Server security is critical in today’s digitally driven environment. The server certificate, a digital document that verifies the identification of a website or server, is fundamental to Internet communication security. Server certificates enable encrypted connections, guaranteeing the confidentiality and integrity of data transferred between users and servers.
Understanding the importance of server certificates is critical for both organizations and individuals since they are the cornerstone of trust in online interactions. In this article, we will explore the intricacies of server certificates, explaining their importance in cybersecurity and why they are essential for protecting sensitive data on the internet.
What are Server Certificates?
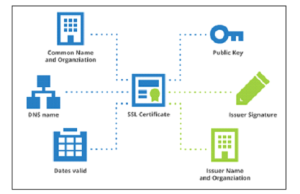
A web server certificate, often known as an SSL/TLS certificate, verifies the validity of a website. A secure sockets layer (SSL) certificate on a server converts the HTTP security protocol to HTTPS. As a result, the online browser visually indicates the website’s legitimacy, usually with a padlock icon, although it may vary from browser to browser and websites will do this to reassure customers about their authenticity.Server certificates are essential for safeguarding other types of servers, such as RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service) servers. RADIUS server certificates authenticate and encrypt communication between network devices and the RADIUS server to protect critical authentication data in remote access scenarios.
SSL certificates offer encryption for data transfers between the browser and the server. This indicates that every data transfer across a website is protected against cyberattacks, such asa fly on the wall trying to steal the information being sent.
An SSL certificate is a digital file with a pair of public and private keys.The public key is provided to the client during the SSL handshake and is packaged with the certificate, while the private key is kept on the server. The website displays the secure padlock icon and changes the protocol to HTTPS as soon as the certificate is deployed on the web server. Data integrity and secrecy are maintained with the use of web server certificates.
What do Server Certificates do?
Server certificates make it possible to employ SSL/TLS encryption protocols to safeguard user privacy when they exchange sensitive information with websites, including credit card numbers, login passwords, and personal information. It enables browsers to authenticate the server to stop impersonation, phishing attempts, and other harmful behaviors.
Aside from being used to surf the web, server certificates are also used to ensure that clients connect to the right servers or to secure communications between servers. As we mentioned previously, server certificates can be assigned to authentication servers such as RADIUS servers to ensure that users are connecting and authenticating to the correct server. To further help protect data integrity, server certificates also enable digital signatures and cryptographic hash algorithms.
The Different Types of Server Certificates
You can use several types of web server certificates to fulfill different security and operational needs. Common types of server certificates include the following:
⦁ Domain Validation Certificates: Enable basic encryption and domain ownership verification to safeguard client-server data transfers and privacy.
⦁ Organization Validation Certificates: To increase trust, provide a more robust identity validation than DV, and include the organization’s verified data in the certificate.
⦁ Extended Validation Certificates: Ensure the utmost security for e-commerce, finance, and government websites through strong encryption and validation.
⦁ Wildcard Certificates: Simplify the process of protecting cloud-based services or several subdomains under one main domain.
⦁ Multi-Domain Certificates: Organizations hosting many websites on the same server can streamline certificate administration by using a single certificate to secure numerous domain names and subdomains.
How Does an SSL Certificate Work?
SSL encryption security relies on asymmetric encryption, often known as public-key cryptography or encryption.
The public key and the private key are the two cryptographic keys that asymmetric encryption uses. Data encryption uses the public key, whereas data decryption uses the private key. Customers will be reassured by this secure encryption, especially as it concerns the security of their transactions. This will also help to create more trust with the customer.
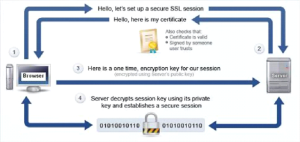
Whenever a client connects to a web server, the following steps occur behind the scenes:
⦁ The browser makes an attempt to establish a connection with a web server or website that is SSL certified
⦁ A copy of the SSL certificate is sent to the browser by the web server.
⦁ After confirming the certificate’s legitimacy, the browser notifies the web server.
⦁ To begin an SSL-encrypted session, the web server/website sends back a digitally signed approval.
⦁ Thus, the browser and web server begin encrypted communication.
