Key Points
- Password managers reduce fatigue but remain a single point of failure. If compromised, attackers gain access to every stored credential.
- Passwordless authentication with certificates leverage PKI to provide phishing-resistant, device-bound authentication that cannot be guessed, reused, or stolen like passwords.
- SecureW2 delivers a complete passwordless ecosystem with Managed PKI, Cloud RADIUS, and onboarding tools like JoinNow MultiOS, and gateways for managed devices.
Everyone uses numerous accounts on the internet these days. Take yourself as an example; you most certainly have a minimum of one social network account, one email address, one for online shopping, and most likely one for online banking. There’s a good chance that a password protects each of these accounts.
It might be challenging to organize them due to the rise in the sheer number of online activities and the need for secure passwords. Users may create, save, and handle passwords securely with the help of password managers. But it’s crucial to look into the security of simple technologies like these. Because of this, we’ll explore just how safe password managers actually are.
The Popularity of Password Managers
The surge in utilisation of password managers can be attributed to the prevailing concerns regarding security of passwords. The platform enables users to create unique and highly secure passwords for individual accounts, which are then stored in a highly protected database. A single master password is all users need to know in order to gain access to their password manager along with all of their previously stored passwords.
The increasing adoption of password managers can be attributed to their user-friendly interface and their potential to enhance password security. The utilization of a password manager mitigates the potential threat of weak or duplicated passwords by obviating the necessity for users to recall multiple intricate passwords.
Password managers address the issue of password fatigue, a common phenomenon where users experience difficulty in remembering a multitude of passwords. With the growing awareness of the significance of secure passwords, password managers are anticipated to maintain their increasing prominence as a reliable mechanism for securely managing online accounts.
The Risks of Weak or Repeated Passwords: Why Password Security Matters
Given that people have several online accounts in today’s digital environment, password security is essential. Security breaches, theft of identities, and monetary damage can occur as a result of using insecure or commonly used passwords, which hackers find to be easy prey.
Cybercriminals break passwords using complex methods including brute force assaults, vocabulary attacks, and phishing attacks. It is critical to use strong, unique passwords for every account and to update them often in order to lower the possibility of a security breach.
Weak or reused passwords are a problem that is resolved by password managers. They generate and store secure, unique passwords for each account, eliminating the need for users to remember several complex passwords. They also reduce the risk of phishing scams by making it simple to auto-fill login information.
Passwordless authentication, which substitutes digital certificates for passwords to authenticate users, is another technique to strengthen password security. By employing this method, which also provides a more secure method of authentication, passwords are no longer required.
How Do Password Managers Work?
Password managers function by establishing and saving distinctive passwords for each of a user’s online accounts. When a user links into an account, the password manager instantly types in the login details.
Password managers normally function by encrypting personal information via a master password or code known only to the user. Even if attackers get entry to the password manager, it will be difficult for them to acquire the login details that have been saved. Password managers are available in a range of setups, such as a cloud-based, local, and extensions for browsers.
Cloud-based Password Manager
Cloud-based password managers utilise encrypted versions of user data that are stored on remote servers, which can be accessed from any location with an internet connection. The utilisation of password managers provides the benefit of ubiquitous accessibility, thereby facilitating users to maintain the currency of their credentials across multiple devices.
Local Password Manager
Local password managers store encrypted user data on a user’s device. This option boosts reliability by not keeping the user’s passcode on an external server. However, utilizing local password managers to maintain passwords across several devices may be tricky.
Browser Extension Password Manager
Browser extensions are a different type of password manager that interacts with an individual’s web browser. When a user connects onto a website, the plugin types in the login details for them. Although convenient, this type of password manager may include security weaknesses, especially if the user’s internet browser is hacked.
The Pros and Cons of Using a Password Manager: Convenience vs. Risk
Consider a virtual assistant that remember all of your password information and inputs it for you whenever you require to access your online accounts. That is precisely what a password manager does.
Password managers simplify safety on the internet by creating unique, strong passwords for every account and proactively entering in the login details. Password managers, like any other innovation, have advantages and disadvantages.
Pros
Generating Strong Passwords
Utilizing a password manager provides a crucial benefit in generating distinct and secure passwords for each account. By utilizing this approach, the requirement to maintain a plethora of intricate passwords is eliminated, thereby reducing the likelihood of data breaches resulting from vulnerable or duplicated passwords.
