Key Points
- WPA2 secures Wi-Fi communication using AES encryption, with WPA2-PSK suitable for home use and WPA2-Enterprise for business environments.
- WPA2-PSK uses a shared password, while WPA2-Enterprise assigns unique credentials to each user for improved security.
- 802.1X uses a RADIUS server for network access control, authenticating users via digital certificates or credentials. It can be used alongside WPA2-Enterprise to secure a network.
- SecureW2 integrates PKI with Cloud RADIUS to enhance WPA2-Enterprise security through certificate-based authentication.
Nowadays, there are numerous methods and types of encryption used to secure networks. Businesses should look beyond using WPA2-PSK, which isn’t secure enough for their needs.
It’s easy to get confused about WPA2-Enterprise and 802.1X, which are both security protocols that address different parts of the Wi-Fi authentication process in the network. We will explain the differences in detail in this article.
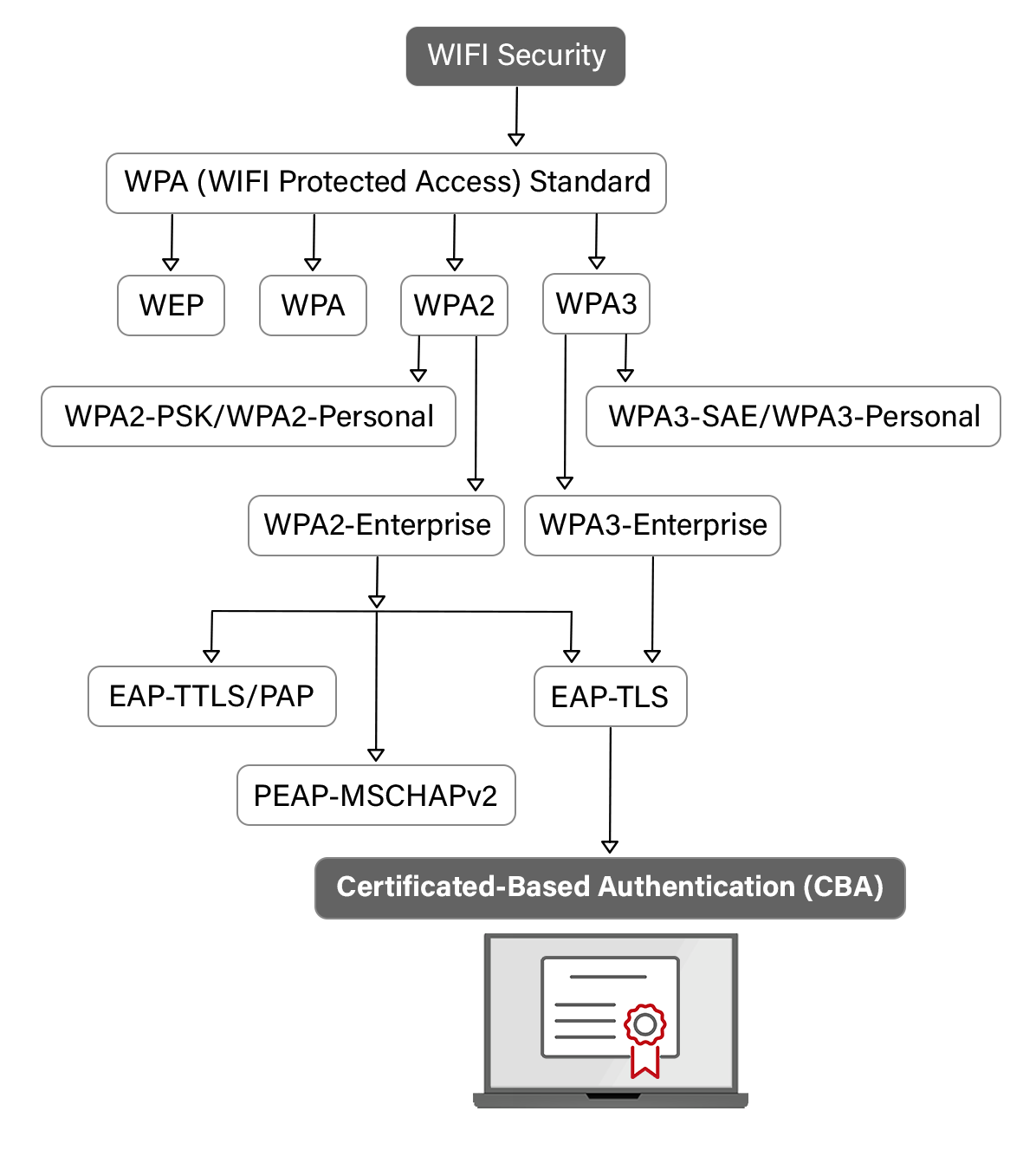
What Is WPA2?
WPA2 is a type of encryption that offers secure communication between a wireless device and an access point. It uses AES encryption to secure data transmission over Wi-Fi networks and is considered to be the most secure option for wireless security. The two main types of WPA2 commonly used are WPA2-PSK and WPA2-Enterprise.
WPA2-PSK (Pre-Shared Key):
WPA2-PSK is a type of network that is protected by a single password shared between the users. It usually accepts single-password authentication to access the Wi-Fi network. This network can connect only with a few devices and can be used either in home or in office.
Users of this type of network face potential various credential theft and MITM attacks because of sharing single for multiple devices.
WPA2-PSK requires client-side configuration and is relatively easy to configure the network.
Advantages of WPA2-PSK (Pre-Shared Key):
- AES encryption is used to provide additional network security.
- It has compatible wireless security standards on both old and new devices with support of TKIP and AES Protocols.
