Utilizing MDMs to establish a highly secure environment is an excellent safeguard for mitigating user error risks and developing consistency in device management. This common practice amongst enterprises is a great way to protect sensitive data for themselves and their clients, as it is a significant risk to allow low-privileged users free-reigns of their devices. However, this can lead to multiple network security risks and productivity problems due to the end-users falling out of compliance with their devices. This can happen for many reasons, such as out-of-date OS, typing in the wrong password too many times, or downloading software that’s yet to be cleared by administration that turns out to be malware.
To improve security, combat the above risk, and ultimately eliminate a need for passwords, the Enterprise uses the EAP-TLS network security protocol integrated with the SCEP protocol for automation. SCEP (Simple Certificate Enrollment Protocol) is used by MDMs such as Intune or Jamf that implement a Microsoft PKI (Public Key Infrastructure) to enroll digital certificates in their domain devices to integrate the MDM device management controls. Why this is a better and more efficient way for administrators and enterprise users to use SCEP due to the creation of a self-governing system of controls that can encrypt their messages with public and private keys, improved productivity with automated authentication via the digital signatures signed by the certificate authorities, using the certificate services CRL (Certificate Revocation Lists) to revoke your past employee’s certificates so insider threats are diminished and much more.
The vast benefits SCEP can bring to an organization are evident, but if not configured correctly, the enterprise will be vulnerable to costly damage. From the certificate creation process to the initialization of the certificates, it is a complex implementation that can go wrong in several different areas, the most challenging being enrollment initialization. This article will cover what errors an administrator may face when attempting to deploy SCEP, how they can be fixed, and what options administrators could use to optimize their network and PKI.
Error: SCEP Certificate Enrollment Initialization for Workgroup
Before trying anything too technical, you must implement the following instructions from Microsoft support whenever you face minor glitches or issues involving SCEP certificate requests.
Error 1: Request fails during the verification phase on the CRP
It happens because the registry keys in the NDES connector registry settings that confirm certificate requests are missing. These keys are necessary for administrators to guarantee that certificate requests are verified smoothly. If they are missing, the enrollment process may become disrupted, and requests may not be approved. Therefore, this issue must be resolved quickly to preserve the functioning and integrity of certificate management systems.
Remedy:
- Open the Services snap-in on the connector-installed server. To do so, open the Start menu, type msc into the search box, and choose Services from the results list.
- Restart the Intune Connector Service from the Services snap-in.
- Check the HKLMSoftwareMicrosoftMicrosoftIntuneNDESConnector registry subkey to ensure the registry keys were generated according to the figure’s instructions.
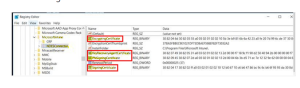
- Open the registry on the NDES machine and look for the following subkey:
HKEY LOCAL Machine\Software\Microsoft\Cryptography\MSCEP
- Restart the server after changing the template values to the default (IPSECIntermediateOffline).
- Check the HKEY_LOCAL_Machine\Software\Microsoft\MicrosoftIntune\NDESConnector when the server restarts. The signing certificates should now be visible.
- Change the template name under HKEY_LOCAL_Machine\Software\Microsoft\Cryptography\MSCEP to the custom template name established for SCEP and NDES when the keys were created.
Error 2: TPM Upgrade
A TPM (Trusted Platform Module) is a cryptoprocessor that enhances the security of any hardware-based system by generating and securely storing cryptographic keys. It is usually located on your system’s hardware (primarily the motherboard), occasionally independent from the memory and the primary CPU.
You might also face SCEP Certificate enrollment issues while switching to Windows 11, as TPM 2.0 has been made mandatory for installing/migrating to Windows by Microsoft in their latest hardware requirements list.
This error can be resolved with the latest update of the Dev-Build in your operating system. Meanwhile, you can cross-examine all the hardware associated with the new operating system, including the latest update of the associated drivers.
Following the latest guidelines to troubleshoot TPM errors is always advisable before escalating the issue to Microsoft Support.
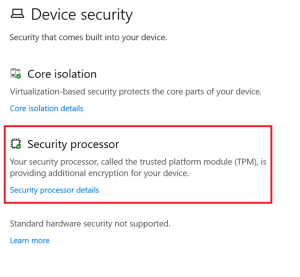
Remedy:
- You can reset the TPM to its factory default settings and let Windows re-initialize it by clearing all its keys.
- If you use TPM 2.0 and are not identified by Windows, ensure your computer hardware has a Trusted Computing Group-compliant Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI). Also, verify that the TPM is not deactivated from the operating system in the UEFI settings.
- If you are using TPM 1.2 and Windows 10, version 1507 or 1511, or Windows 11, the TPM could be switched off and must be reactivated, as stated in Turn on the TPM. When you restart it, Windows will re-initialize it.
- If you’re attempting to set up BitLocker with the TPM, check which TPM driver is installed on the machine. Microsoft recommends always using one of the BitLocker-protected TPM drivers provided by them.
- Installing a non-Microsoft TPM driver may prevent the default TPM driver from launching and cause BitLocker to indicate that there is no TPM on the system. Remove any non-Microsoft drivers before allowing the operating system to initialize the TPM.