Auto-filling Login Credentials
The ability of a password manager to effortlessly input in username and password makes it easier to sign into accounts. This saves valuable time and reduces the likelihood of consumers becoming victims to phishing scams, which attempt to trick users into providing their login credentials on bogus websites.
Centralized Management
Password managers compile all of your passwords into a single spot, making it easier to reset passwords for various accounts and keep them. Because of this, it is simpler to guarantee that passwords are consistently changed and that each account has a unique, safe password.
Multi-platform Support
Several password managers have cross-platform functionality, allowing users to access their credentials on a range of platforms and devices, such as desktop computers, smartphones, and tablets. This makes managing passwords across various devices easy.
Cons
Single Point of Failure
One of the major drawbacks of using a password manager is the single point of failure. All passwords kept in the password manager might be affected if it is hacked. Use a trustworthy password manager and create strong master passwords in order to lower this danger.
Initial Setup
A password manager’s setup might be time-consuming and may need technical expertise. Users may need to spend time inputting their login details for each account into the password manager, which might include a learning curve.
Dependency on Third-party Provider
It is imperative to trust an external service for ensuring the security of your credentials while utilising a password manager. It is imperative for customers to exercise due diligence in selecting a trustworthy supplier and remain cognizant of potential security threats before availing their services.
Cost
Despite the fact that there are many public password managers available, certain professional password managers need an annual or monthly fee. Those seeking ways to save cost or who are reluctant to pay for a long-term membership might find this issue to be a drawback.
Risks of Password Managers and the Benefits of Digital Certificates for Enhanced Security
Password managers can benefit users in many ways, but there are also certain risks related to security that users need to be mindful of. A few of these risks include breaches of information, attackers, and flaws in the password management tool itself. In this part, we’ll discuss password managers’ safety concerns as well as how, generally speaking, digital certificates could fill their place.
Password managers provide a significant risk for data breaches since they store all of a user’s login information in one place. If the password manager is hacked, a hacker might instantly access the passwords of every user. By employing a trusted password management service with solid master passwords, this risk might be reduced.
Hacking is another issue with password managers. If an attacker gains permission to use a user’s device or network and is able to look over the passwords that have been stored, the password manager’s safety features may be bypassed. By selecting secure, unique passwords for the password manager itself and, if appropriate, turning on two-factor authentication, threat can be reduced.
Master Password Potential vulnerabilities are the last group. By inputting the master password, you may access every password that has been saved. Its flaw or vulnerability might lead to the disclosure of every password.
Replacing Password Managers with Digital Certificates
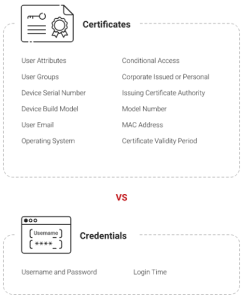
A password manager solution that provides higher security and lessens many of the hazards is the use of digital certificates. Public key infrastructure (PKI) is used by digital certificates to enable robust security and authentication for transactions over the internet. As opposed to using a password, users identify oneself utilising a digital certificate which is stored on their device.
Digital certificates have a variety of benefits over password managers. Passwords are not stored, which lowers the possibility of data breaches. Instead, the unique digital certificate for the user’s device is utilized for authentication. As they encode information as it is being transferred, they also offer more security.
Go Passwordless With SecureW2
For businesses looking to deploy passwordless authentication using digital certificates, SecureW2 offers a complete solution. Everything needed for a flawless implementation is covered by our platform, from managed PKI to onboarding technology.
Both administrators and end users can benefit from using digital certificates for authentication in a number of ways. Certificates offer improved safety and safeguarding against breaches of information since they are less vulnerable to phishing and other hacking attempts. Additionally, they completely do away with the requirement for passwords, reducing the danger of password-related security issues like reusing passwords or guessed password attacks.
SecureW2’s platform provides a full Passwordless solution, comprising onboarding methods suitable for managed and unmanaged devices. While our managed device gateways enable automated onboarding of managed devices, our JoinNow MultiOS solution makes BYOD onboarding straightforward. The necessary infrastructure for certificate issuance, administration, and revocation is also provided by our managed PKI.
Contact us today to learn more about how we can assist you in improving your organization’s security posture with our complete onboarding solution.