tied back to a verified entity. This simplifies audits and helps meet standards such as NIST 800-63, SOC 2, and PCI DSS. - Maintains Trust in the Certificate Supply Chain
Continuous authentication ensures that only trusted, compliant systems control certificate operations. This preserves organizational integrity.
Continuous Authentication in Action: Example Use Cases
IoT Device Onboarding at Scale
An energy company deployed thousands of smart meters across multiple regions, using certificates to ensure the secure identity of these devices. With continuous authentication in place, the system continuously checks device posture after it is onboarded. When a batch of meters was compromised, the continuous authentication system detected suspicious behavior, such as unusual access patterns, and flagged it. This triggered automated revocation workflows and sent alerts to the security team.
Outcome: Unauthorized devices were immediately blocked from accessing the network, preserving the integrity and availability of critical services. The company also met regulatory compliance requirements by demonstrating an active and responsive system for securing IoT devices, ensuring that compromised devices could not escalate into larger security issues.
Automated SaaS Certificate Renewal
A healthcare provider automated the renewal of certificates for dozens of Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) applications critical to their operations. Each renewal request was assessed with continuous authentication, which included real-time checks against pre-defined policies for authorized domains. When someone attempted to renew a certificate for an unauthorized domain, the policy engine immediately flagged the request as a potential security breach and blocked it.
Outcome: By leveraging continuous authentication, the organization successfully avoided potential credential compromise by preventing unauthorized certificates from being issued. This safeguard helped the healthcare provider maintain HIPAA compliance, ensuring that sensitive patient data remained secure and that the organization was aligned with stringent healthcare regulations.
Challenges and Strategic Considerations
Balancing automation speed with security rigor is the key challenge. Overly strict policies can disrupt workflows. Loose controls leave openings for exploitation.
Embedding security into the automation pipeline ensures that identity becomes a core element in all certificate-related actions.
Integrating Network Security Automation with CLM Pipelines
Integrating automated network security tools with CLM workflows enhances situational awareness and threat response. For example:
- SIEMs can correlate anomalous CLM activity, such as suspicious issuance, with network behavior.
- SOAR platforms can automate responses such as quarantining non-compliant endpoints.
- Firewalls and microsegmentation tools can dynamically adjust access based on certificate trust signals.
- RADIUS-based automation can enforce network access based on validated certificate posture.
These integrations turn certificate data into real-time security intelligence.
Automating Certificate Management: Best Practices
- Define clear policies for issuing, renewing, and revoking certificates.
- Automate certificate discovery and maintain a centralized inventory.
- Leverage CLM platforms with API-driven automation such as ACME and dynamic SCEP.
- Embed continuous authentication into request and renewal workflows.
- Automate credential rotation and secure storage.
- Monitor and audit all CLM operations for anomalies and compliance.
SecureW2’s Approach to Continuous Authentication
SecureW2 enables continuous authentication in CLM workflows by embedding real-time identity checks into every certificate event on our JoinNow Platform, including issuance, renewal, and revocation.
Using Cloud RADIUS and Dynamic PKI, our platform evaluates trust signals from IdPs, MDMs, and network context. Short-lived tokens and identity-aware gateways govern access by continuously validating user and device posture.
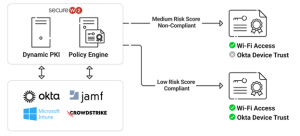
If a device becomes non-compliant or a session expires, access is automatically restricted or revoked. This ensures that even machine-to-machine certificate workflows remain secure, policy-bound, and fully auditable.
Conclusion
As certificate automation scales, static trust models are no longer enough. Continuous authentication secures every step in the CLM process by continuously validating identity and context.
By embedding continuous identity validation into automated certificate workflows, organizations can reduce risk, streamline compliance, and enforce Zero Trust principles without slowing innovation.