Error 3: Compliance
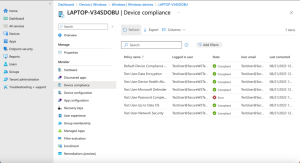
Outdated operating systems, software, and apps are a major problem that might make the enrolling process more difficult. Administrators might suggest that users upgrade their programs, operating systems, and apps to guarantee a smooth certificate enrollment process. Disabled user accounts in the database may also make enrolling difficult.
Administrators must activate these accounts only after obtaining the necessary approval or authorization to resume access. Furthermore, network encryption and other location-based access restrictions are essential for a successful registration. For example, open networks cannot allow connections therefore encryption is required for compliance. It is imperative to swiftly address these compliance concerns to enable effective certificate enrollment procedures.
Remedy:
- Enrollment difficulties can stem from more straightforward reasons as well, such as
- Out-of-date OS, Software, and Applications
- Have the User Update their system, software, and apps to ensure certificate enrollment.
- User Account Disabled
- Enable the User account if they’re disabled in the database only after being cleared or granted permission to regain access.
- Location-Based Access Example: The network must encrypted; an open network will not be accepted for connection.
- Out-of-date OS, Software, and Applications
Error 4: Server Issues
Server issues can seriously interfere with certificate enrollment procedures in business settings. A common problem is that the Certificate Authority (CA) server is unavailable, meaning it cannot be accessed to issue certificates. Furthermore, customers suffer difficulties getting certificates if the web application responsible for registration is misconfigured or the on-premises server experiences an outage. Compatibility problems exacerbate the matter, especially regarding non-Microsoft devices and those running Microsoft Windows Secure Trusted Execution Platform (WSTEP), which may find it difficult to interact with the CA server.
Remedy:
Administrators should do periodic maintenance checks to guarantee the CA server’s continued availability and performance to handle these server-related issues. Another workable option is to use cloud services, which give redundancy and accessibility even during on-premises server outages.
Moreover, misconfigurations may be fixed, and smooth connections between devices and the CA server can be restored by changing connectors and URLs linked to the web application for registration. Administrators may minimize interruptions to certificate enrollment procedures and preserve the security and integrity of company networks by taking proactive measures to fix server faults through these corrective activities.
Error 5: Misconfiguration Issues
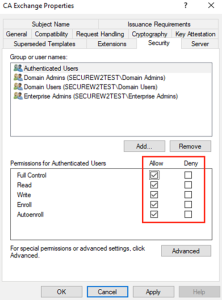
“Misconfiguration Issues” refers to problems that can occur from incorrect configuration or configuration inside the architecture of the certificate management system. Enrollment procedures may be hampered by permission problems for certificate templates, which prohibit people or devices from accessing the files required for certificate issuance. Misconfigurations within the configuration profile can also result in differences between planned and actual configurations, which can be confusing and interrupt operations.
Furthermore, when the Intermediate Certificate and Certificate Authority (CA) do not have the same signature, server certificate validation becomes troublesome and might result in security threats and authentication failures. Moreover, reinitialization oficates is necessary to correct mistakes and ensure correct operation. Not only may inaccurate validity periods result in premature expiry or prolonged exposure to security threats, but overly permissive settings can also represent a security issue by allowing unneeded access or privileges. Finally, improper certificate assignment to user groups may lead to operational inefficiencies or unapproved access.
Remedy:
It is recommended that administrators thoroughly examine the certificate management system to address these misconfiguration concerns regarding misconfiguration. This involves checking certificate template permission audits to ensure users and devices have the right amount of access. Misconfiguration problems can also be reduced by updating the configuration profile to comply with best practices and organizational standards.
For server certificate validation, the CA and Intermediate Certificates must have the same signature; if differences are found, modifications must be made. Administrators should also check and modify certificates to fix any issues or misconfigurations. Strict access control implementation and validity period verification can assist in guaranteeing compliance and prevent security flaws. Finally, verifying that user groups have been assigned the right certificates improves the organization’s data security and operational effectiveness.
Smooth SCEP Certificate Enrollment
Your organization must be backed by a reliable Microsoft Cloud PKI (Public Key Infrastructure) for certificate enrollment (and future management) to effectively manage the entire SCEP certificate onboarding and minimize configuration errors. Otherwise, a scenario of manually installing each certificate will likely occur, which is time-consuming and error-prone, like the ones we previously encountered.
The good news is that Securew2’s Cloud Managed PKI integrates with all major vendors, including Intune and Jamf. It’s also designed to work with your existing architecture, minimizing errors and avoiding costly infrastructure upgrades.
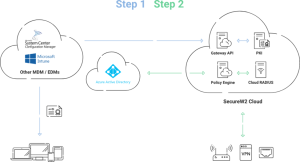
Our PKI automatically enrolls managed devices in certificate-based authentication and can issue certificates through any MDM using our efficient API Gateways. Furthermore, our user-friendly management interface provides several certificate management features, enabling you to address the whole certificate lifecycle. In our management portal, you can modify your certificates with dozens of policies, providing the perfect authentication solution for your unique needs.
The list does not end here; we provide industry-unique enhancements for your favorite MDMs like Intune and Jamf. Our most recent upgrade is a certificate auto revocation on expiry feature. We believe in constantly upgrading ourselves to retain our ever-expanding consumer base. If you want to broaden your cybersecurity horizons, check out our prices to learn more.