Importance of TLS Server Certificates
Are TLS/SSL certificates required for servers? The brief response is unambiguously “yes.” By safeguarding information sent between clients and servers, they assist enterprises in maintaining data integrity and privacy in the rapidly evolving threat landscape of today. They are especially essential for enterprises like e-commerce that gather sensitive customer information.
Secure Web Transactions
TLS server certificates improve e-commerce transaction security by guaranteeing that data such as client information and payment details are delivered securely, preventing unauthorized access, interception, and alteration. In addition to lowering the risk of fraud and chargebacks, encryption and security procedures assist organizations in adhering to security regulations like the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS).
Gain Customer Trust
You show authenticity when it comes to securing client data by using a padlock icon in the address bar, a valid server or SSL certificates, and HTTPS in your web URL. These trust symbols assist you in presenting a trustworthy and professional image to the customer. This,helps to draw in new clients and offers them confidence to finish their business. Furthermore, confident and happy clients are more inclined to make additional purchases from a website they trust.
The Vital Role of Server Certificate Validation
A vital first line of defense against possible vulnerabilities in digital security is server certificate validation. Systems are exposed to several risks when comprehensive validation is not performed. Initially, in the absence of appropriate authentication, malevolent entities may carry out Man-in-the-Middle (MitM) assaults, snooping on confidential information sent between the client and the server. This interception facilitates data breaches, identity theft, and unauthorized access to sensitive information. Furthermore, the lack of validation leaves systems vulnerable to spoofing attacks, in which attackers pose as genuine services to trick unwary users into providing important information.
Conversely, with careful server certificate validation, businesses reduce many risks. By confirming that the server is, in fact, the entity it purports to be, validation guarantees the server’s legitimacy, preventing MitM attacks and maintaining the confidentiality and integrity of data while it is being sent. Additionally, by verifying the server identity, server certificate validation protects against phishing efforts by making it far more difficult for attackers to pose as trustworthy organizations. By implementing strong validation standards, organizations may strengthen their defenses against cyber threats and protect their assets and users’ confidence.
Certificate validation is essential for guaranteeing the security and integrity of remote authentication procedures concerning RADIUS servers. By confirming the RADIUS server’s legitimacy, server certificates reduce the possibility of MitM attacks and illegal access attempts. Validation thwarts phishing attempts by creating trust in the server’s authenticity and strengthening defenses against fraudulent operations that target authentication methods.
Client and Server Certificates – The Difference
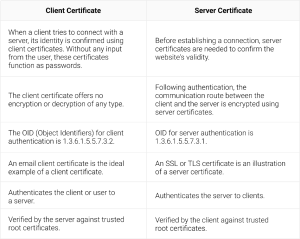
A client certificate and a server certificate are both critical to safe communication in today’s digital era. Server certificates provide data secrecy and server authenticity, whereas client certificates authenticate users or devices to servers. Both certificates, which a reliable Certificate Authority provides, are essential for protecting sensitive data in a world where cybersecurity is critical. It is imperative that individuals and organizations that are dedicated to upholding the highest standards of security in their online interactions comprehend the distinctions and importance of these certifications.
It’s important to know the distinctions between the two before purchasing any of these two certificates as it will enable you to purchase the one that’s most beneficial. This is a tabular comparison between the server and client certificates.
Strengthening Network Security With SecureW2’s JoinNow MultiOS
Validating server certificates is critical for ensuring strong network security and preventing cyberattacks. For various organizational requirements, SecureW2 is a certificate provider and passwordless RADIUS service that provides complete solutions designed to handle the challenges of certificate validation.
Organizations may safeguard the integrity of their network infrastructure by utilizing SecureW2 services. Our Cloud RADIUS solution supports authentication procedures for increased security by offering the required certifications to confirm the legitimacy of RADIUS servers. Furthermore, our technology effortlessly integrates with server management tools such as Ansible and Puppet, enabling the management of SSL certificates for private and internal web servers.
Take advantage of our simple Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) platform, which allows administrators to manage the whole certificate lifecycle, including zero-touch distribution and quick revocation. Our Managed Cloud PKI as a Service makes passwordless authentication easier by automating certificate management, integrating seamlessly with various environments, and offering secure, centralized PKI infrastructure to enterprises of all sizes.
Contact us now to see how SecureW2 can provide your organization with seamless server certificate validation and strong safety measures.