Disadvantages of WPA2-PSK (Pre-Shared Key):
- WPA2 requires of processing power to protect the network.
- The high traffic network can decrease performance.
What Is WPA2-Enterprise?
WPA2 is a wireless security standard. PSK or personal, as you know, has one password for all users and devices connecting to the network. WPA2-Enterprise, on the other hand, requires each user to have their own username and password to access the Wi-Fi. WPA2-Enterprise doesn’t automatically require use of certificates, but we obviously recommend that over passwords.
What Is 802.1X?
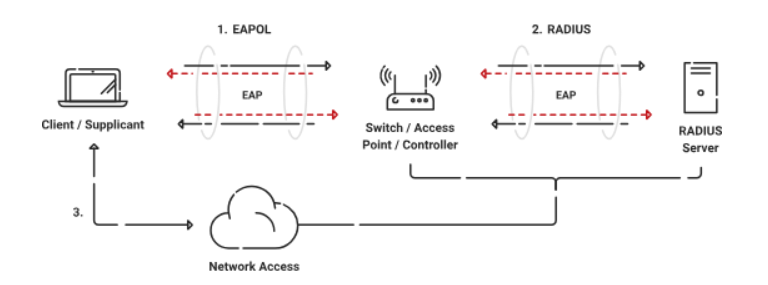 802.1X is a network port-based access control standard and defines the way devices authenticate to your network. It is commonly used in enterprise networks along with digital certificates that offer protection to your devices.
802.1X is a network port-based access control standard and defines the way devices authenticate to your network. It is commonly used in enterprise networks along with digital certificates that offer protection to your devices.
The 802.1X authentication protocol allows access to the network with the help of a RADIUS server. It checks the user’s credentials, whether they are an active user or not, and based on pre-defined network access policies, it grants access to the network through password-based authentication, Token-Based Authentication, and Certificate-Based Authentication (CBA).
802.1X can work transparently on the wireless network. It also utilizes the Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) to set up a secure tunnel between participants during authentication.
802.1X requires three main components:
- A Client/Supplicant
- An Access Point
- A RADIUS Server
What You Need for 802.1X
Client/Supplicant
The Supplicant needs to be installed in the network for the device to participate in the 802.1X authentication. The Supplicant is involved with the initial negotiation of the EAP transaction with a switch or controller and packs the user credentials with 802.1X.
If the client doesn’t have a supplicant, the EAP frames sent from the switch will not authenticate to devices. SecureW2 offers an 802.1X supplicant for devices that don’t already have one, but most modern devices come with them already.
Access Point
The Access Point/Wireless plays a vital role in 802.1X authentication. The 802.1X exchange is the only communication between the Access point and the client, who will get access to the internet after successful authentication.
The Controller/Access Point starts the exchange by passing the EAPOL start packet to the client when it connects to the network. It also sends the client responses to the right RADIUS server based on the configuration in the Wireless Security Settings. After authentication is completed, the switch will decide to authorize the device for network access based on the user’s activity.
RADIUS Server
The Remote Authentication Dial-in-user server (RADIUS) helps with the initial authentication, authorization, and accounting time. It is a Wi-Fi security necessity that replaces a pre-shared key with unique credentials for a specific user or device.
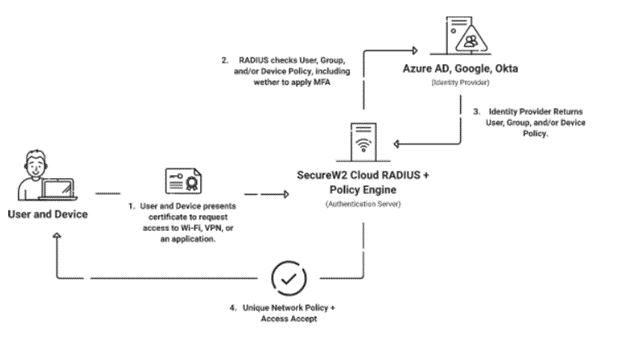
A RADIUS server can be considered a “Security Guard” of the network that the user gets connected to, and the RADIUS can verify the user’s identity and allow them to access the network. A user can access the network after enrolling for a certificate from the PKI (Private Key Infrastructure) or validating their credentials.
The RADIUS verifies the user’s credentials each time they connect, ensuring they are legitimate, and also stops unauthorized users from connecting to the network. The RADIUS server can also authenticate the user status from different organizations and provide secured network access.
802.1X With WPA2-Enterprise
802.1X is a standard used for encrypting and authenticating users to a network through the use of a RADIUS server. WPA2-Enterprise, on the other hand, provides improved encryption. When they work together, what happens is you have a network wherein all users have their own unique credentials or certificates they use to connect, rather than sharing a single password.
Organizations can choose to use their own self-managed RADIUS server or utilize a managed RADIUS service like Cloud RADIUS.
Integrating PKI and Cloud RADIUS Into Your Network
In a nutshell, WPA2 is a wireless security standard that has different iterations, although the most common are PSK and Enterprise. WPA2- PSK provides password-based authentication that’s suitable for home use but isn’t secure enough for a business’s security needs.
WPA2-Enterprise differs by having individualized credentials for users rather than a single password, but it’s even more secure when you use certificates for authentication instead. SecureW2’s managed PKI and onboarding technology makes creating and issuing certificates for a range of use cases — including Wi-Fi authentication — simple.
Our Cloud RADIUS server provides policy-driven 802.1X authentication designed for certificate-based authentication and ensures that only authorized users can connect to your WPA-2 Enterprise network. We have affordable pricing options for every size of organization. For more information, click here to see our pricing.
